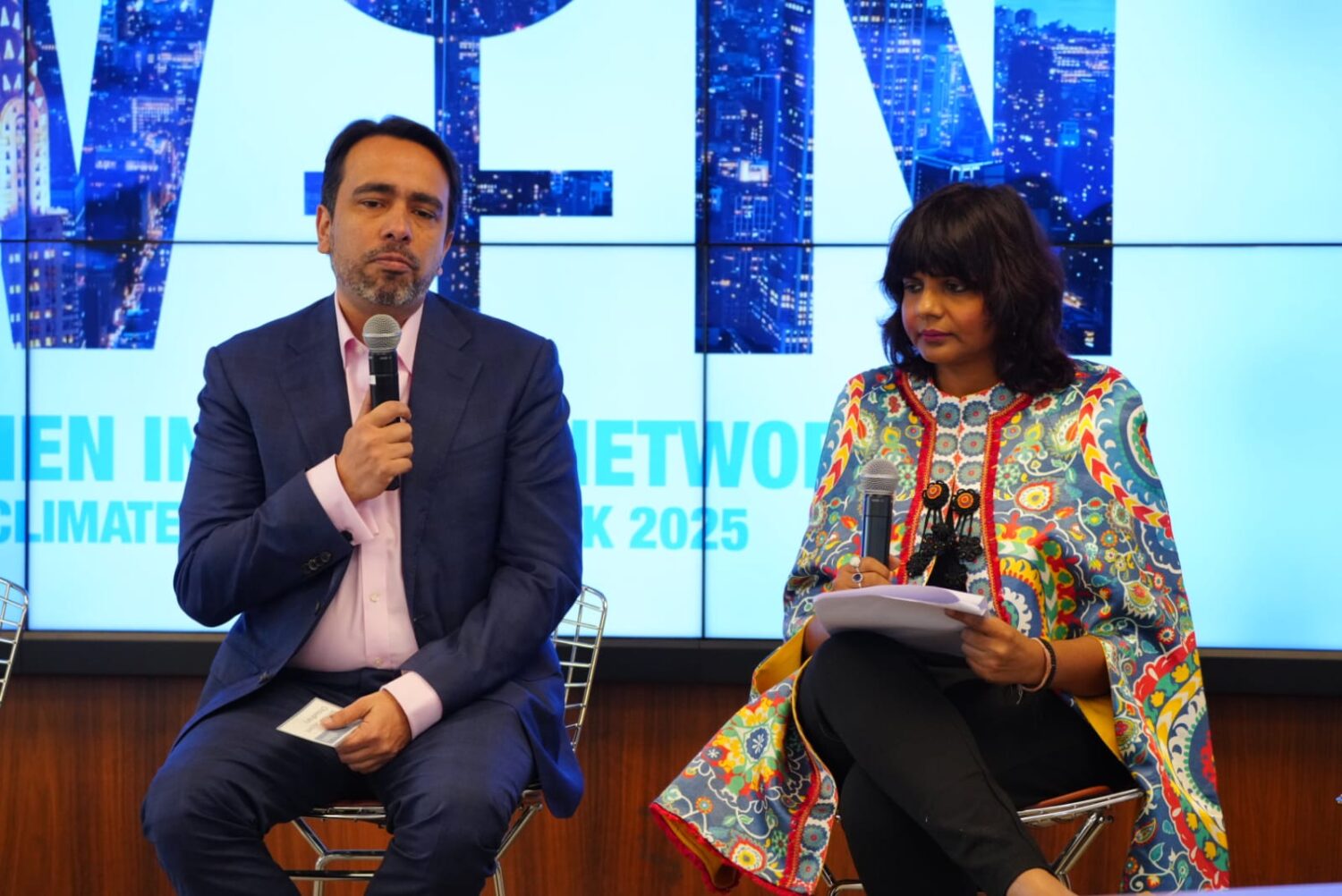
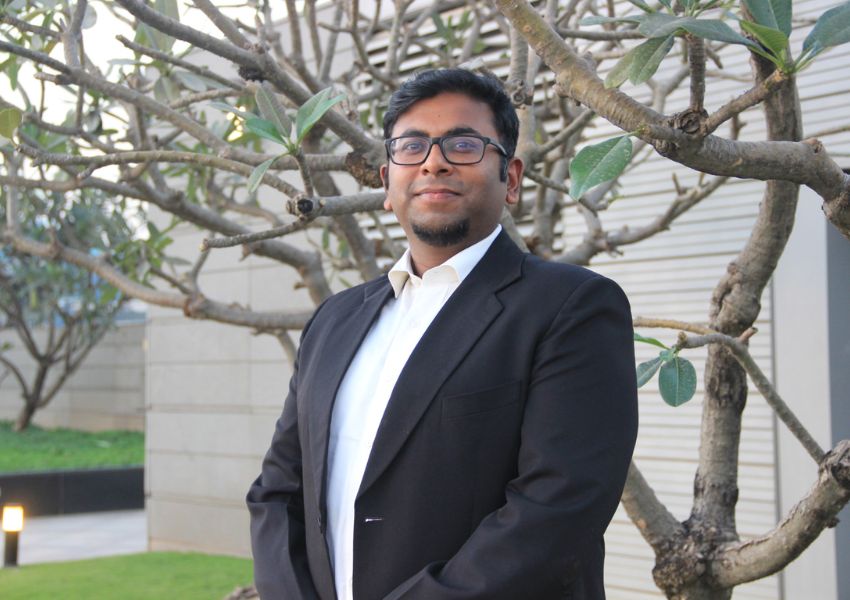
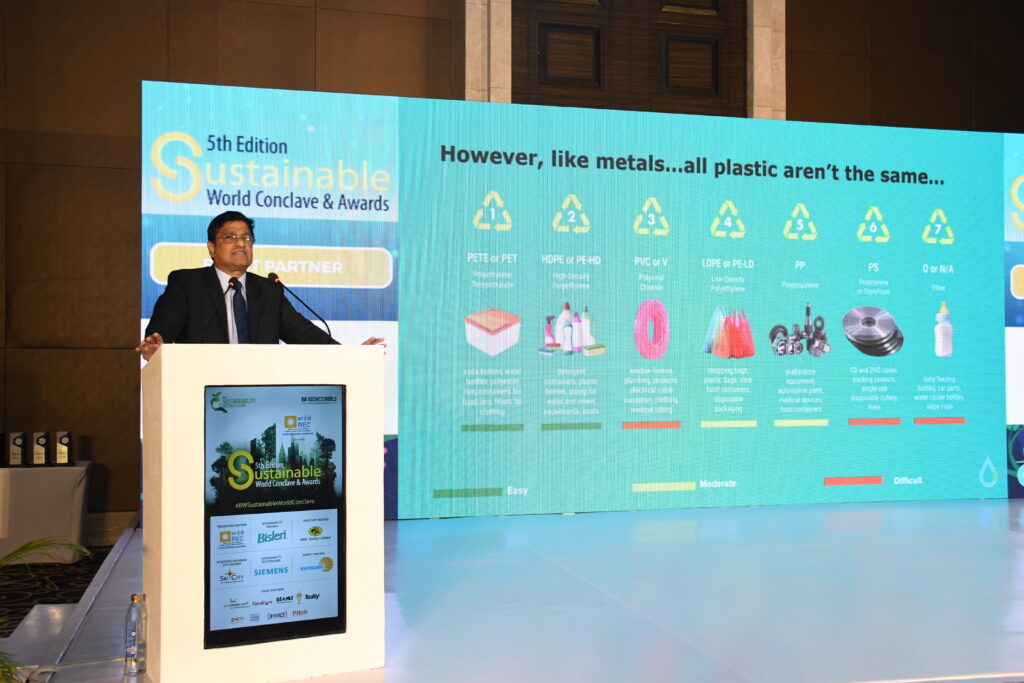
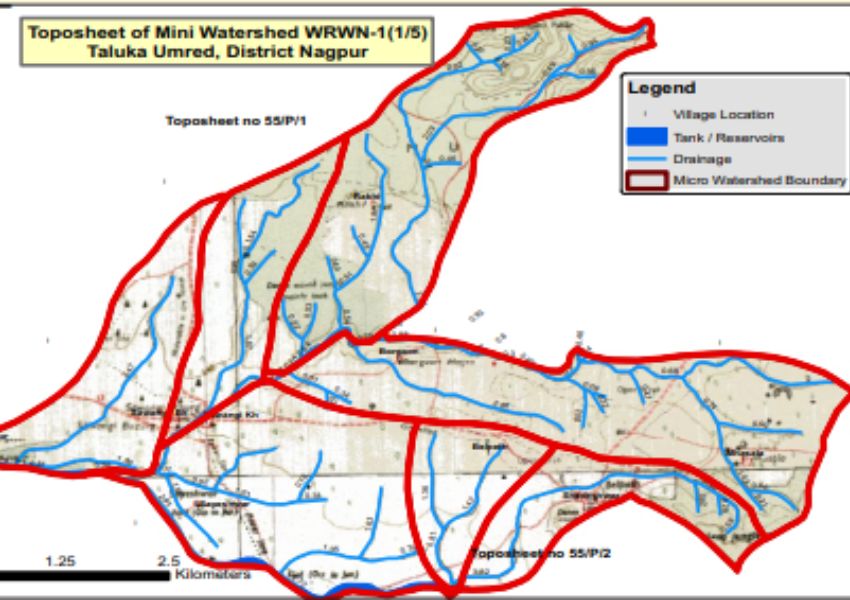
Green Skills: The Catalyst for Inclusive Tech Access And Environmental Solutions: Manav Subodh, 1M1B

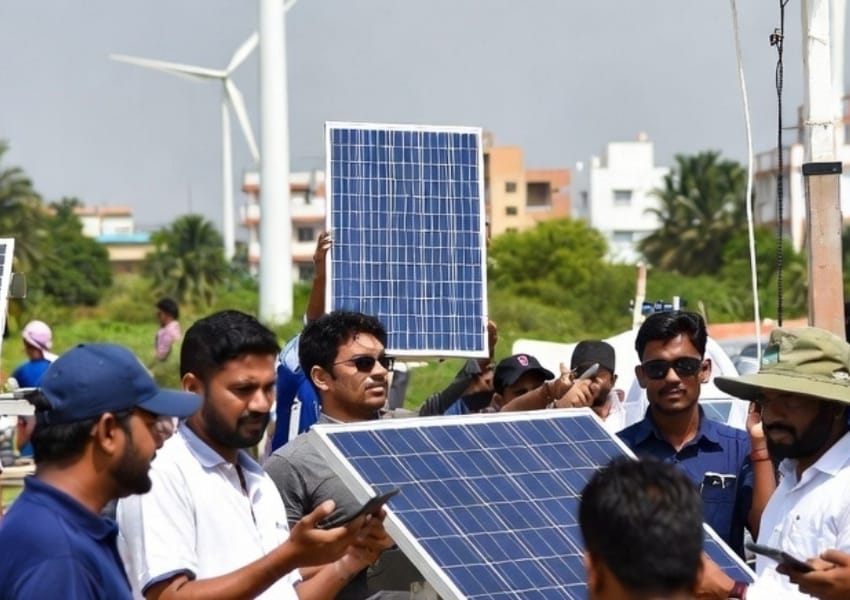
Subodh says that, with respect to environmental and economic impact, 1M1B is currently running