Green Buildings: How Technology Is Shaping Sustainable Construction

India’s Energy Conservation Building Code (ECBC) enforces energy efficiency standards for new commercial buildings, supporting the nation’s broader goals of reducing carbon emissions and achieving net-zero emissions by 2070
Byline: Marc Nezet
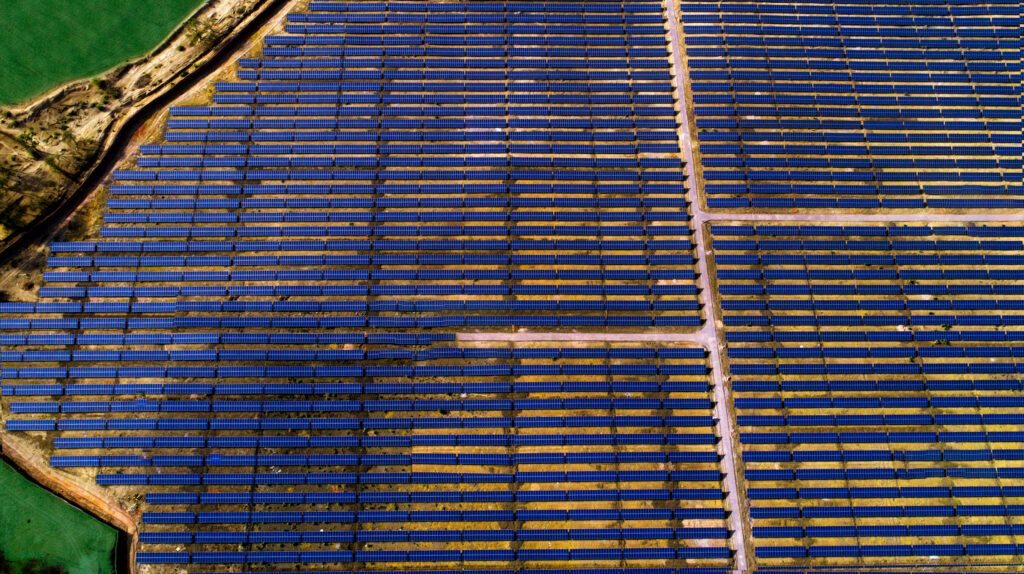
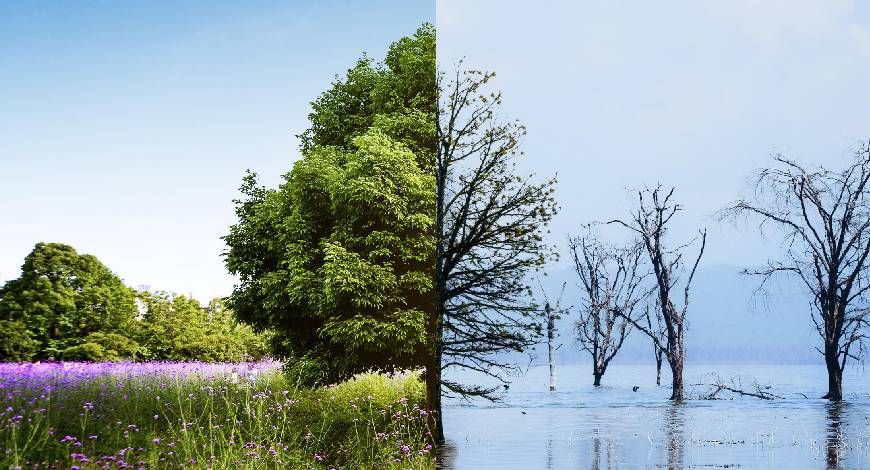
The construction industry is increasingly focussing on sustainability, with green buildings leading the charge in eco-friendly development. These buildings aim to minimise environmental impact by utilising resource use, reducing waste, and creating healthier living and working environments. They play a significant role in cutting greenhouse gas emissions and conserving natural resources. As awareness of climate change grows, technology is driving the evolution of green building practices, making them crucial in combating climate change and promoting sustainable development.
The origins and technological advancements driving green buildings
Green building practices began in the 1960s with ecological architecture, gaining momentum during the 1970s energy crisis, which highlighted the need for renewable energy and energy-efficient designs. By the 1980s, the sustainable development movement promoted energy-saving systems in construction. A notable milestone in India was the CII-Sohrabji Godrej Green Business Center in Hyderabad, the first building outside the US to receive a Leed Platinum rating, showcasing India’s commitment to sustainability.
