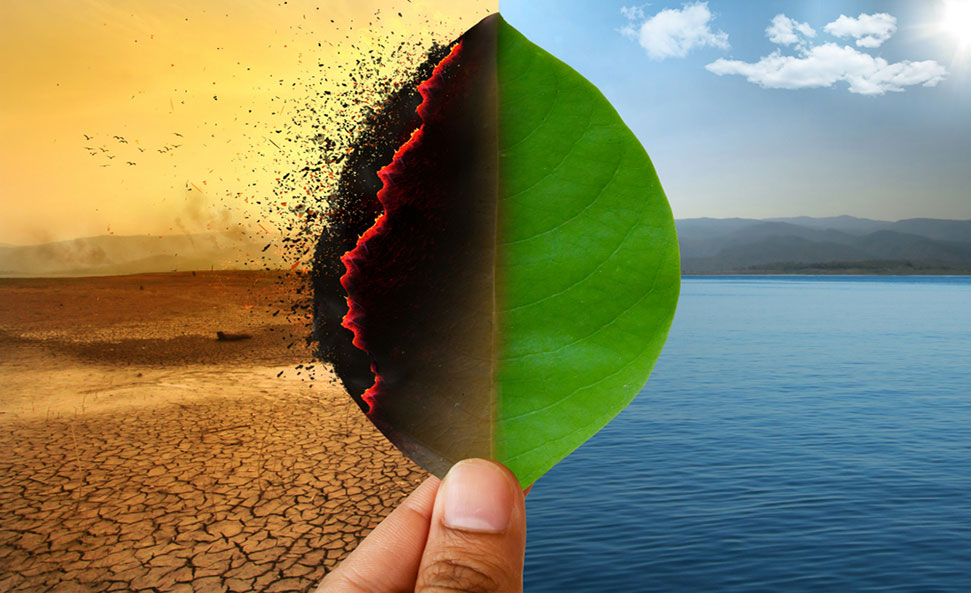
Green Jobs: Empowering A Sustainable Future Through Skill Development And Innovation

As industries evolve towards sustainability, the demand for green skills grows, creating new job opportunities and driving environmental progress
Byline: Smitha Gopalkrishnan, Asia Sustainability Leader for 3M
“I feel proud that my work today will benefit the planet for future generations. This perspective inspires me to stay motivated and contribute to my job.”
These are words spoken by an employee of an organization that echo the views of a new breed of working professionals who are environmentally conscious and find purpose in working for companies that use sustainability as a growth driver.
This is the new workforce that is pursuing green jobs that require green skills.
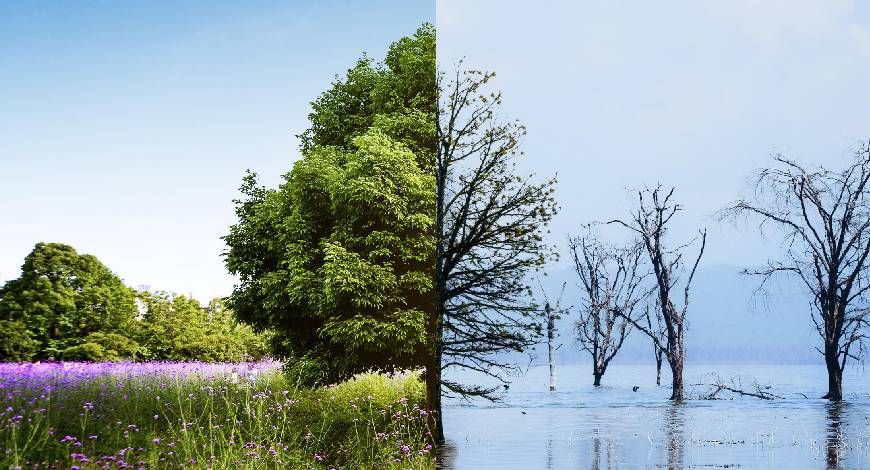
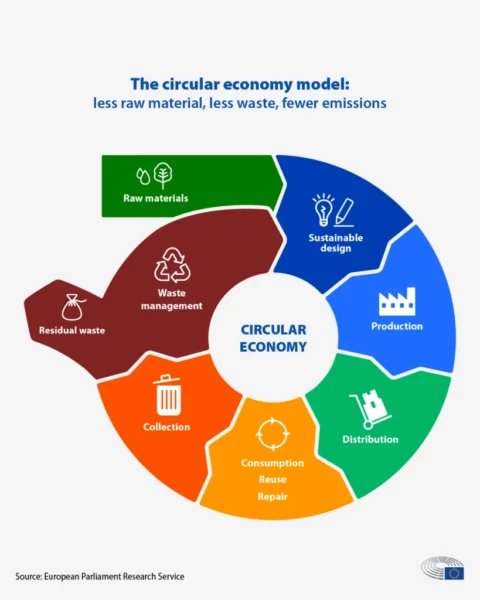
The definition of a green job has sustainability at its core. Jobs that contribute to preserving and restoring our environment and planet and can be performed with extensive knowledge of green skills are termed green jobs. Green skills refer to those needed to adapt processes, services, and products that directly help combat climate change and support the environmental regulations related to it.