a ‘sustainability accelerator’ program where 6,000 children have applied for it and are undergoing green skills training
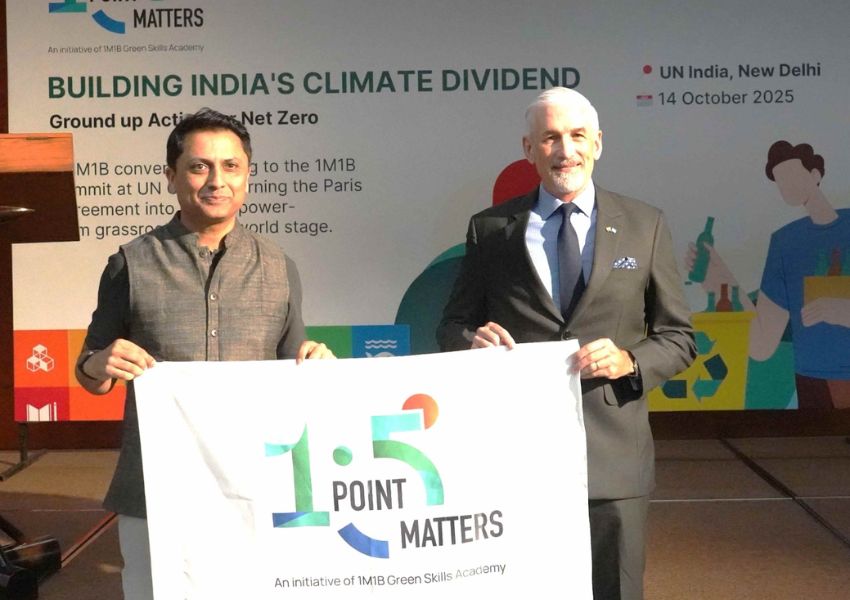
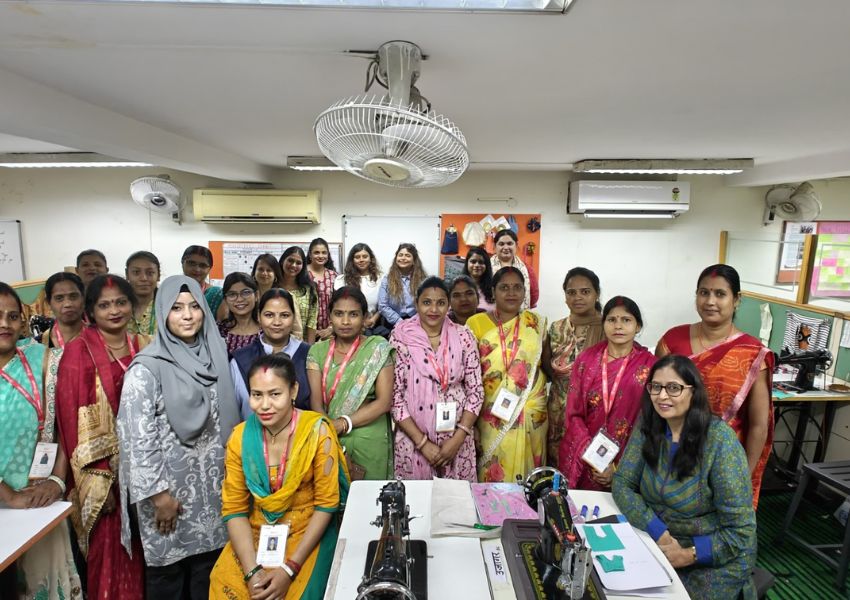
In an interview with BW Businessworld, Manav Subodh, Founder, 1M1B has said their ‘sustainability accelerator’ program in partnership with Aditya Birla Fashion and Retail (ABFRL) has already reached 525 schools and plans to expand to provide more opportunities for students to work in the sustainability domain.
Q1) In light of the significance of your vision to position India as the ‘front office crisis lab’ for the world, how is the utilisation of technologies in education and skilling reshaping the way to address concerns related to the environmental global crisis?
The goal is to ensure that students and children in rural areas have equal access to technology. By integrating new technologies from the ground up, we can avoid the need to catch up later and instead adopt a more grassroots approach. In the current era of AI and digital advancements, we can take a bottom-up approach, aiming to empower individuals facing challenges by providing them with the benefits of technology.