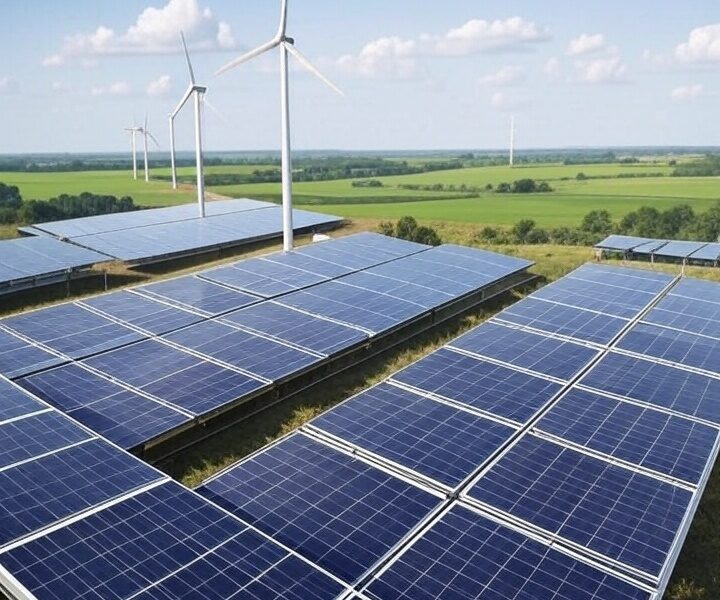
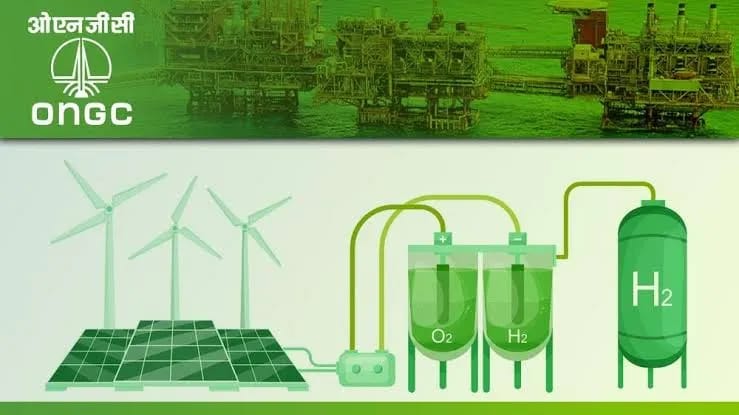
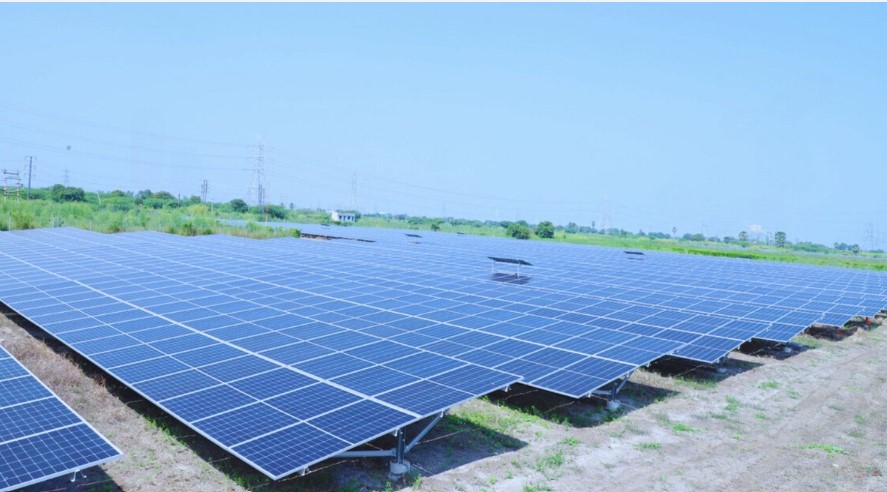
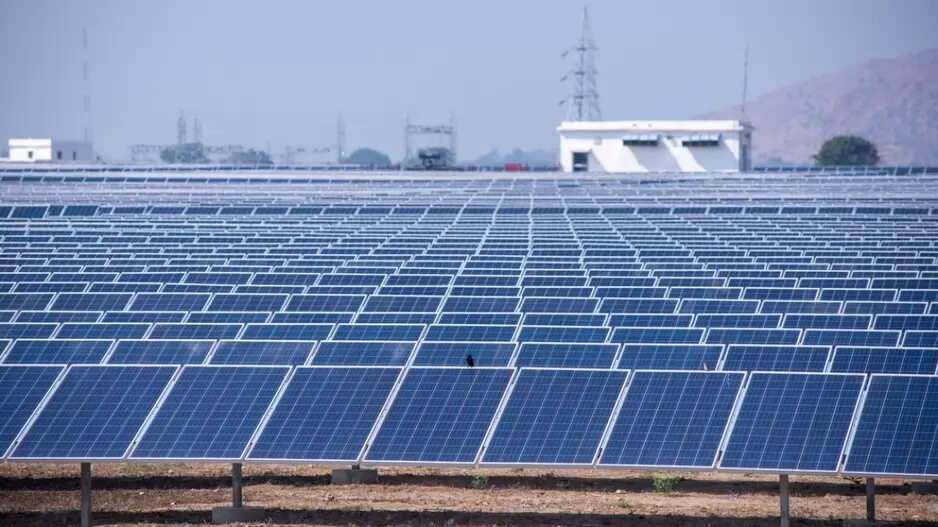
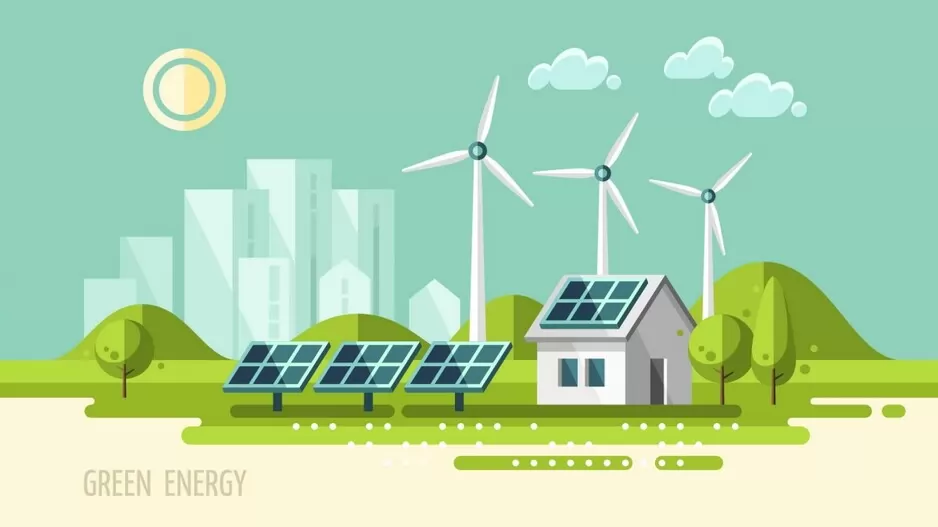
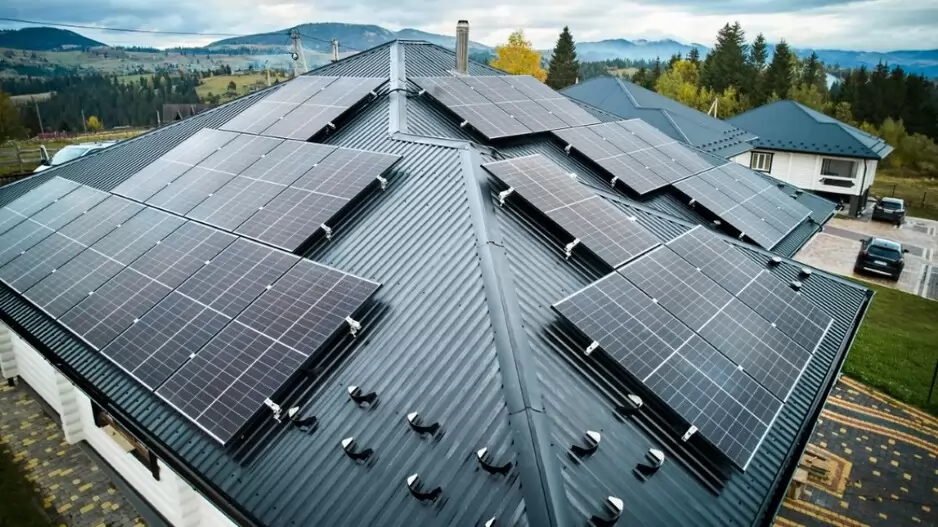
Energy efficiency is at the heart of green buildings, and technological advancements have been crucial in improving it. High-performance insulation, energy-efficient windows, and advanced HVAC systems are now standard in many green buildings. Renewable energy sources like solar and wind power allow buildings to produce their own clean energy, while smart technologies such as sensors and automation systems adjust heating, cooling, and lighting based on occupancy patterns, enhancing energy efficiency. India’s Energy Conservation Building Code (ECBC) enforces energy efficiency standards for new commercial buildings, supporting the nation’s broader goals of reducing carbon emissions and achieving net-zero emissions by 2070.
