Climate Change Impacts India’s Food Security, Stability Of Major Food Crops Threatened

Reduced crop yields, soil degradation, and increased vulnerability to pests and diseases are some of the challenges that will likely cause food production instability
It is important to note that human activity across all industries contributes to global warming. Aside from fossil fuels, the food production system is the next biggest contributor to greenhouse gas emissions.
One-third of global anthropogenic GHG emissions come from the food sector. This increase in global warming and climate change leads to more extreme weather events and increased climatic variability. It significantly negatively impacts multiple sectors, including agriculture, food production, nutrition security, and livelihoods, particularly in less developed regions and countries.
Climate change is a significant global challenge, that impacts all aspects of human life, including food security. India, one of the world’s largest agricultural producers, is highly vulnerable to the effects of climate change, particularly on its food production systems.
Studies have shown a relationship between gradual climate change and crop yields. Therefore, ensuring food security for the country’s growing population, home to more than 1.3 billion people, under these changing conditions is challenging for policymakers.
Food security is food availability and people’s access to it, with the assurance that this access will not diminish. It encompasses various physical, environmental, economic, and social aspects. Everyone should have access to adequate and safe food that meets their dietary needs for a healthy and active lifestyle. This means having both the quality and quantity of food required for good health.
Food security refers to having reliable access to sufficient, safe, and nutritious food. It comprises four dimensions: availability of food, accessibility of food (both economically and physically), utilisation of food, and the stability of the other three dimensions over time.
Food security objectives can only be achieved when all four dimensions are fulfilled simultaneously at all levels, from national to regional to household.
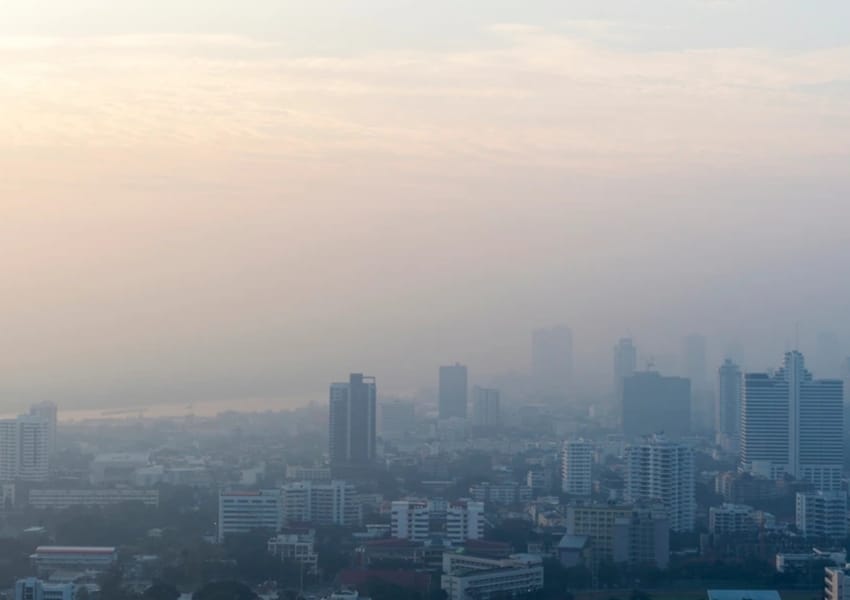
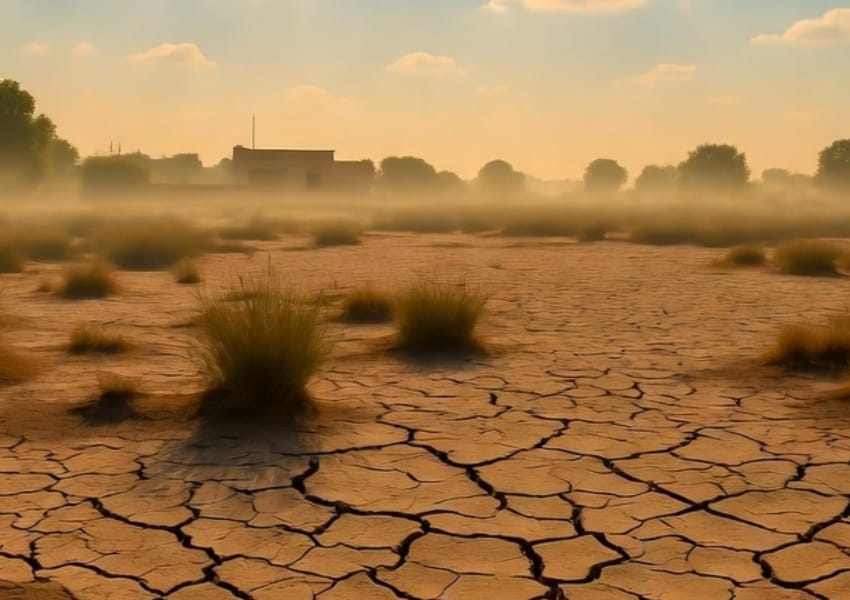
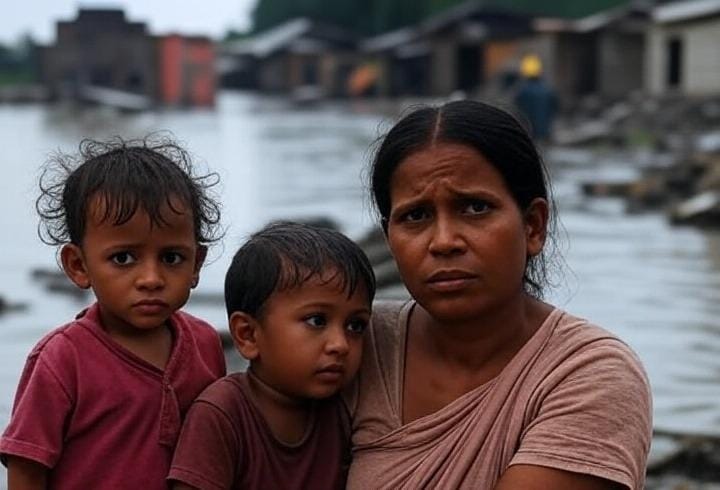
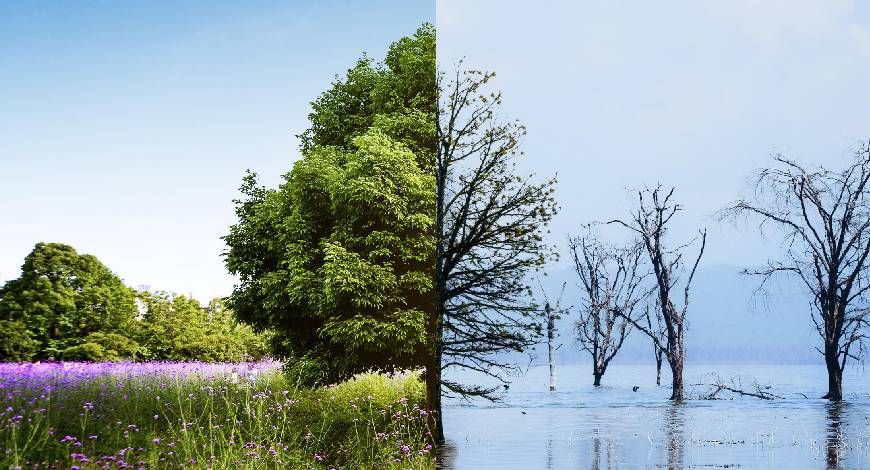
Climate change significantly impacts food production stability in India, with far-reaching consequences. The country, where malnutrition is a major concern, is now threatened by the adverse effects of climate change on its food production systems.