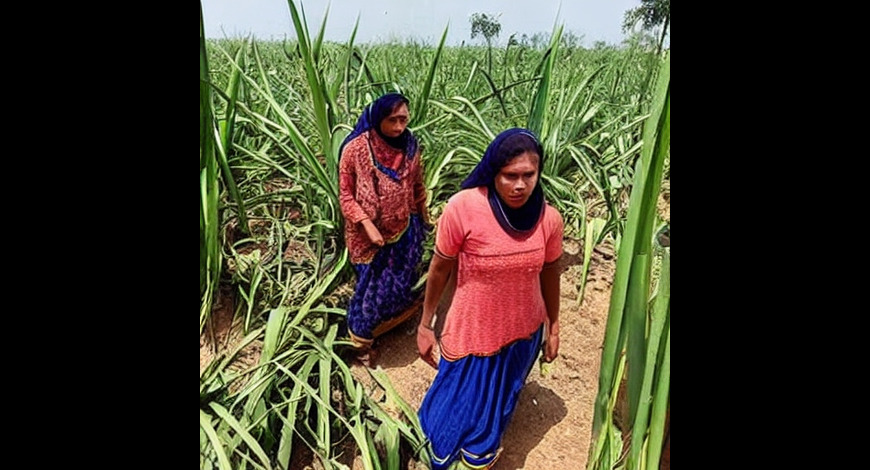
For example, one of my students developed a practical solution using a drone-based application equipped with a camera. This application, when deployed over a farm, analyses the entire area, and uploads the information to software. The AI tool developed by the student then assesses whether the crops are infected and, if so, identifies the stages of infection. Given the significant impact of climate change on farmers, including issues like pesticide use, insufficient rainfall, and unpredictable weather patterns, such technological innovations can be particularly valuable.
Q2) Despite 13 per cent digital growth every year, only 31 per cent of the rural population uses the internet, compared to 67 per cent in urban areas, according to the 2022 data.
Your organisation, 1M1B, talks about inclusion. How can the integration of green skills training programmes and the use of communication tools contribute to environmental sustainability and inclusivity in skilling initiatives?
About 600 million people in India, roughly half of the population with smartphones, are already using WhatsApp, a widely adopted and practical communication tool for business. Our approach involves hands-on training at the grassroots level. We prioritize providing tools to students at this level, emphasizing the importance of accessibility. Additionally, we offer applications tailored for smartphone use.
In Bangalore, where our operations are based, numerous skilling programs exist. Our goal is to extend similar programs to the grassroots level, delivering them in local languages. The core of the program remains consistent across locations, ensuring uniformity in the equipment provided. Our efforts are focused on fostering inclusivity through this approach.
Q3) How does implementing green skills training for technicians and architects contribute to meeting the workforce needs in the shift to a net-zero economy, particularly in empowering youth to drive sustainable solutions for small companies in the context of climate action?
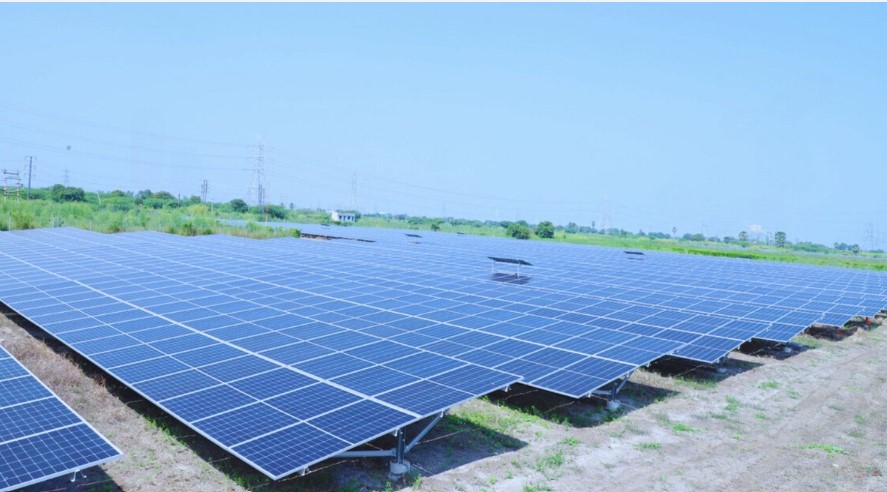
As the world moves towards achieving net zero emissions, a major challenge is ensuring an adequate workforce. We require skilled technicians for solar technologies and architects who can design energy-efficient buildings. The shift towards renewable energy is expected to create numerous job opportunities, making it crucial to focus on training people with green skills for a sustainable economy.
Our specific initiative involves setting a goal to engage 1000 small companies in climate action. Recognizing that smaller businesses may lack access to advanced technologies, we are actively hiring and deploying a significant number of young individuals to work with these companies and develop solutions.
Q4) How can the education system adapt to cultivate green skills among students, considering the projected high demand for green jobs in the future job market?
