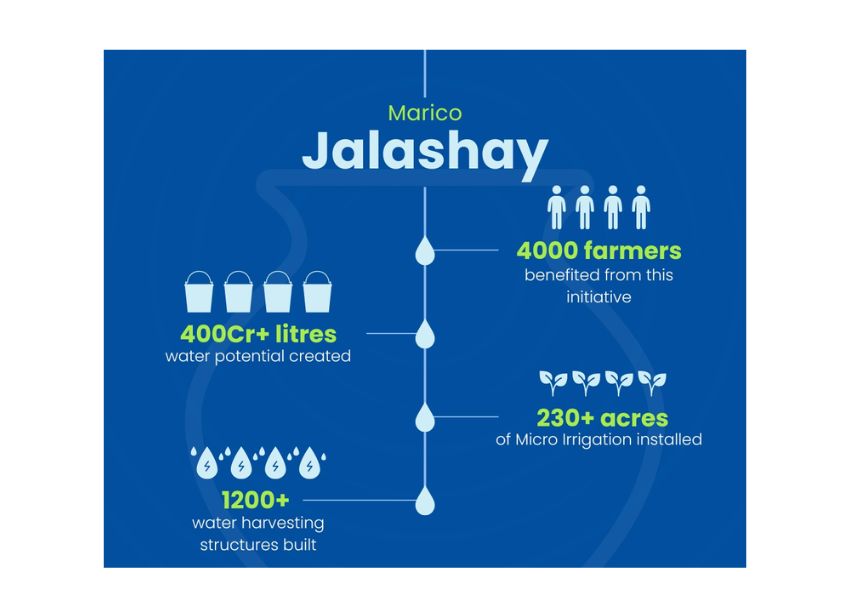
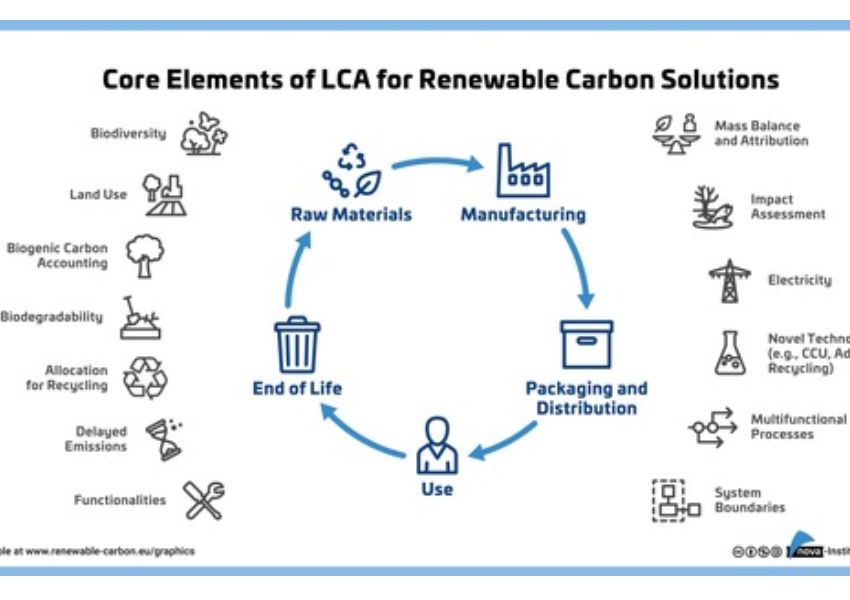
Deloitte India Introduces Innovative Initiative: Enterprise Conscious Code

Pioneering Sustainable, Inclusive, and Accessible Software Development, Aiming to Reduce Software-Generated Emissions by Up to 30 per cent
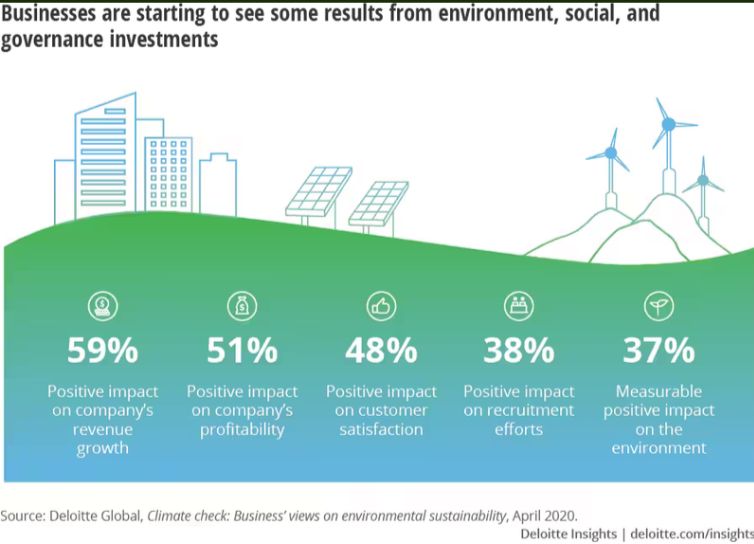
Enterprise Conscious Code (ECC), a project aiming at promoting sustainable and ethical software development, was announced by Deloitte India at the World Economic Forum in Davos. Global issues about reducing carbon footprints, increasing energy consciousness, and ensuring accessibility for everyone are addressed by this programme. With a focus on the triple bottom line of people, earth, and profits, ECC provides workable solutions for the development of environmentally friendly software. Remarkably, the Information and Communications Technology (ICT) industry accounts for 1.58 billion tonnes, or 3 per cent, of the world’s annual carbon emissions. In this domain, ECC can reduce emissions by up to 30 per cent that are attributable to software alone, which translates into notable savings on power and storage expenses.
ECC tackles the need for inclusive software development by putting a focus on taking into account people with different abilities, like colour blindness and astigmatism. ECC is in line with organisational objectives by promoting sustainability and inclusivity, which improves profitability through effective cost control. The CEO of Deloitte South Asia, Romal Shetty said, “We are proud to introduce this new initiative, as a testament to our commitment towards sustainable growth of the technology industry. Innovation must go hand in hand with our responsibility to minimise the environmental impact of technology. By embracing such conscious practices, we aim to lead the way in creating software solutions that not only meet the highest standards of performance but also contribute to a greener and more inclusive future.”
Through the use of completely automated methods and frameworks created especially to determine the carbon footprint of an organisation’s technology ecosystem, ECC seeks to generate comprehensive measurements. Many international organisations now fail to monitor or account for these emissions. The automated tools from ECC will make it easier to calculate the carbon footprint of the company’s digital landscape, identify bottlenecks, and offer an accessibility score in addition to a green health score, index, and debt. In order to maximise savings and lower emissions, ECC will also suggest remedial actions and the relevant software code versions.
The project highlights software emissions that are frequently disregarded but discreetly increase greenhouse gas emissions. If every page is seen, the 200 million active websites in India alone account for half of the world’s CO2 emissions, which is equal to a gasoline-powered automobile travelling 10 kilometres per user. The substantial environmental impact is highlighted by Deloitte India’s examination of well-known Indian websites, which shows that each website releases CO2 comparable to what about 20 trees would absorb every day.