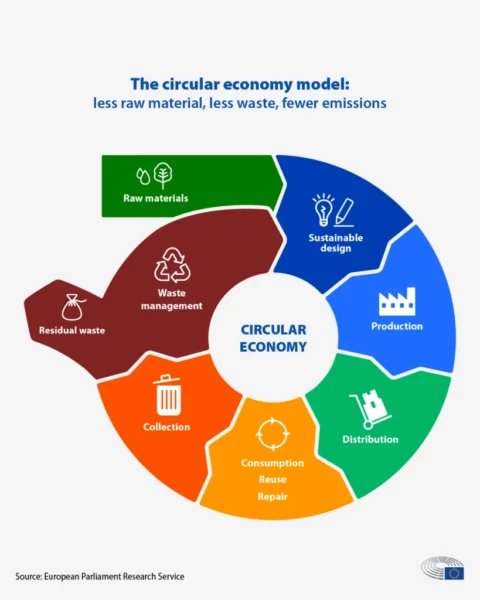
Effective Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) Strategies: Driving Sustainable Product Lifecycle Management

Experts stress about promoting environmental accountability and sustainable practices in manufacturing
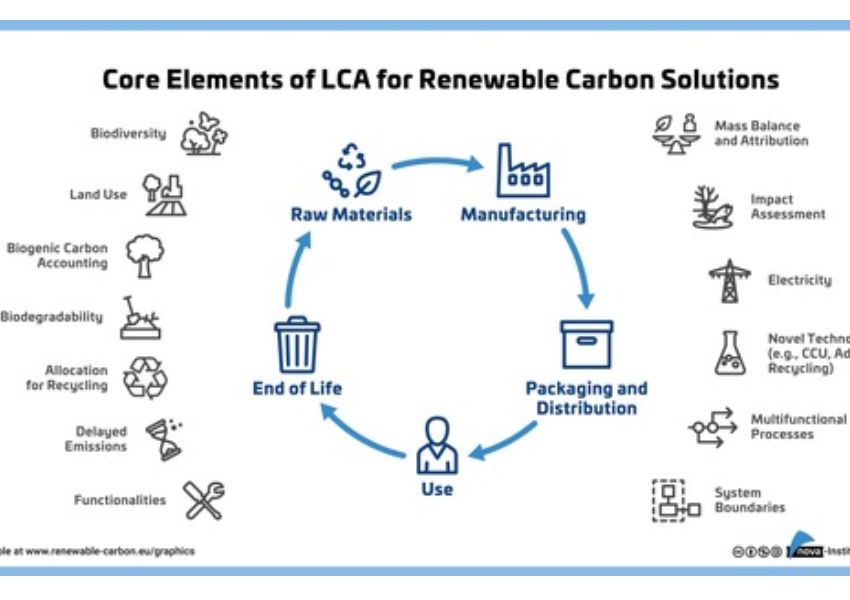
In today’s environmentally conscious world, effective Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) strategies are gaining increasing attention. Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) is a principle that holds manufacturers responsible for the environmental impact of their products throughout their entire lifecycle.
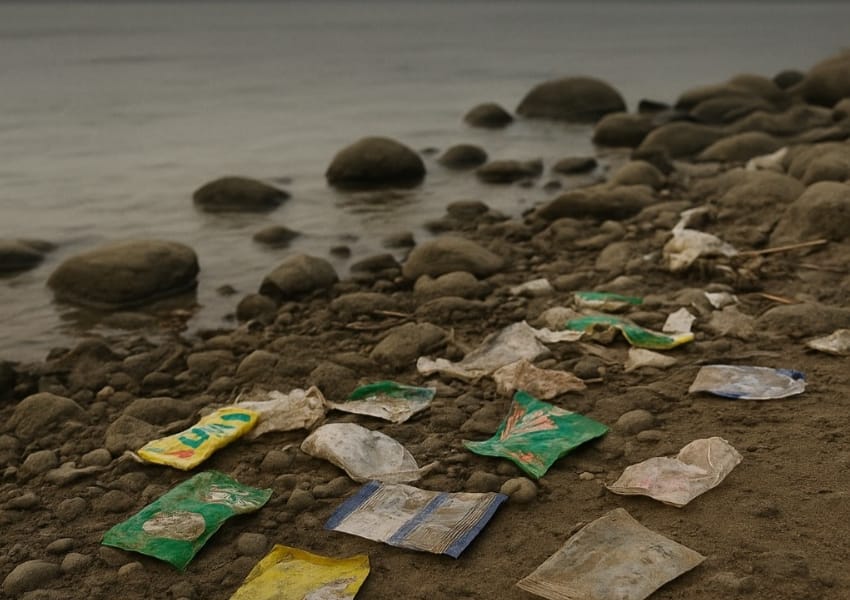
Sanchita Jindal, Former Adviser (Scientist G), Government of India, Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change says, “We have whole environmental problems due to our consumption problems. In India, we produce 68 million tonnes of waste. We have very unsure data of waste because of data inefficiency.”
