Evolution Of Corporate Governance: Embracing Sustainability, Technology, And Ethical Leadership

In recent times sustainability, technology, and ethical leadership are gaining significance in boardrooms as well as the policy corridors
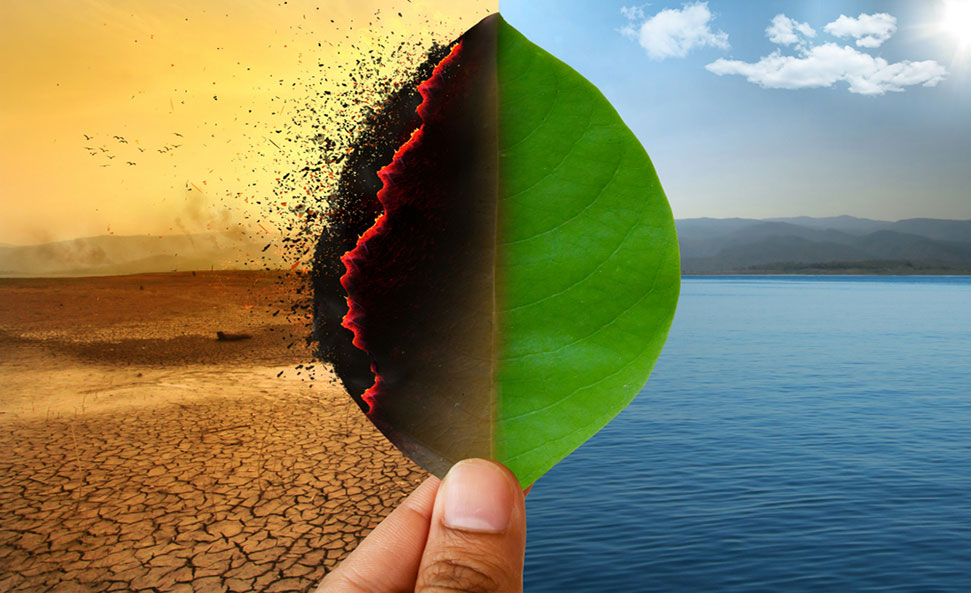
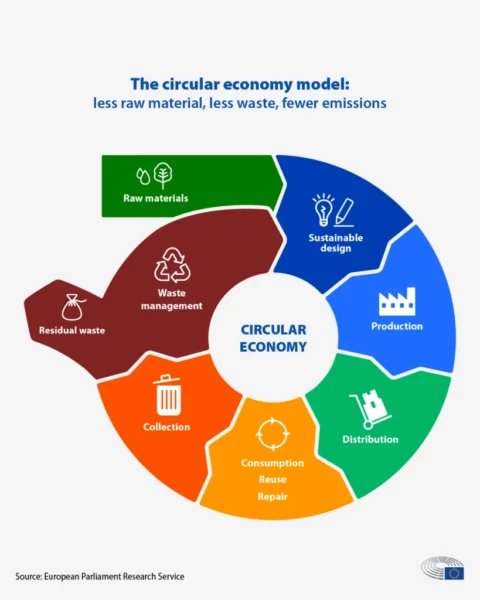
The landscape of corporate governance has undergone a vivid transformation, evolving from a system primarily concerned with directing and controlling companies to a more empowered and dynamic mechanism. Traditionally centred around board composition, independence, shareholder rights, and related-party transactions, corporate governance now encompasses emerging elements that play a vital role in shaping the operational ethos of organisations.
In the corporate governance framework, multiple layers dictate how a company operates, regulates, and adds value to a broad spectrum of stakeholders, including employees, vendors, customers, society, the environment, and shareholders. In recent times, the domains of sustainability, technology, and ethical leadership have gained increasing prominence in boardrooms and policy corridors.
