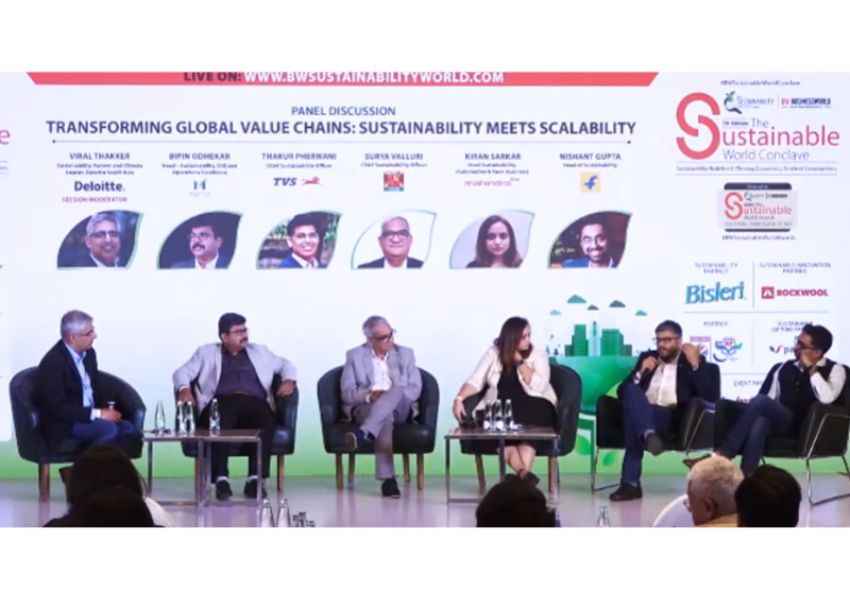
Power Exchanges: Catalysts For Building A Robust Green Energy Market

India aims for net-zero emissions by 2070, sourcing 50 per cent of energy from renewables by 2030. Power exchanges drive efficiency, enable renewable integration, and save costs, pivotal for India’s sustainable energy future
At the seminal COP26 climate summit in 2021, India boldly pledged to achieve net-zero carbon emissions by 2070. This commitment represents a monumental stride towards energy transformation. The target is aligned with an ambitious plan of meeting 50 per cent of the nation’s energy requirements from renewable sources by 2030. These goals reflect India’s dedication to sustainable development and desire to assume climate leadership on the global stage.
Within this overarching vision, power exchanges will become crucial catalysts playing an instrumental role in realising India’s green energy and net-zero objectives. Since its establishment in 2008, power exchanges have revolutionised the landscape by introducing competitive and transparent price discovery mechanisms for electricity. These platforms have facilitated efficient planning for DISCOMs and offered flexibility in procurement, thus ensuring an uninterrupted 24×7 power supply to consumers while maintaining strong financial liquidity. The evolution has been remarkable, with platforms now offering diverse trading options catering to India’s dynamic electricity market. Currently trading more than 100 billion units annually, equivalent to around 7 per cent of the country’s total generation, power exchanges provide around 25 contracts across various market segments. These include the Day Ahead Market (DAM), Real-Time Market (RTM), Term Ahead Market (TAM) serving up to 90 days, Green Market, and Ancillary Market.
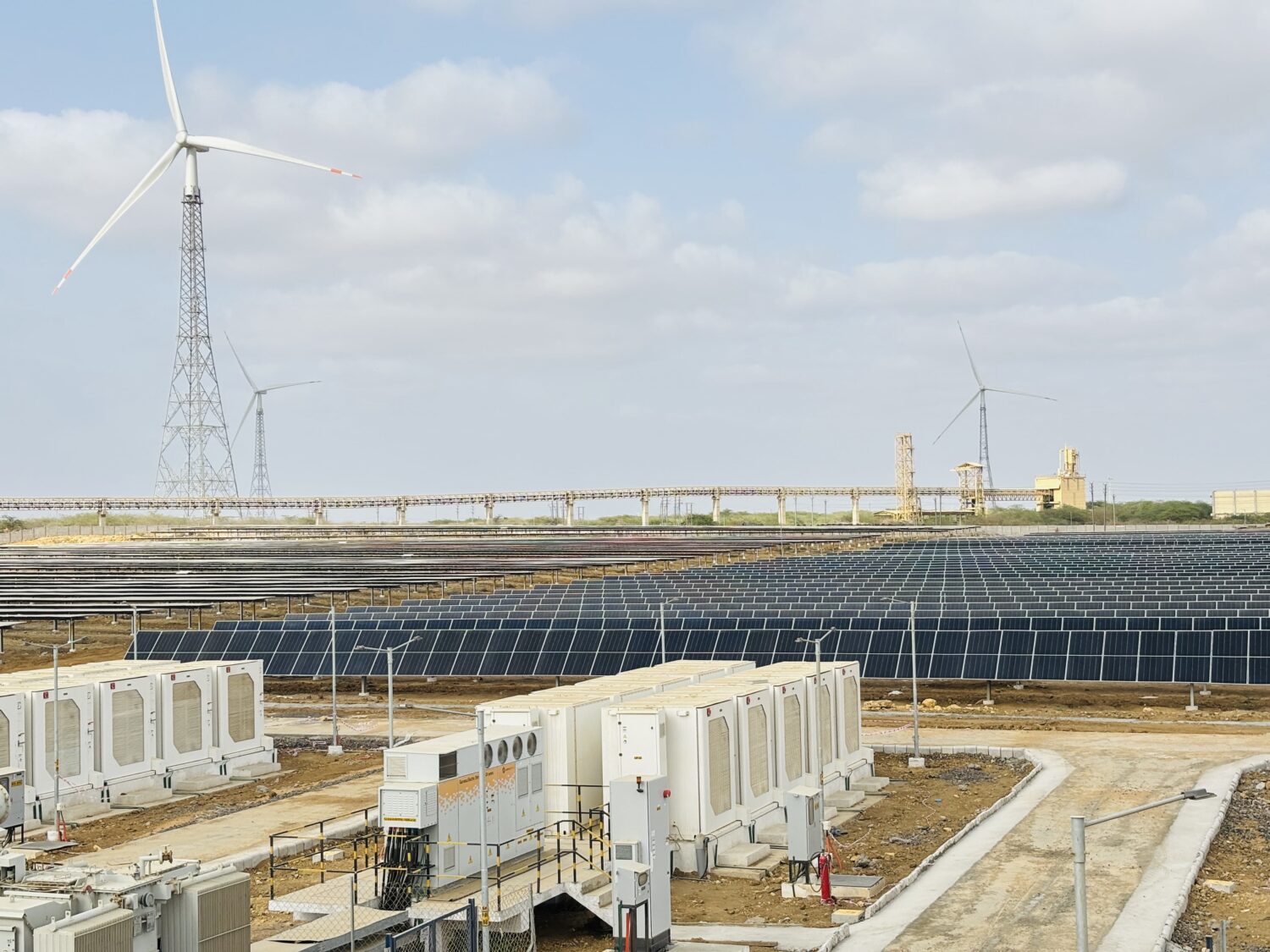
