Budgeting For A Sustainable Tomorrow: Unlocking India’s Renewable Energy Potential

As India’s global leadership in renewable energy solidifies, all eyes are now on the upcoming budget to set the course for sustainable growth and energy independence
Byline: Amit Paithankar, Whole-time Director & CEO, Waaree Energies
The Union Budget for FY 2025-26 comes at a defining moment for India’s renewable energy sector. Over the past year, the sector has experienced remarkable growth, powered by progressive policy interventions, advancements in technology, and consistent investments. As India’s global leadership in renewable energy solidifies, all eyes are now on the upcoming budget to set the course for sustainable growth and energy independence.
Approved List of Models and Manufacturers (ALMM): Expanding the Framework for a Self-Reliant Supply Chain
The Ministry of New and Renewable Energy’s Approved List of Models and Manufacturers (ALMM) has been a cornerstone in ensuring quality in solar PV modules, fostering confidence among developers and consumers alike. The next step is to expand this framework to include wafers and ingots, which remain critical components in achieving a truly self-reliant supply chain. While ALMM for PV modules has already proven beneficial for the industry, and ALMM for cells is slated for implementation by June 2026, the upcoming budget must accelerate this progress by making a policy statement on ALMM for ingots and wafers made applicable at an appropriate future date. This will not only ensure better quality control across the supply chain but also strengthen India’s position as a global renewable energy hub.
Empowering Rooftop Solar Adoption
In alignment with the Honourable Prime Minister’s vision of empowering lower- and middle-class households with solar rooftop systems, schemes like the Pradhanmantri Suryodaya Yojana (PMSY) and PM Surya Ghar: Muft Bijli Yojana have made significant strides. Notably, the PM Surya Ghar scheme has received 5.15 lakh registrations as of December 2024, marking a game-changing start for India’s solar adoption journey. These programs enable households to generate additional income through surplus power while reducing carbon footprints. To amplify this success, the budget should focus on the further expansion of such schemes, coupled with measures like low-interest loans, streamlined regulatory approvals, and enhanced subsidies for installations. By scaling these initiatives, we can democratize access to clean energy, reduce energy poverty, and drive robust job creation across the solar value chain.
Strengthening the Production Linked Incentive (PLI) Scheme
The Production Linked Incentive (PLI) scheme for solar manufacturing has been a resounding success, driving significant capacity additions. With an allocation of Rs 19,500 crore under the PLI program, India is expected to achieve over 65 GW of domestic solar PV module manufacturing capacity by 2026, covering the entire value chain from polysilicon to modules. This initiative is already catalyzing investments and creating approximately 1.5 lakh direct and indirect jobs in the renewable energy sector. To sustain this momentum, the budget must consider the further extension of the PLI scheme to polysilicon, wafers, and ingots, as these components are critical to achieving complete self-reliance in the solar supply chain. Encouraging investments in these areas will strengthen India’s upstream manufacturing capabilities, reduce import dependency, and ensure long-term cost competitiveness.
Accelerated Depreciation for Key Production Equipment: Keeping Pace with Technological Evolution
In the fast-evolving renewable energy manufacturing sector, technological advancements are occurring at a rapid pace, with new innovations constantly reshaping production methods. As the sector races to stay competitive, the need to upgrade production equipment every 3 to 5 years is inevitable. To maintain India’s position in the global technology race, it is crucial that accounting practices evolve accordingly. A shift towards allowing accelerated depreciation for key production equipment would incentivize manufacturers to invest in cutting-edge technologies more frequently. This change would not only help Indian manufacturers stay at the forefront of innovation but also bolster the country’s competitive edge in global markets.
Driving Innovation through Research & Development
Investments in Research & Development (R&D) are pivotal to the growth of India’s renewable energy sector. To accelerate advancements, it is crucial to incentivize research in areas such as high-efficiency solar modules, battery storage, hydrogen technology, and grid management solutions. Collaborative efforts between academic institutions, industry players, and government agencies must be strengthened to build an innovation ecosystem. Establishing dedicated funds and offering tax incentives for R&D initiatives will enable India to become a global hub for renewable energy innovation.