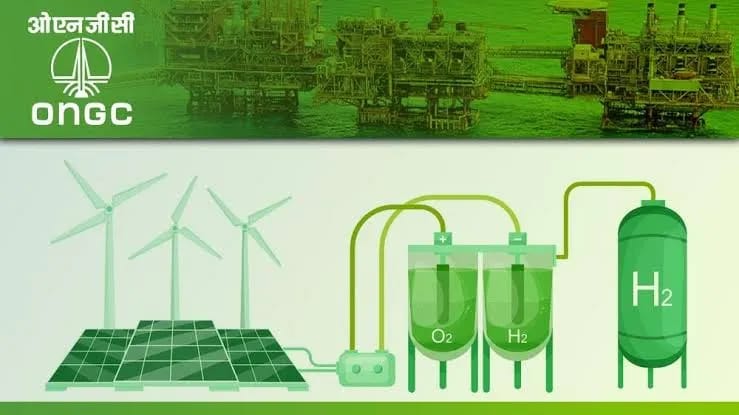
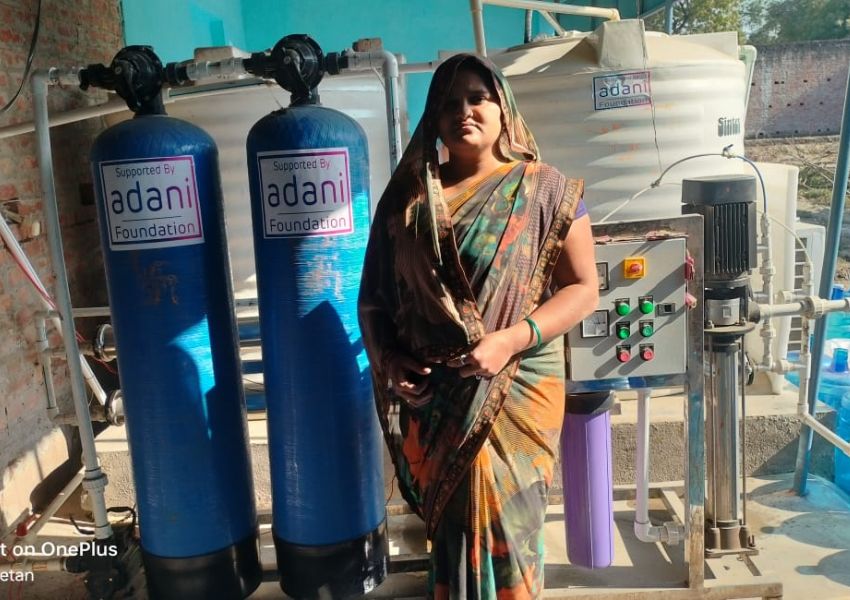
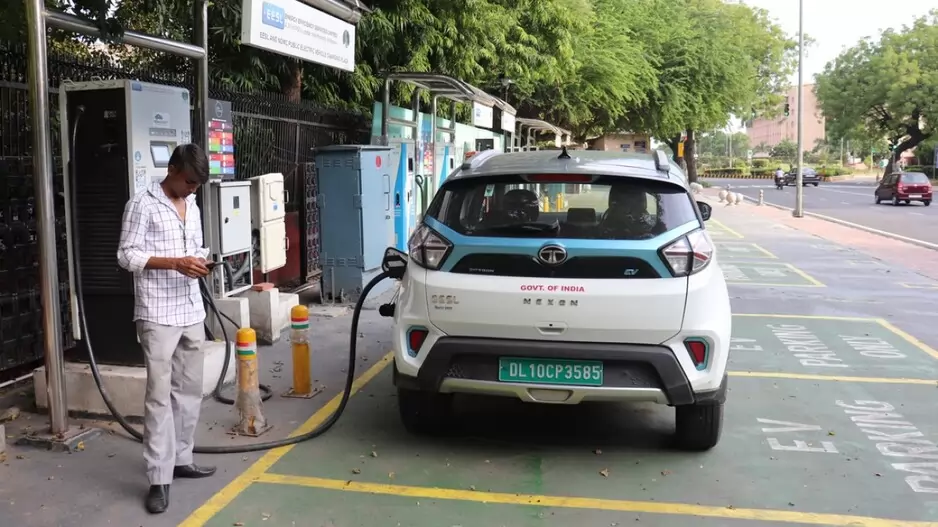
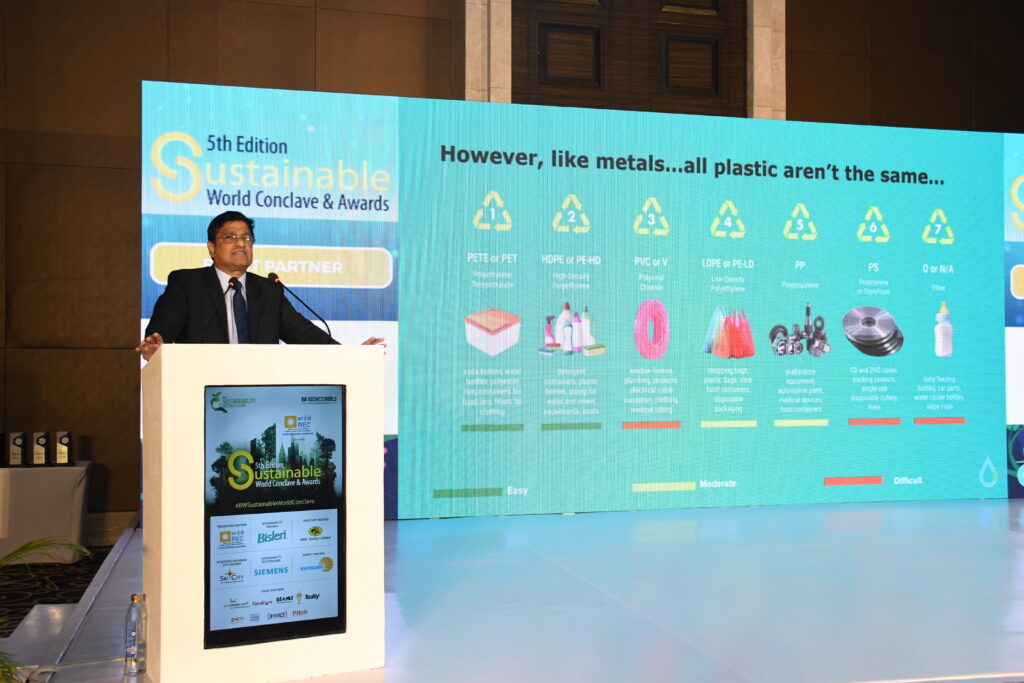
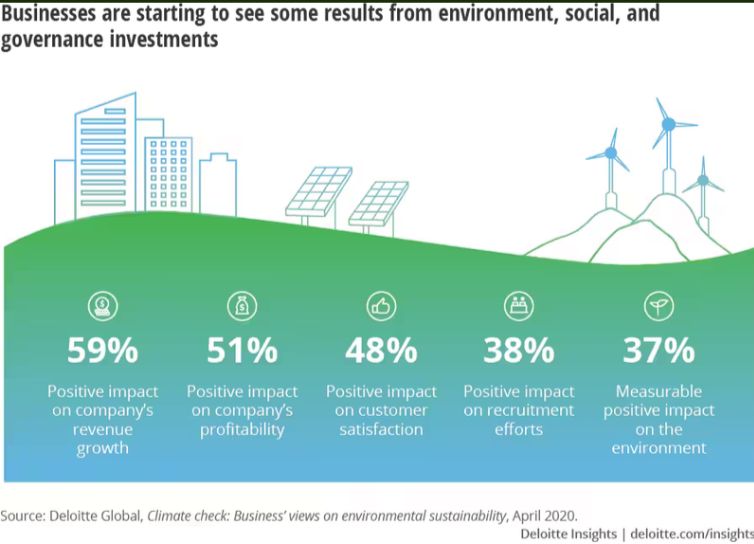
Sustainability has emerged as a pivotal factor in evaluating corporate performance, particularly for companies with global exposure. Elements such as emissions reduction, waste management, and human capital practices have a profound impact on stakeholder confidence and the long-term resilience of businesses. Various sectors are adapting to sustainability in distinct ways. For example, the automotive industry is transitioning from internal combustion engines (ICE) to electric vehicles (EV), focusing on environmental compliance, technology partnerships, and customer-centric innovation. The chemical industry is emphasising green chemistry, renewable feedstocks, and circular solutions to reduce harm to human health and the environment.