A green-skilled workforce is essential to address climate challenges today and fulfill our ambitious climate goals for the future.
The world needs more people in green jobs with the skillsets necessary to innovate and scale up solutions. The talent gap is significant. According to 3M’s proprietary research, State of Science Insights, 75 per cent of respondents expect the green jobs market to grow over the next five years. However, addressing this gap isn’t solely about hiring more scientists, engineers, and innovators. We need to transform all sectors of our economy and empower every individual to make a tangible impact on our communities and the planet.
Where are the green jobs?
Industries such as utilities, manufacturing, construction, transportation, and textiles present significant opportunities for green skills development, which plays a crucial role in helping these sectors achieve their climate targets.
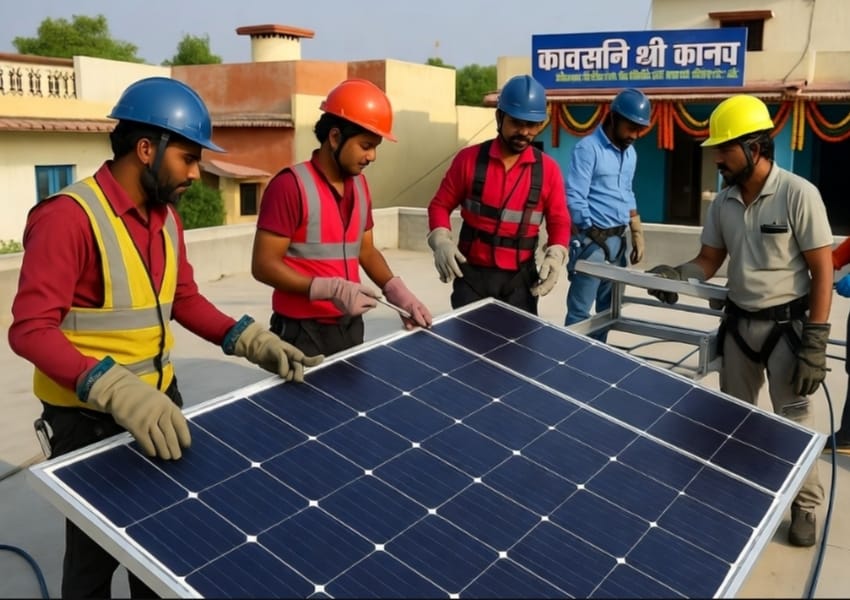
In the utilities sector, green skills are increasingly important, as utilities transition to renewable energy sources and navigate the complexities of maintaining grid stability.
In construction, regulations and certifications related to green buildings and energy efficiency are driving the demand for sustainable construction practices and solutions.