In the coming years, jobs like sustainability managers, air quality engineers, and energy engineers are expected to be among the top-paying positions in their respective fields. These roles go beyond just tree planting and involve building a workforce focused on green practices. It’s crucial to start training students for these jobs now. Research indicates that 16 per cent of high school students already have a sustainability mindset. If more students get involved in this field, we could potentially cut down 19 gigatons of carbon dioxide emissions by 2050.
Q5) How has the ‘sustainability accelerator’ program, launched in collaboration with Aditya Birla Fashion and Retail (ABFRL), impacted the environmental and economic landscape by providing green skills training to school students?
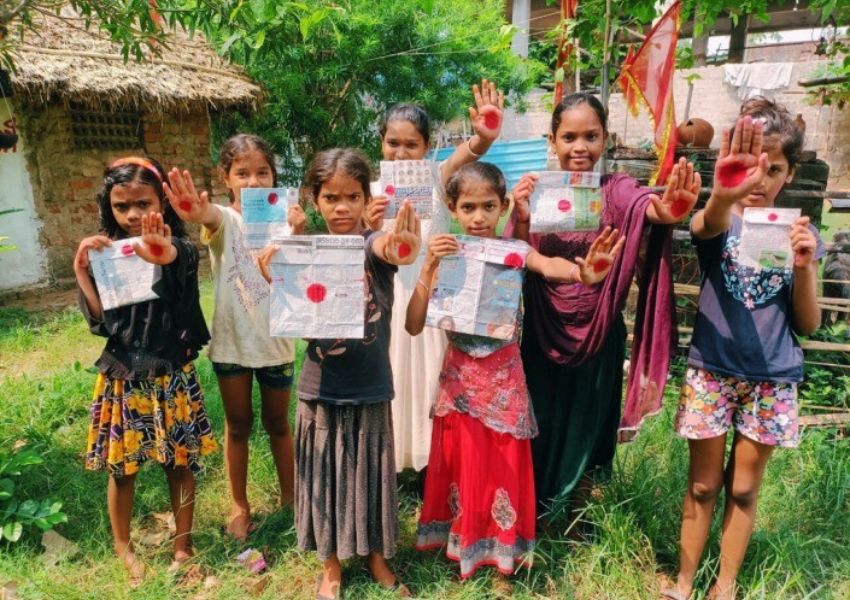
To address both environmental concerns and economic considerations, we initiated a ‘sustainability accelerator’ program in collaboration with Aditya Birla Fashion and Retail (ABFRL). As part of this initiative, ABFRL provided internship opportunities for numerous students. We also introduced a program targeting school students, attracting 6,000 applicants. These students underwent green skilling, with hundreds selected for prototype development and a few earning internships with ABFRL.
Recognising the importance of incorporating green skilling into the curriculum, we aim to educate students on sustainability from an academic perspective. The program has already been implemented in 525 schools as the inaugural batch within the past eight to nine months. Considering its success, we plan to expand the program, emphasizing the need for students not only to acquire green skills but also to gain experience in a sustainability-focused work environment.
Q6) How can the integration of green skills contribute to ensuring safety, data protection, and effective governance in the evolving Metaverse landscape?
As we delve into the realm of 3D technology, ensuring the safety of citizens becomes paramount. Our ‘Digital Nagrik’ initiative serves as a comprehensive program, equipping individuals with the knowledge to navigate and safeguard themselves in this digital landscape. It educates them on responsible conduct, self-protection, and the importance of securing their data. In the evolving landscape of the Metaverse, it is crucial for citizens to be aware of resources like cyber cells in case of harassment and to be acquainted with reporting guidelines.
With India not only embracing immersive technology but also having a data protection bill in place, the constitutional imperative is clear there must be collaboration among private entities, public institutions, and the government. Looking ahead to the next decade, particularly in the Metaverse, addressing these issues necessitates a framework of governance.
Additionally, considerations for green skills are integral to this paradigm shift. With a significant increase in online meetings and a reduction in transportation costs, the shift to virtual platforms like the Metaverse will become a staple for various activities. Thus, incorporating sustainable practices and fostering skills that align with environmental consciousness will play a substantial role in shaping the future of this digital frontier.