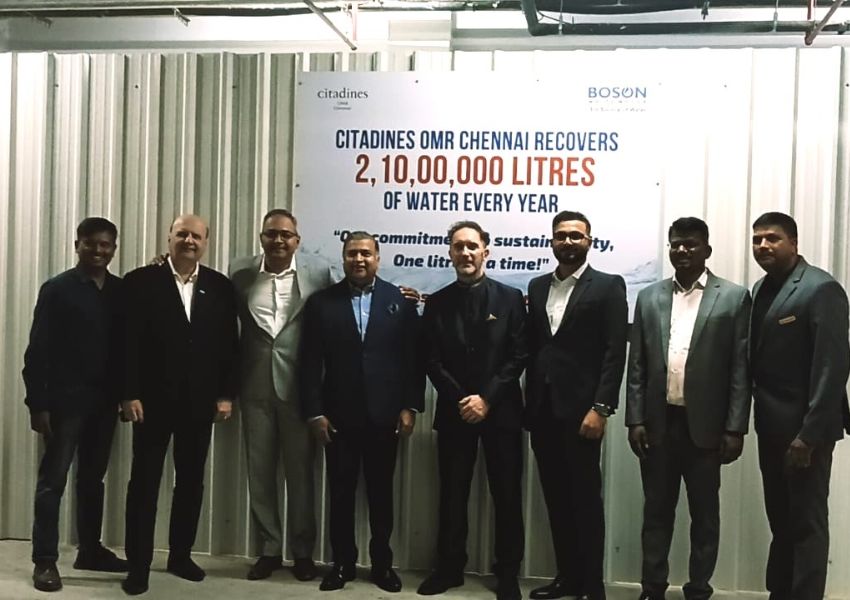
Water conservation is another critical aspect of green buildings. Advanced plumbing fixtures, rainwater harvesting, and greywater recycling systems help reduce water usage. Smart irrigation systems adjust watering schedules based on weather and soil conditions, while water-efficient appliances and drought-resistant landscaping further cut down on water consumption. India, grappling with declining per capita water availability, has rolled out various water conservation initiatives, including the Jal Shakti Abhiyan and programs like Har Ghar Jal Yojana and Jal Jeevan Mission, aimed at providing safe drinking water to rural households.
The use of sustainable materials is also gaining traction in the building industry. Innovative materials like Aerocon panels, which facilitate quick on-site assembly, and recycled content materials reduce resource consumption and waste. India’s green building materials certification system and government incentives like tax benefits and subsidies further encourage the adoption of these materials, promoting sustainability across the construction sector.
Building Information Modeling (BIM) has emerged as a powerful tool for enhancing the sustainability of green buildings. This digital representation of a building allows architects, engineers, and construction professionals to collaborate more effectively, optimising planning, design, and management processes. BIM reduces waste, improves resource management, and increases efficiency throughout a building’s lifecycle. In India, BIM is increasingly used in government projects, including infrastructure and smart city initiatives, driven by the potential for cost savings and improved sustainability.
Market growth and regulatory support
India’s green buildings market is set for significant growth, with projections showing it could reach $39 billion by 2025. This expansion is fueled by an increasing focus on sustainable construction, supported by regulatory frameworks like the ECBC and the Green Rating for Integrated Habitat Assessment (GRIHA). Government incentives such as tax benefits, low-interest loans, and fast-track project approvals make green building practices more financially viable and encourage private sector investment.
Certification systems and standards play a crucial role in promoting green building practices. The Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design (LEED) certification, managed in India by the Green Business Certification Inc. (GBCI), sets global benchmarks for sustainability. These standards help guide the industry towards greener, more efficient practices, aligning with India’s broader sustainability goals.
Future outlook
The future of green buildings looks promising, driven by technological advancements, regulatory support, and growing public awareness. As global commitments, like those made at COP28, push for increased renewable energy capacity and improved energy efficiency, green buildings will be central to meeting these targets. Moving forward, enhanced building codes and sustainability standards will continue to encourage the adoption of greener practices, helping reduce carbon footprints and promoting healthier, more sustainable living environments.