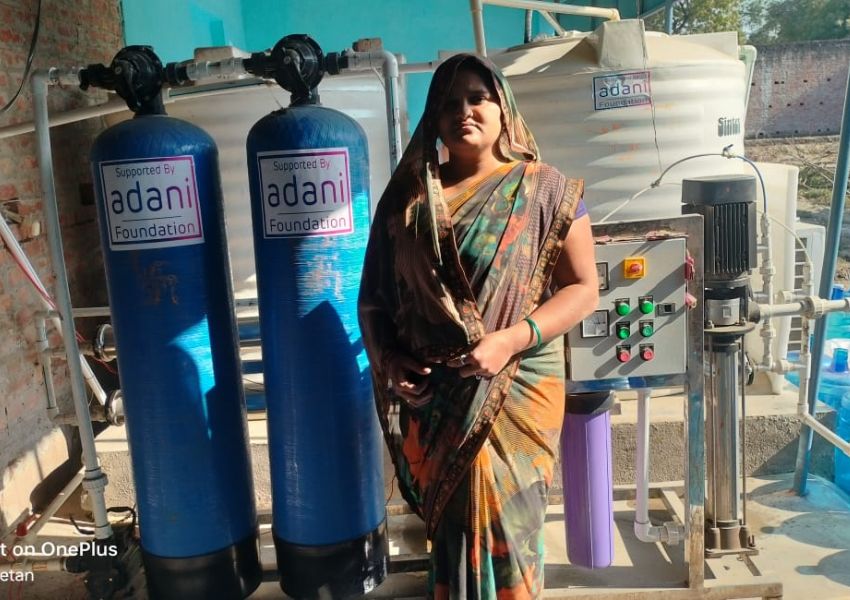
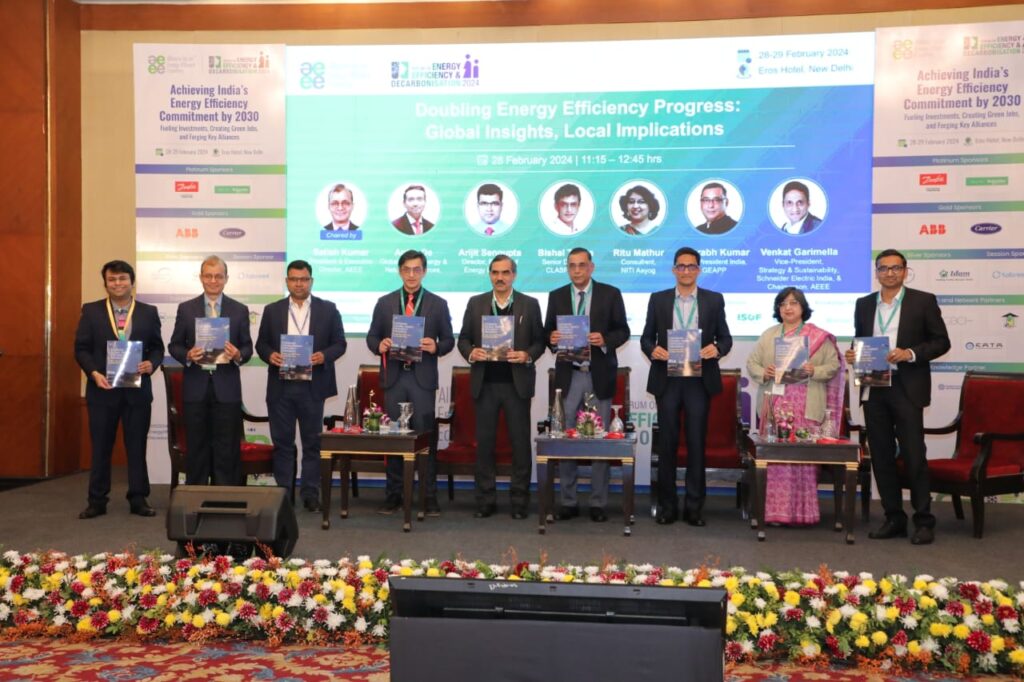
Hindu Kush Nations Derive Only 6% Of Energy From Clean Sources: Report

Report highlights that of 882 gigawatts (GW) of hydropower potential across Afghanistan, Bhutan, Bangladesh, China, India, Myanmar, Nepal and Pakistan
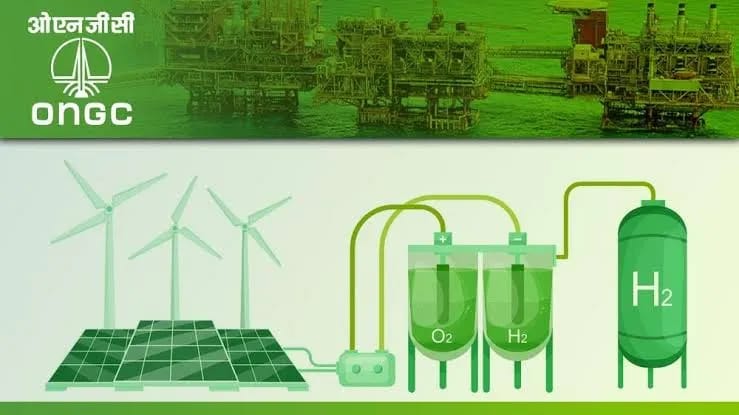
