Rooftop Solar Panels Along Delhi-Ghaziabad-Meerut RRTS To Reduce Emissions: NCRTC

NCRTC aspires to cover 70 per cent of the total energy requirement of the entire Delhi-Ghaziabad-Meerut RRTS corridor through solar energy
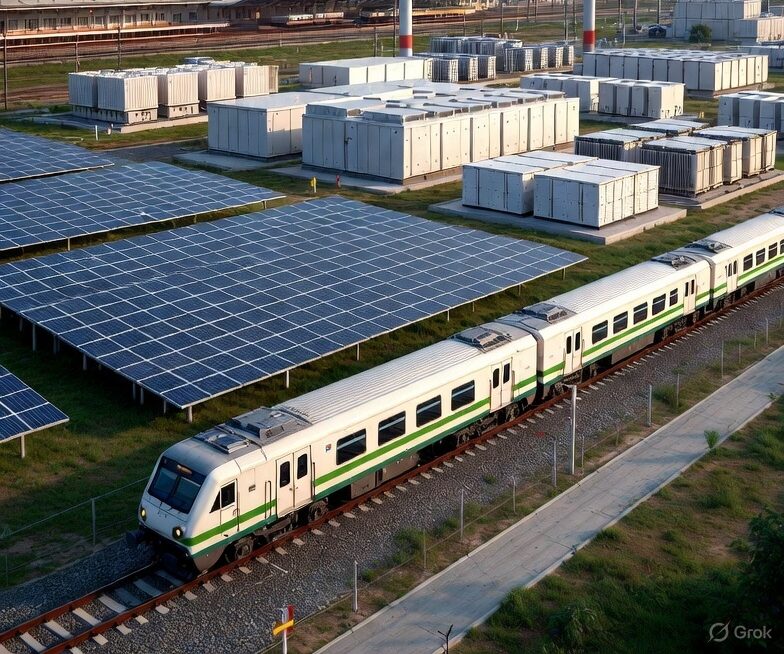
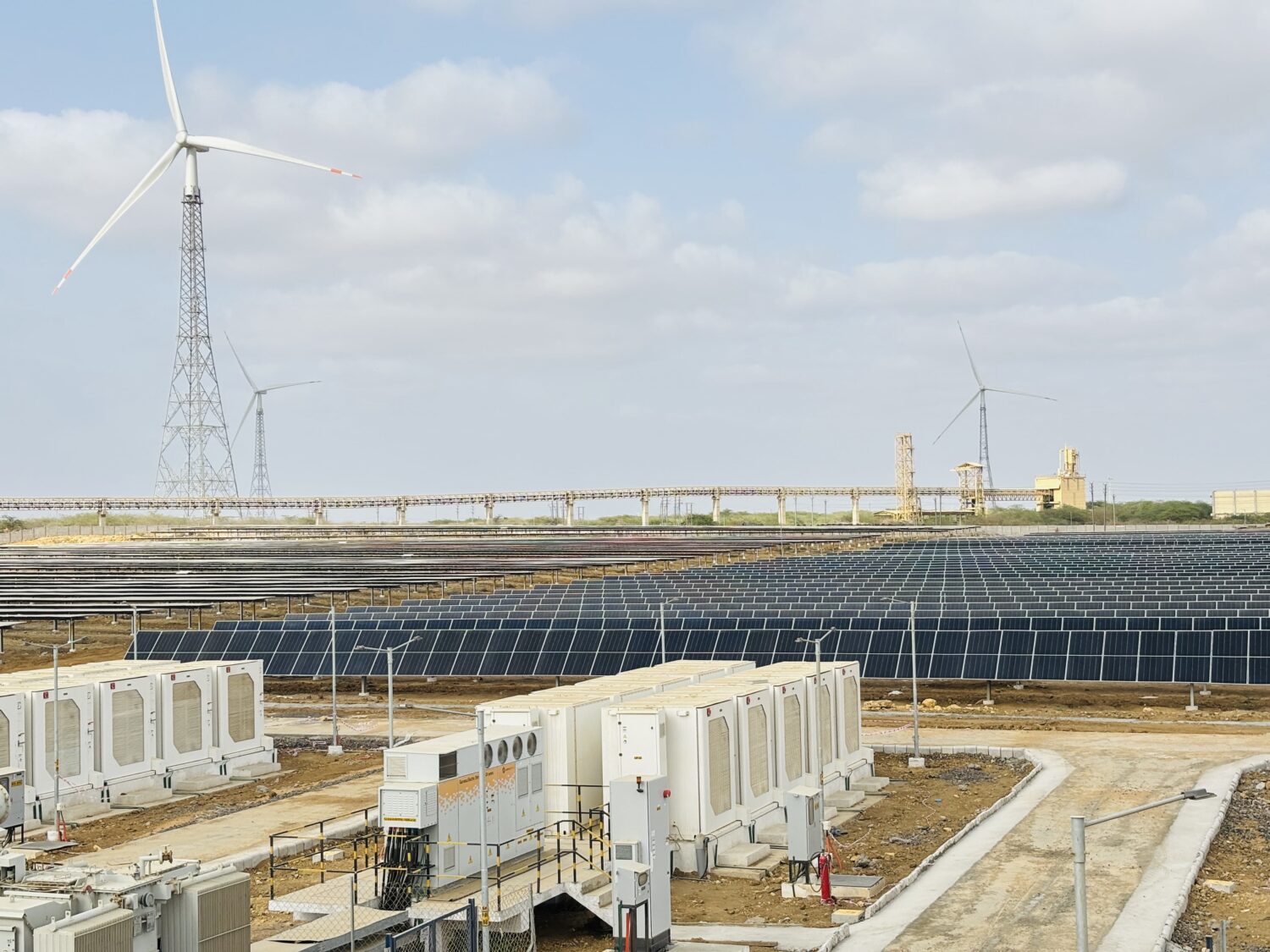
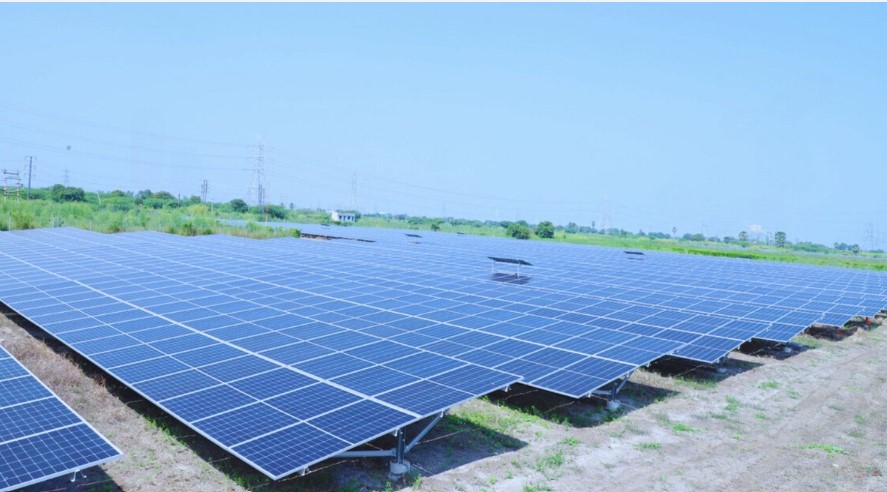
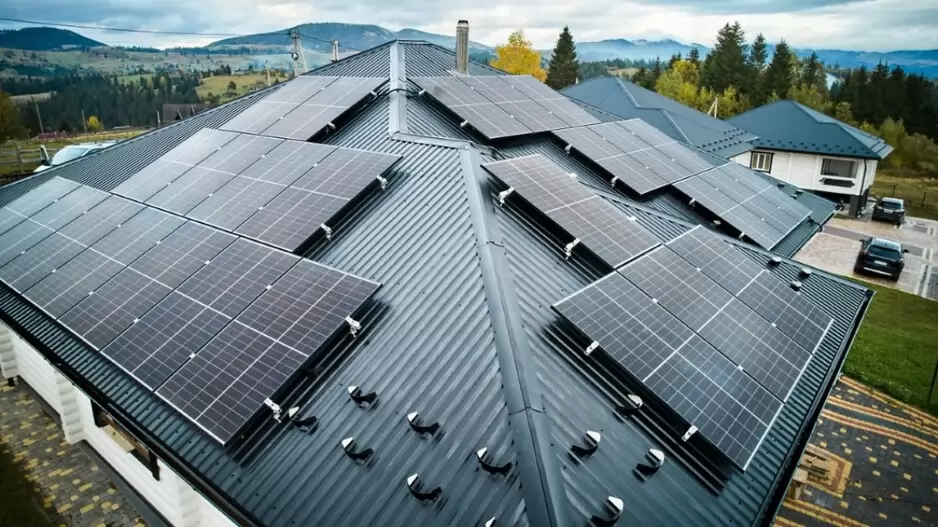
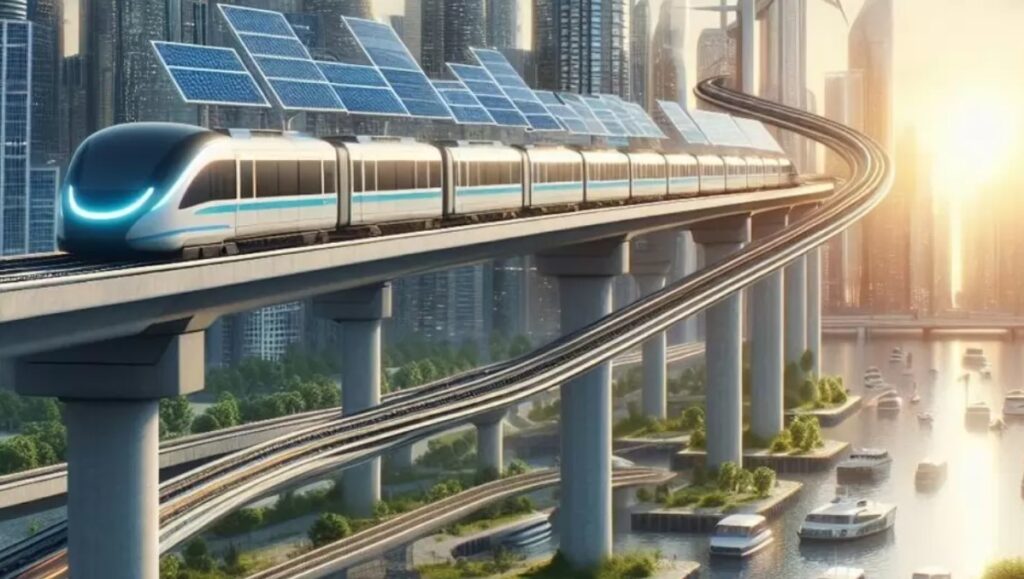
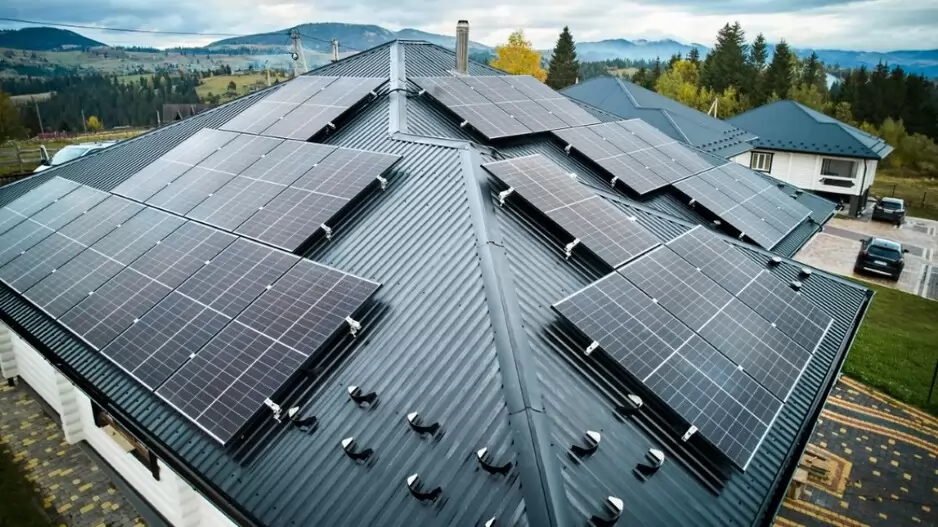
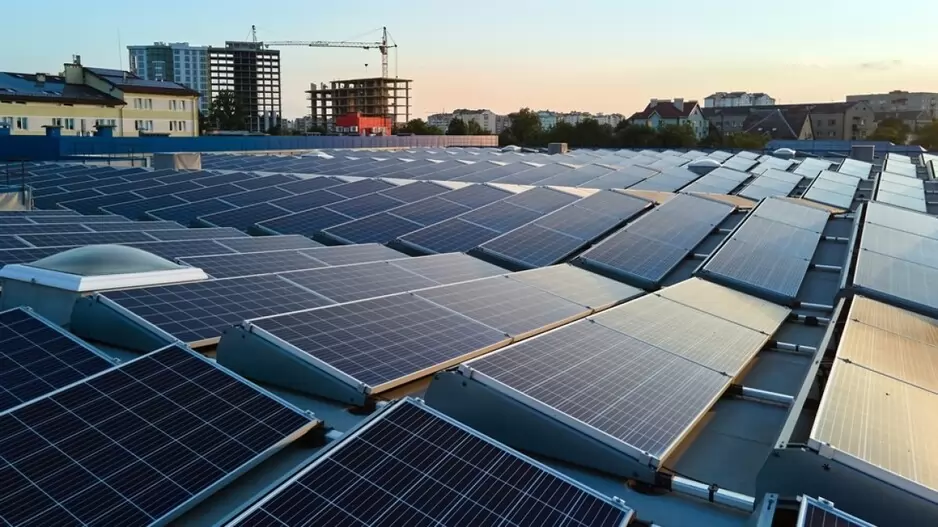
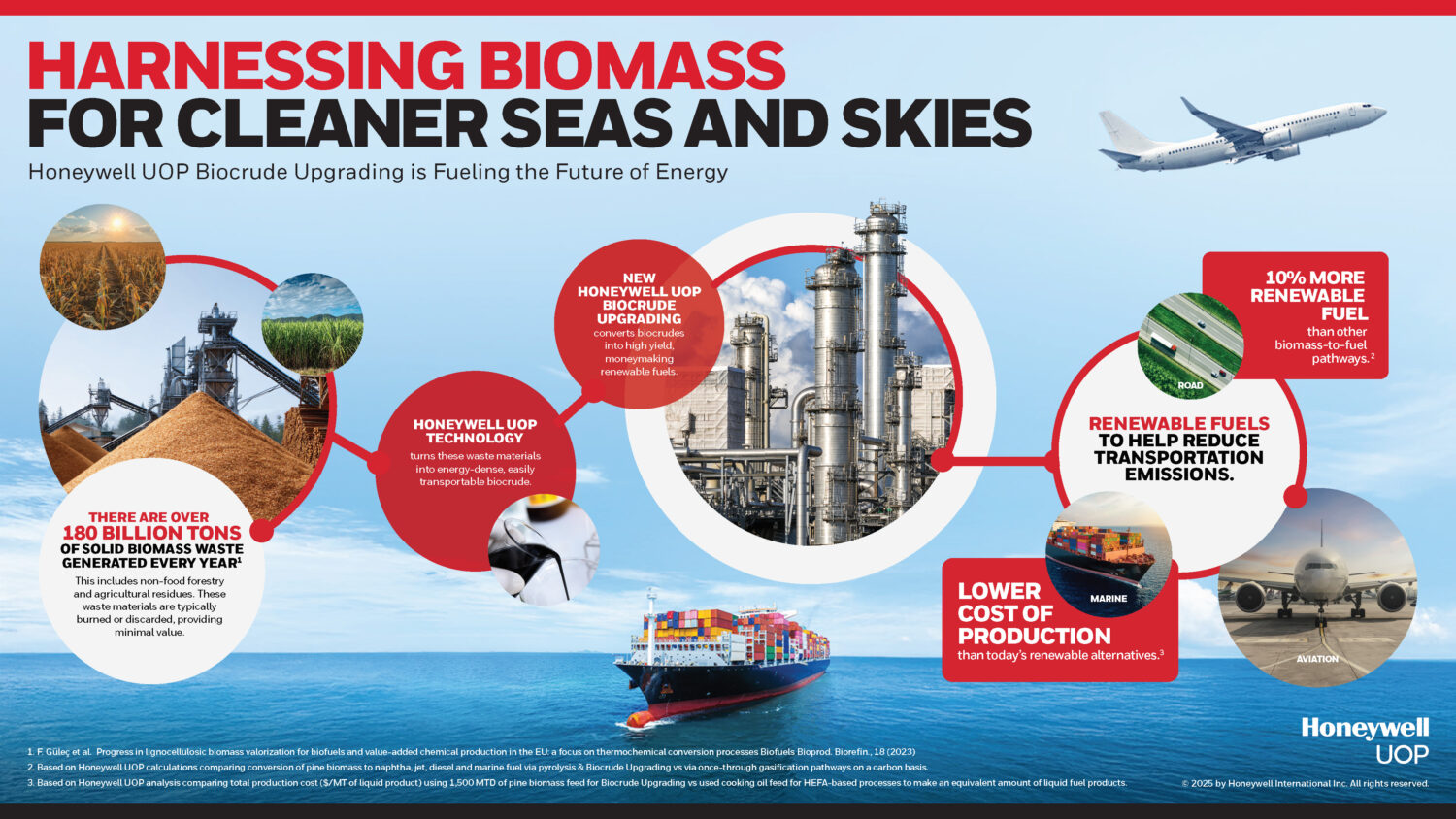