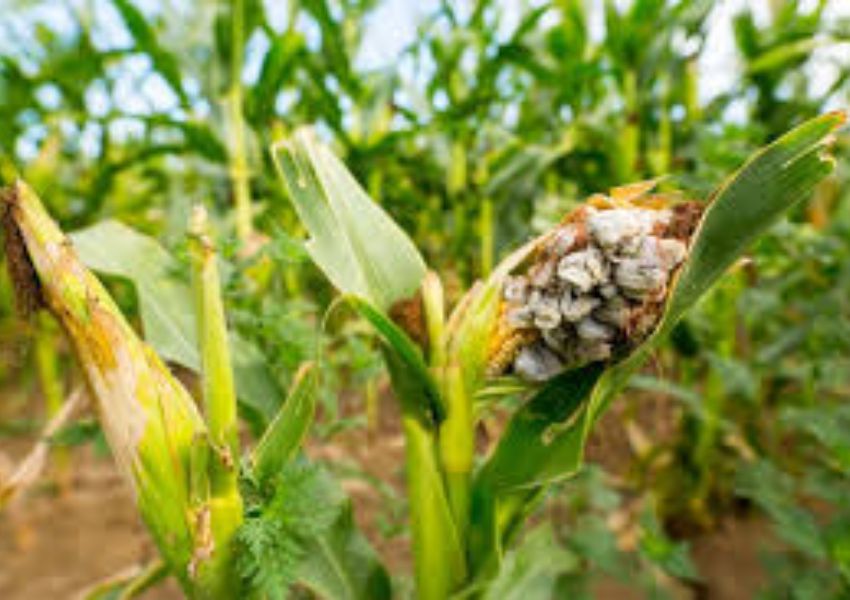
Reduced crop yields, soil degradation, and increased vulnerability to pests and diseases are some of the challenges that will likely cause food production instability. As a result, food scarcity, higher prices, and further food insecurity are expected, especially for the most vulnerable populations.
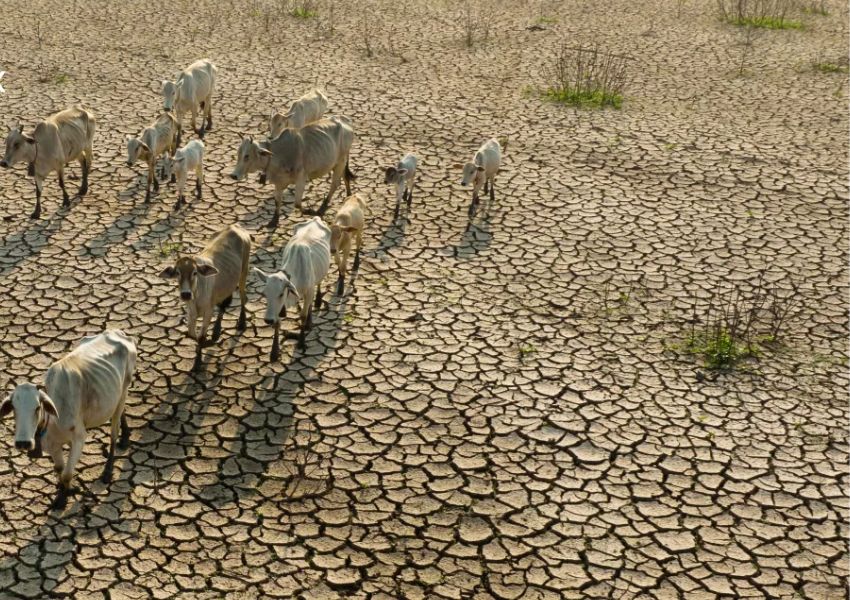
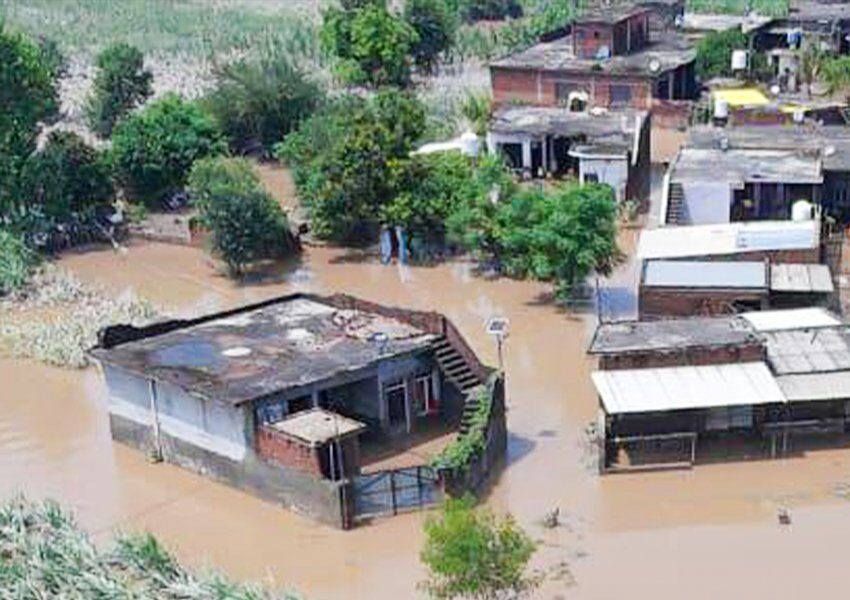
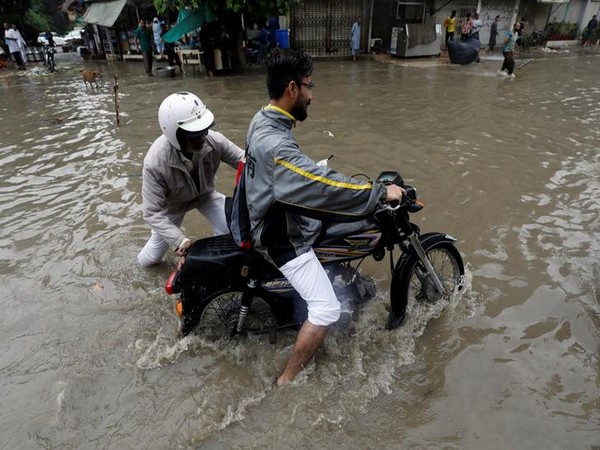
Changes in precipitation patterns significantly impact food production in India, in addition to the rising temperatures. Unpredictable rainfall, droughts, and floods affect water availability for irrigation and crops.
Droughts, in particular, cause crop failures and reduce yields, leading to food scarcity and insecurity. On the other hand, floods can also have a major impact by causing crop damage, disrupting transportation and food supply chains, and increasing the risk of waterborne diseases. These challenges further exacerbate the difficulties faced by farm and food systems in India.
The stability dimension of food security is a critical aspect of a country’s food security policy. Climate change poses a higher risk of production instability, resulting in price volatility due to short supply and changing market perception. Therefore, this research focuses on how climate change and variability affect food security’s fourth dimension, stability.
Lack of food stability is often associated with malnutrition and a lack of essential nutrients. Numerous studies have been conducted worldwide to assess the impact of climate change on food security and its various dimensions. Some of these studies conclude that climate change affects different dimensions of food security.
Climate change has significantly impacted food security and its various dimensions. In their exhaustive review, a multi-disciplinary team of researchers from several countries provided an overview of how these changes have affected each dimension, such as availability, accessibility, utilisation, and stability. The negative impacts of climate change on food security and nutrition (FSN) are particularly felt in poorer populations experiencing social inequality.
The main effects of climate change on FSN are related to access, production, nutritional quality, and the volatility of food prices (Alpino et al., 2022). However, there is little evidence available on the impact of climate change and variability on food stability at the country level, which is critical for designing suitable food security policies.
Therefore, a study was undertaken to evaluate the impact of climate change on the stability status of major food crops at the district level in India.