Technology, as a formidable enabler, has become ubiquitous in modern business design. A holistic digital strategy empowers organisations to enhance agility, responsiveness, and resilience while engaging positively with their ecosystem. Technology is being leveraged for real-time reporting, data analytics, risk management, cybersecurity, data protection, shareholder engagement, voting, internal controls, reporting, and compliance. However, while technology offers significant advantages, it also raises ethical and moral concerns, particularly when its use lacks proper vigil and accountability, potentially leading to obfuscation and manipulation.
Ethical leadership, considered the cornerstone of governance, revolves around character and culture. Ethical leaders exhibit qualities such as independence, rationality, fairness, trust, transparency, flexibility, and intellectual humility. The importance of ethical leadership is underscored by past instances of corporate misconduct across various industries in India, resulting in severe reputational damage and legal repercussions. Proactive engagement and a commitment to operating with integrity and fairness play a pivotal role in building a culture of ethical leadership, aligning organisations with greater accountability and ownership.
From a mere facade of governance to a deeply ingrained and sometimes enforced ethos, the governance landscape has witnessed a profound shift. Ethical leadership forms the foundation upon which other governance practices thrive, offering better protection than numerous introduced laws. Investors are increasingly willing to attribute higher valuation premiums to companies that exhibit ethical leadership, leading to improved perception-to-earnings ratios.
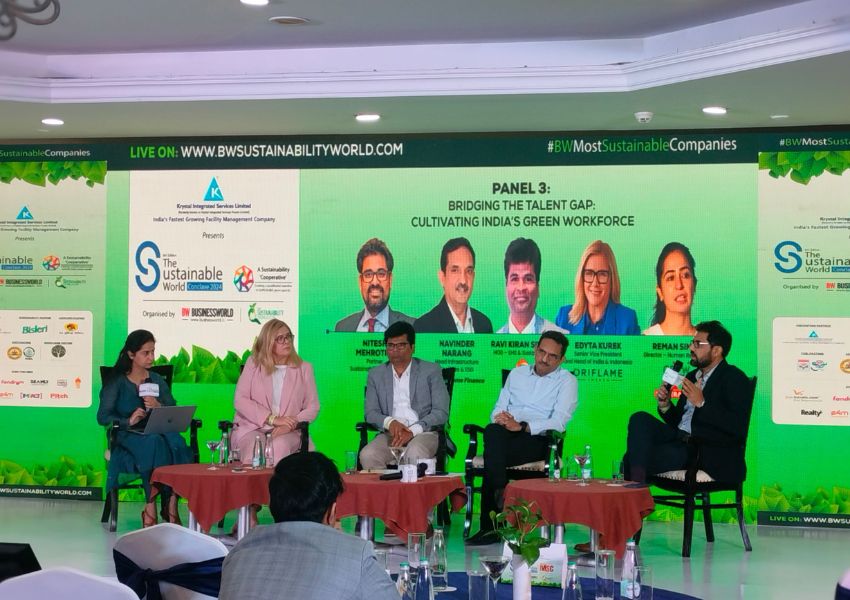
For more insights on governance for sustainability, join us and the sustainability stalwarts from different industries on the 21st of November at The St. Regis, Mumbai. Register here https://bwevents.co.in/bw/the-sustainable-world-conclave-mumbai/#Register to grab your spot!