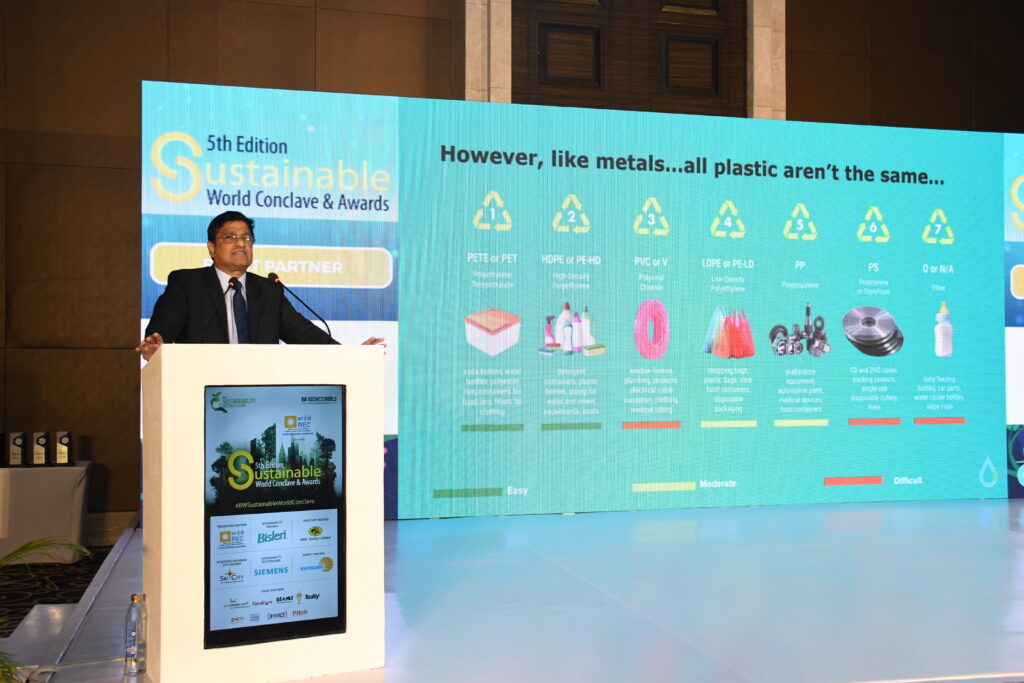
She also says that without the identification of the problems, solving them is impossible. “Plastic waste is 9.8 million tonnes according to the CPCB (Central Pollution Control Board) report. India generates 2.2 million tonnes of electronic waste, making the country the third largest to generate most of the electronic waste.”
The Production Phase:
“At the heart of effective EPR strategies lies the production phase,” says Hitesh Sharma, South Asia Lead-sustainable Impact & Compliance, APJ Region Domain Lead- Circular Economy, HP Inc. “We need to be careful of three key things – Context in which it is going to be applied. Characters who have an interplay of that strategy. And last, Content, the whole idea of how it all drives back and what narrative it sets.”
Product Design for Recyclability:
Ashish Jain, Director, the Indian Pollution Control Association, highlights, “Government formed rules in 2016 for organisations about EPR strategies and action plans, which came into effect properly in 2018. CPCB also started working deeply on waste management techniques.” He adds, “Focusing on the segregation methods of waste should be the main focus, as they are the ones putting the most effort and getting the least benefits. Waste pickers are the segregators. Conservation of recycled products will solve the problem.”
Collection and Recycling Initiatives:
Nikeeta N Jaiin, CEO, Vardhaman Auto Recycling, emphasises, “We need to work according to the geographical needs of India. In this instance, we can learn from other economies who are managing this well with penalties and stricter laws and regulations and it is working in favour of the environment.” She also points out, “The biggest challenges are risking leaving carbon footprints and the policies which restrict for the products to come back to the producers. Awareness can play a major role, so consumers need to be aware of what the hazardous wastes are and what value of harm they carry.”
Collaboration and Stakeholder Engagement:
Effective EPR strategies also involve collaboration and engagement with various stakeholders. Jain notes, “The most beneficial thing is feedback, the government is getting feedback from all the industry leaders as well as the waste recyclers. Which is helping them to create better policies and methods to tackle the waste management industry better and create a sustainable environment.”
As sustainability becomes increasingly important, effective EPR strategies play a vital role in promoting responsible product lifecycle management. From production to recycling, companies are embracing their environmental responsibilities and working towards a more sustainable future.