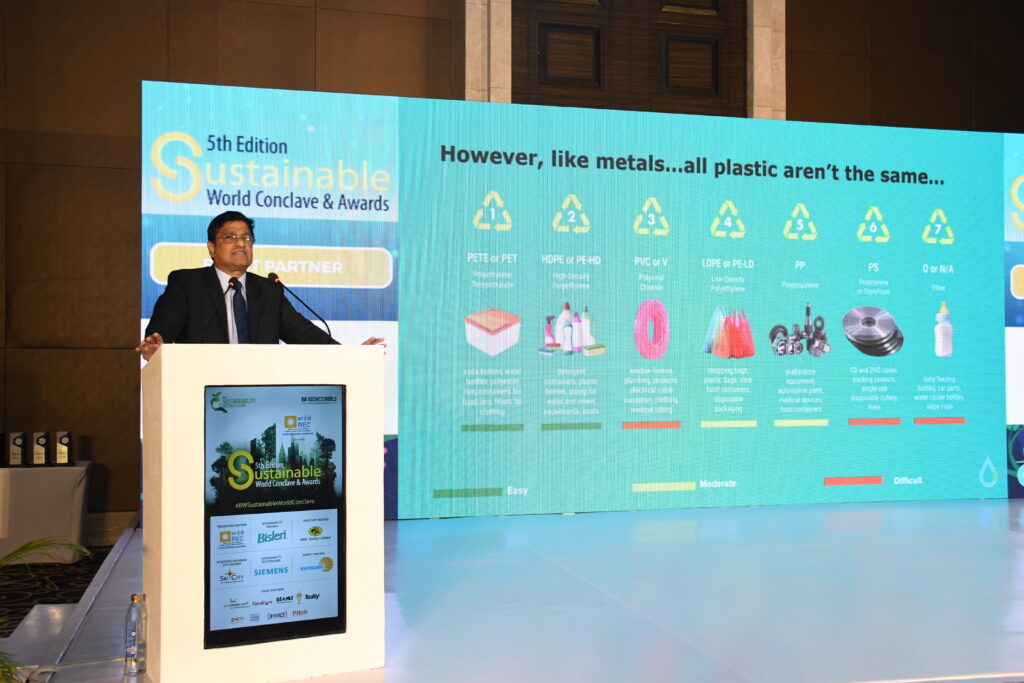
Integration Of Social Learning Essential For Effective Green Tech Subsidies

A new study in The US says that government subsidies for green technology fall short because price tags are only one of the many consumer hang-ups over adopting EVs
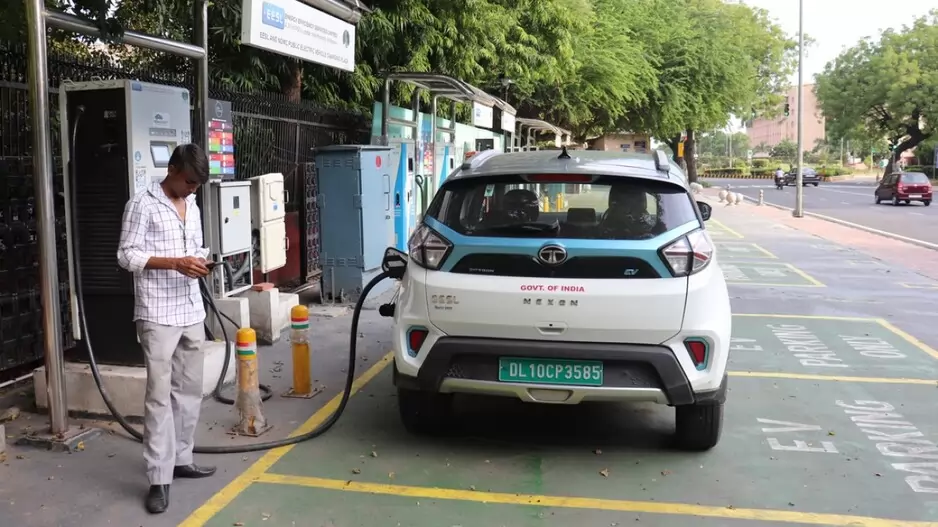
In 2023, the average cost of electric vehicles (EVs) in the US stood at approximately USD 54,000, presenting a significant barrier to consumer adoption. In response, the US government has introduced subsidies of up to USD 7,500 for new EV purchases. Despite this incentive, EV sales remain sluggish due to various factors beyond price, including the scarcity of charging infrastructure and consumer apprehensions about the technology’s novelty and long-term costs, particularly regarding battery replacement expenses.
To navigate these uncertainties, consumers often turn to online reviews and seek advice from early adopters, engaging in what researchers term “social learning” to inform their decisions. A recent study conducted by Huang, MIT Sloan professor and interim dean Georgia Perakis, and George Mason University professor Hang Ren underscores the importance of incorporating social learning dynamics into government subsidy strategies for emerging green technologies like EVs.
The researchers developed a model to simulate the dynamics of markets for green technologies, wherein government subsidies influence consumer behavior. Their findings reveal that while social learning among consumers can potentially drive adoption, it also introduces market uncertainties for suppliers. Positive reviews may lead to overwhelming demand, while negative feedback could result in excess inventory and production cutbacks.
In light of these insights, the study suggests tailoring government subsidies to account for the impact of social learning. For smaller markets, a gradual increase in subsidies over time may be more effective, offering suppliers greater certainty as consumer sentiment evolves. Conversely, in larger markets with significant potential benefits, an initial high subsidy that tapers off could better manage demand fluctuations and supply uncertainties.
However, the researchers caution that subsidy design should consider various market factors beyond social learning dynamics. While these recommendations offer valuable insights into subsidy optimization, policymakers must carefully weigh all relevant factors to maximize the effectiveness of green technology incentives.