The integral flexibility of Real-Time Market (RTM) platforms has enabled market participants to adapt swiftly to demand variations, support large-scale renewable energy integration, and enhance grid security. By providing efficient price signals, power exchanges have fostered the integration of renewable energy into India’s power grid. Over the last 15 years, exchange prices have consistently proven to be more competitive than alternate modes of power procurement, resulting in significant financial savings for distribution companies and large industries alike. The missing link for renewable power integration has been energy storage, and Battery Energy Storage Systems (BESS) are identified as a future growth driver for the sector. SECI’s recent award of India’s first pilot project of a 500 MW battery storage, with 40% open capacity to be sold through power exchanges, marks a significant milestone in this direction.
Furthermore, the growing emphasis on renewable energy resources has prompted the trading of market-based instruments such as Renewable Energy Certificates (RECs) and Energy Saving Certificates (ESCerts) on exchanges since 2011. These instruments not only reduce India’s carbon footprint but also support the government’s Perform Achieve Trade (PAT) policy, showcasing the pivotal role of power exchanges in promoting sustainable energy practices.
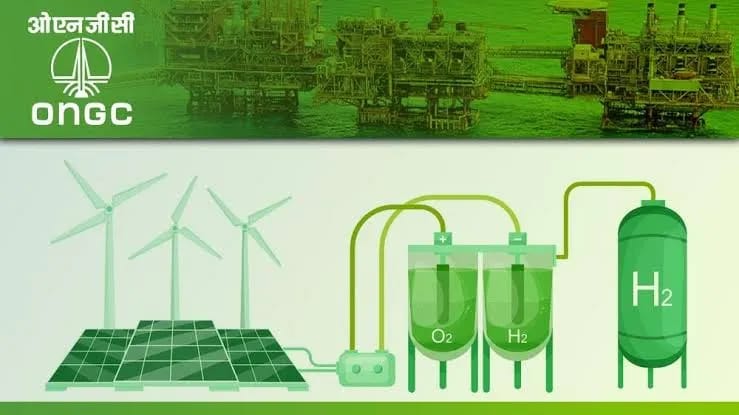
As electrification expands and the focus intensifies on green energy banking solutions such as pumped storage, battery, and hydrogen, power exchanges will adapt by introducing new products to cater to India’s evolving energy mix and growing energy demand. The emergence of Green Hydrogen and Peer-to-Peer (P2P) Trading presents untapped opportunities that are set to revolutionize the energy sector, aligning India’s energy landscape with global trends towards decentralized energy solutions.
In essence, power exchanges emerge as foundational pillars propelling India towards a greener and more sustainable future. Their role as catalysts for building a robust green energy market is undeniable, and their continued evolution and innovation will be instrumental in shaping India’s energy landscape for generations to come.