Building towards 500 GW
India’s ambition of achieving 500 GW of renewable energy capacity by 2030 is underpinned by rising investments and private-sector participation. The budget must sustain this momentum by incentivizing renewable energy developers, enhancing grid infrastructure, and simplifying approval processes for large-scale projects. Two important aspects for renewable energy capacity growth in a nation are reforms in land acquisition and power evacuation through increasing grid capacity. Prioritizing land allocation for solar farms and offering national-level tax credits for renewable energy investments will further accelerate capacity additions and solidify India’s position as a global renewable energy leader.
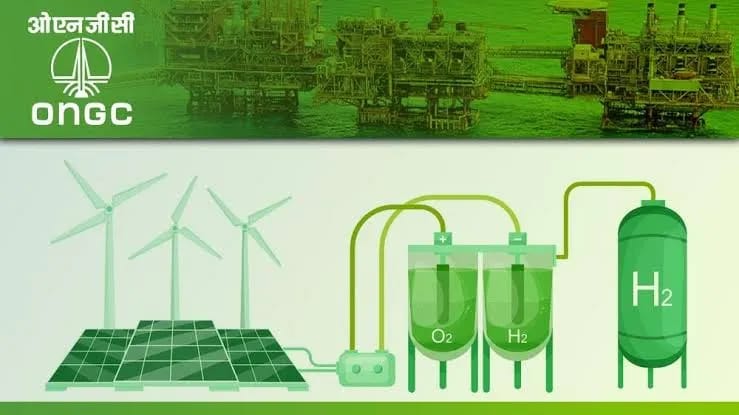
Advancing the National Green Hydrogen Mission
To contribute to India’s vision of Aatmanirbhar Bharat and inspire the global clean energy transition, the production and export of green hydrogen in-house will prove highly beneficial. With a mission to produce at least 5 million tonnes of green hydrogen by 2030, this initiative positions hydrogen as a key solution for sectors that are challenging to decarbonize. To accelerate progress, the budget could introduce fresh initiatives to support the development of hydrogen production infrastructure and provide tax incentives for manufacturers of electrolysers and fuel cells. In addition, increased funding for research aimed at scaling up hydrogen production technologies and reducing costs will further solidify India’s position as an emerging nation in the green hydrogen sector.
Empowering Independent Power Producers (IPPs)
Independent Power Producers (IPPs) are integral to diversifying India’s energy mix and driving renewable energy adoption. Streamlined approvals for new projects, competitive tariff structures, and improved access to green finance are critical to their growth. Establishing a dedicated renewable energy development fund will provide IPPs with the financial security needed to scale operations. High transmission charges at both state and central levels often increase project costs and raise electricity tariffs for end consumers. Rationalizing Inter-State Transmission System (ISTS) and state-level transmission charges is crucial to lowering Power Purchase Agreement (PPA) values and making solar energy more competitive.
Anti-Dumping Duty: Striking the Balance with Timely Implementation
The introduction of anti-dumping duties has played a pivotal role in curbing imports of low-quality components and nurturing domestic manufacturers. It is a rightly taken step to make our ecosystem more self-reliant. However, for this measure to be truly effective, its implementation must be timely and calibrated. An abrupt rollout can lead to market fluctuations and disrupt project timelines. A phased and transparent approach will allow the industry to adapt while maintaining stability in the supply chain. As India aims to become self-reliant in renewable energy manufacturing, the budget must signal a balanced strategy that supports both domestic players and seamless project execution.
Looking Ahead
The Union Budget for FY 2025-26 will most certainly be a catalyst for India’s renewable energy transformation. From fostering domestic manufacturing and incentivizing rooftop solar adoption to advancing the green hydrogen mission and strengthening the PLI scheme, the measures introduced in this budget will define the trajectory of India’s clean energy future. By creating an enabling environment for innovation, investment, and collaboration, the government can unlock the full potential of the renewable energy sector and position India as the world’s largest producer of solar energy. This effort is essential for India to embrace its role in Vasudhaiva Kutumbakam- the idea that “the world is one family.” As one of the world’s significant emitters of greenhouse gases, it is our shared responsibility to lead by example. By resolutely promoting renewable energy and making it a dominant part of our energy grid, we not only reduce our emission intensity but also contribute meaningfully to the global fight against climate change.