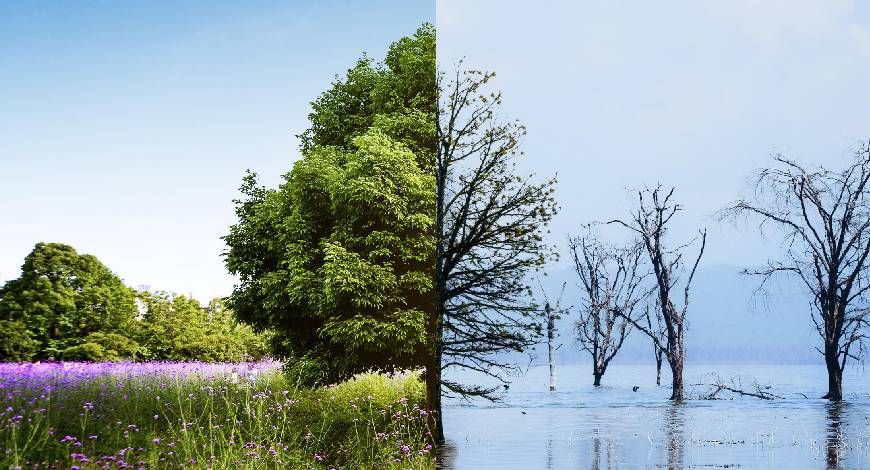
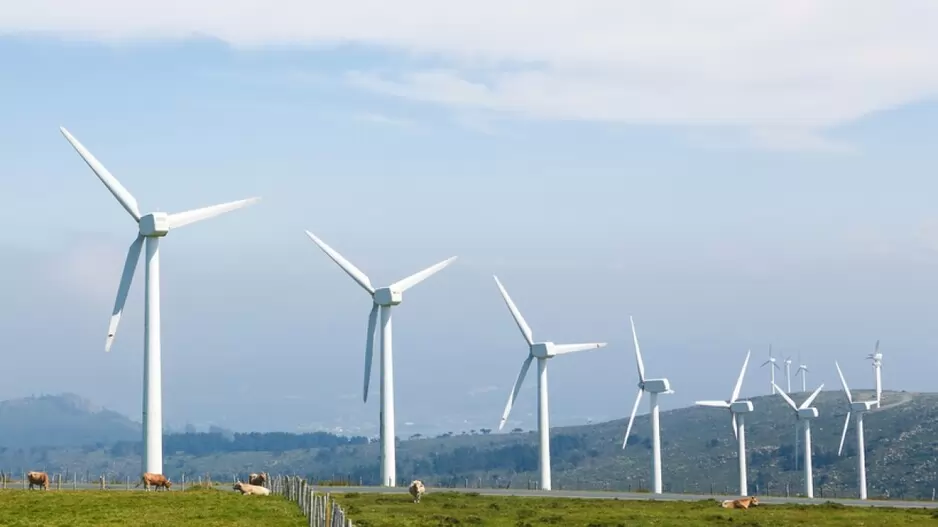
Countries of the Hindu Kush Himalaya (HKH) region, despite vast renewable potential, derive just 6 per cent of their total primary energy from clean sources, according to a new report released by the International Centre for Integrated Mountain Development (ICIMOD).