The National Capital Region Transport Corporation (NCRTC) is making significant strides towards renewable energy adoption, with plans to install approximately 11 megawatts of solar capacity across its rooftop spaces along the 82 km-long Delhi-Ghaziabad-Meerut Regional Rapid Transit System (RRTS) corridor. Officials anticipate this initiative to generate 12.5 million units of solar energy annually, resulting in a substantial reduction of 11,500 tonnes of carbon dioxide emissions per year. Already, solar panels with a capacity of around three MW have been installed over the platform sheds of RRTS stations at Sahibabad, Guldhar, Duhai, Duhai Depot Station and Duhai Workshop within the priority section. These installations are expected to cater to the auxiliary load requirements of these stations effectively.
The Sahibabad station’s solar power plant, equipped with 1,620 high-efficiency solar panels, boasts a total capacity of 729 kilowatts, poised to generate approximately 10 lakh units of electricity annually. Similarly, the Duhai Depot accommodates a solar power plant with an installed capacity of 585 KW. Looking ahead, NCRTC aims to extend solar power infrastructure to the remaining stations of the RRTS corridor gradually. Their vision encompasses covering 70 percent of the total energy requirement of the entire Delhi-Ghaziabad-Meerut RRTS corridor through solar energy.
Throughout the project’s lifecycle, NCRTC has prioritised environmental sustainability, integrating green technologies and low-carbon initiatives from the pre-design stage. Initiatives such as the use of fly ash bricks, efficient waste disposal, energy-efficient designs and extensive utilisation of solar energy underscore NCRTC’s commitment to sustainable practices. Moreover, landscaping efforts at Sahibabad station and Ghaziabad RSS, along with efficient space utilisation beneath the RRTS viaduct, contribute to minimising energy consumption and carbon footprint.
Looking forward, NCRTC is committed to exploring additional avenues in electric and transformative mobility, as well as alternative fuel and energy sources, to further reduce the project’s carbon footprint. With the 17-km-long priority section of the Delhi-Ghaziabad-Meerut RRTS corridor already operational, NCRTC is actively working towards extending services to the additional 25-kilometer section from Duhai to Meerut South within the next two months.