Greening The Grid: Bridging Sustainability And Smart Distribution At Scale

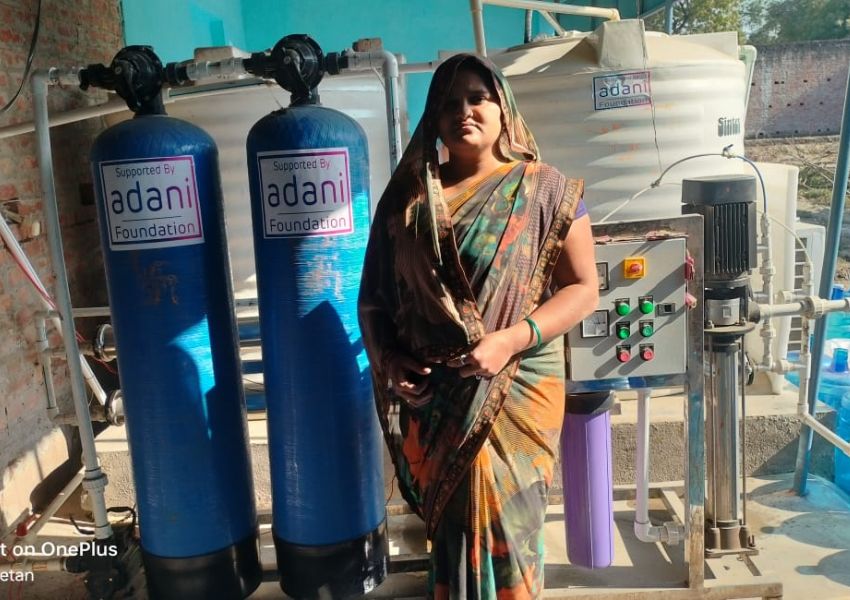
By mid-2025, over 32 million smart meters had been deployed under the Revamped Distribution Sector Scheme (RDSS), which targets 223 million installations nationwide (Power Line Magazine) and this rollout aims to create a countrywide, real-time energy data network
Byline: Abhishek Ranjan, Member of Governing Council – PowerGen India and CEO, BSES Rajdhani Power
India’s power distribution industry is undergoing a historic transformation—from passive service providers to intelligent, data-driven energy partners. This shift, powered by Advanced Metering Infrastructure (AMI), Artificial Intelligence (AI), and the Internet of Things (IoT), is redefining how energy is delivered, managed, and consumed.
Smart meters form the core of India’s distribution transformation. Beyond billing, they enable advanced grid surveillance and real-time monitoring. By mid-2025, over 32 million smart meters had been deployed under the Revamped Distribution Sector Scheme (RDSS), which targets 223 million installations nationwide (Power Line Magazine). This rollout aims to create a countrywide, real-time energy data network.
Smart meter data—integrated with IoT sensors on feeders, transformers, and other grid assets—powers Advanced Metering Infrastructure (AMI), providing granular insights into consumption, power flow, and grid health. GPS-enabled asset tracking further enhances visibility and control.
Key benefits include:
Reducing AT&C losses: Historically a major challenge for DISCOMs, AT&C losses averaged 16.12 per cent in FY 2023-24 (Power Line Magazine). Utilities that adopted smart grid technologies have seen losses fall to single digits. RDSS aims to lower losses to 12–15 per cent by 2024-25 (PIB). Smart meters and IoT sensors play a critical role in detecting theft and pinpointing technical inefficiencies.
Boosting operational efficiency: Real-time monitoring enables predictive maintenance, allowing utilities to address equipment issues before they cause outages. This improves reliability, reduces downtime, and optimises network performance.
The Brains of the Grid
AMI and IoT deliver the raw data—AI turns it into operational intelligence. By applying machine learning and predictive analytics, utilities can transform grid operations from reactive to proactive.
Key AI applications in the grid:
Demand Forecasting – Analyses historical consumption, weather trends, and socioeconomic factors to predict demand with higher accuracy. This supports prudent power procurement, cost savings, and grid stability.
Predictive Maintenance – Identifies subtle equipment anomalies in sensor data before they lead to failures, allowing timely maintenance and extended asset life.
Outage Management – Locates faults automatically, isolates affected areas and reroutes power to minimise downtime. This “self-healing” grid capability enhances service quality and customer satisfaction.
Empowering the Prosumer
The stronger focus on smarter utility management and technologies integrates the rise of smartphones and electric vehicles (EV). This technology shift also requires smarter management on the consumer’s side. The emergence of smart meters and rooftop solar grids alongside EVs integrates a new category of consumers defined as “prosumers”, who simultaneously consume and produce electricity. “The intelligent grid” is critical for the effective integration of prosumer technologies (DERs).
To proactively manage energy consumption with the help of mobile applications, consumers require mobile smart meters that provide real-time data. The data from smart meters is critical for informing the consumer. As of June 2025, India’s renewable energy figures stand at 235.7 GW, including 100.8 GW worth of solar energy, as per PIB. The implementation of solar energy systems offers real-time analytics, smart meters, dynamic tariff structures, and demand response systems, which further improve solar energy efficiency by shifting energy demand to off-peak periods, all of which help improve grid reliability.
In a nutshell, India’s energy landscape, the change from wire to wisdom is more than a necessity; it’s a strategic move. It is not just about safeguarding a power supply for all, but by embracing technology, actively construct a smarter, more resilient grid, which in turn motivates a new generation of conscious consumers, empowering the leaders to pave the way for a more sustainable future.
From Wires to Wisdom
This transformation is not optional—it is strategic. Moving from basic power delivery to intelligent grid management ensures reliability, resilience, and sustainability. By embracing AMI, IoT, and AI, India’s utilities can reduce losses, integrate renewables, and empower consumers to become active participants in the energy system. The leaders who invest now will set the blueprint for a cleaner, smarter, and more inclusive energy future.