The manufacturing industry is under scrutiny not only because it provides products and solutions to other sectors but also due to Scope 3 emissions, which are often the most challenging to address. Therefore, green skills development must occur across the entire value chain.
As artificial intelligence (AI) and related technologies become more prevalent, companies are investing in data center capabilities that also require green skills.
In the transportation industry, as it moves toward automotive electrification, job opportunities are emerging in hybrid and electric vehicle production, sales, and repair.
Additionally, the demand for green skills is growing due to regulatory requirements. Mandatory environmental, social, and governance (ESG) reporting frameworks, such as the Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD) in the EU and the Business Responsibility and Sustainability Report (BRSR) in India, necessitate enhanced skill sets for reporting. Policies like the Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR), which require brand owners to recycle the plastic waste they generate and report on these activities, have led to the creation of new roles and departments within organizations to manage and oversee plastic waste management.
Lovely Kuruvilla (EPR Lead, Product Stewardship) at 3M India shares some of the skills essential for a role that is driven by regulation like EPR, “Aside from having a deep understanding of regulatory frameworks and environmental laws and standards, other critical skills for a green role also include expertise in data analysis, knowledge of product lifecycle and project management skills which are also essential to develop and execute strategic action plans.”
The growth of green skill development lies in changing how we do business with a focus on material use, procurement, ecosystem management around waste, energy, and water, impact assessment, and risk analysis.
India’s Green Jobs Potential
India has the potential to create 35 million green jobs by 2047 through its LiFE (Lifestyle for Environment) Mission and the “Panchamrit” plan for achieving net-zero emissions. The country’s leadership in global initiatives like the International Solar Alliance supports the development of a green economy.
Key sectors driving this growth include Renewable Energy, Waste Management, Electric Vehicles, Sustainable Textiles, and Green Construction, which are expected to generate the most jobs, especially in urban areas.
Bridging the skill gap
Strategies to overcome the challenges in skilling the green ecosystem will have to address:
• The skilling of entry-level professionals (both from the formal and informal sectors)
• Upskilling workers in traditional industries to enable them to transfer their skills to take on enhanced skills for the green economy
• Leveraging the Gen Z workforce which is keen to be part of the climate solution
• Leveraging women who make up just a third of green talent worldwide
• Leveraging corporate philanthropy as a channel to finance green skill development with a focus on the informal sector and low-income group workforce
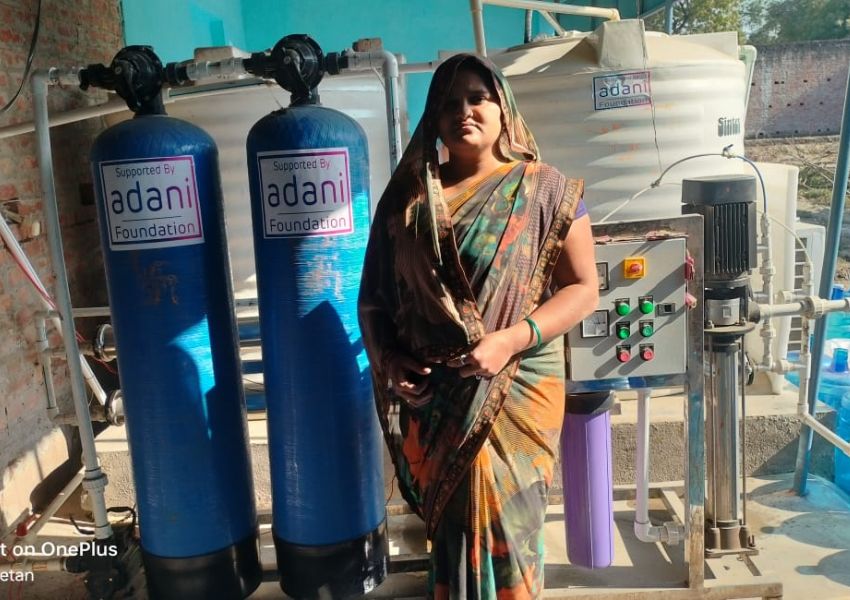
The renewable energy sector like solar energy offers huge potential for jobs requiring green skills, especially for the low-income group workforce. 3M India has been working with Selco India and Selco Foundation to establish solar infrastructure for rural health centers in Pune, Maharashtra, as a part of its CSR initiative. Selco Foundation works with grassroots communities in India to alleviate poverty and fight climate change through decentralized renewable energy-driven solutions. Speaking about the potential for green skill development for job creation in the informal sector, Sudipto Ghosh, Dy General Manager, Selco India says, “Renewable energy’s decentralized nature presents significant opportunities for job creation and entrepreneurship, particularly in providing energy as a service and powering micro-enterprises at the community level. A large-scale skilling and entrepreneurship development program, spearheaded by a partnership between Government, private, and philanthropic institutions, can unlock this potential by focusing on youth and women.”
You can turn your job into a green job anytime.
Awareness about emerging opportunities and upskilling are essential to stay relevant in today’s evolving job environment. Organizations are introducing upskilling programs to build awareness and understanding of Sustainability and ESG topics. Green skills are vital not just for emerging roles or future jobs, but they also create career pathways for individuals in existing industries as these sectors shift towards more sustainable practices. A green job embodies three key elements: innovation, responsibility, and community.
To continue advancing sustainable solutions and improve the impact of our operations and products, every employee at 3M is encouraged to see their job as a green job—no matter their function. Established in 2022, the 3M Employee Sustainability Council released a set of Job Function Action Guides to guide 3Mers on how they can make sustainability a part of their role to drive positive impact.
Alex Varghese, (Product Development, Automotive & Aerospace Solutions Division, 3M India) who has seen his role evolve with changing customer and market developments says, “In a rapidly transitioning industry like automotive, customer awareness around carbon footprint, emissions control, and climate change has led to the adoption of innovative approaches using sustainable materials and simplified manufacturing process. A Do-More-With-Less approach is helping translate problem statements into engineered product solutions to meet these requirements.”
Avani Macwan, (EHS Facilities, 3M India) is responsible for the Environment, Health and Safety for non-manufacturing sites at 3M India. Her passion for the environment started at a young age, which influenced her career choice to pursue environmental engineering, intending to work with industry to develop sustainable solutions. She shares, “As an environment health and safety professional for non-manufacturing sites at 3M India, I look for opportunities to safeguard the environment, not only from a regulatory compliance perspective but also through resource conservation and opting for greener alternatives where possible. Problem-solving is an important skill to develop as we look to adopt more sustainable practices.”
It will take all of us
Ultimately, the innovation required to drive the green economy will require contributions from everyone, regardless of industry, expertise, or experience. 3M’s new docuseries, “Green Works”, was developed to build awareness for the vast opportunities available in the green economy and inspire more professionals to join the effort—no matter their industry, expertise, or experience level.
The series celebrates five people working to address climate challenges and the critical need for more talent to support the green transition. With roles in renewable energy, electric vehicles, climate education, reforestation, and sustainable fashion, they demonstrate the powerful impact of green jobs on our planet and its future. You can Watch it at Green Works | 3M US.
Bridging emerging gaps in green skills will necessitate stronger collaborations among governments, educational institutions, and the corporate sector. Companies should focus on engaging untapped talent pools and integrate green skilling programs through learning and development initiatives. Governments must take the lead to create an enabling environment that facilitates the transition towards a greener economy, while effectively measuring the success of these initiatives. Lastly, educational institutions play a key role in ensuring students are equipped with up-to-date and relevant curricula and skills that cater to the needs of the green economy.
To conclude, Avani Macwan’s observation about green jobs sums up the journey. “You need to experience the problem by being on the ground to see it, listen to the community, and then, be a part of the solution”.