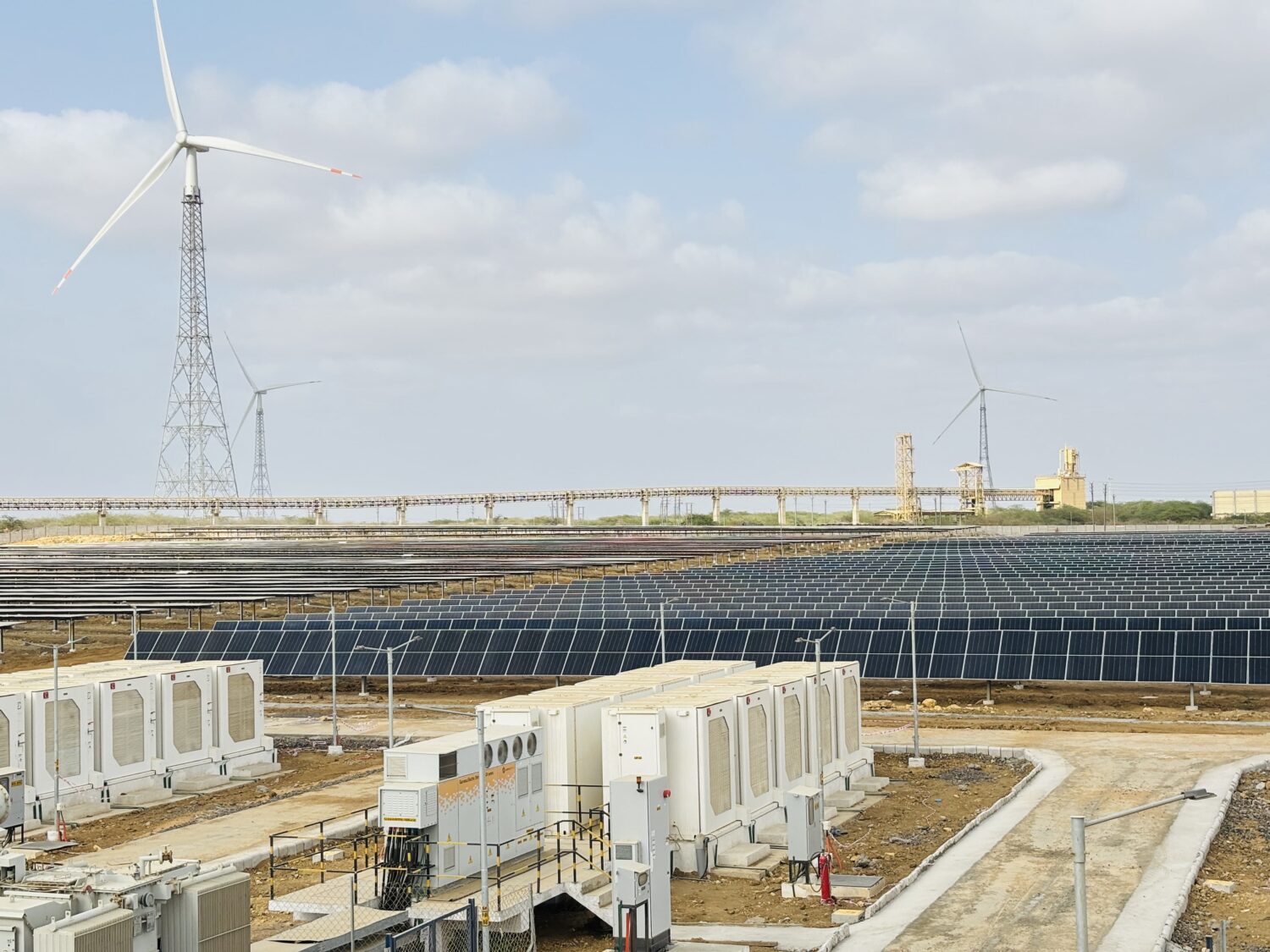
The assessment, unveiled during Asia-Pacific Clean Energy Week in Bangkok, highlights that of 882 gigawatts (GW) of hydropower potential across Afghanistan, Bhutan, Bangladesh, China, India, Myanmar, Nepal and Pakistan, nearly 635 GW lies in the transboundary rivers of the HKH. Only 49 per cent of this potential has been tapped so far. The region’s non-hydro clean energy potential solar and wind stands at 3 terawatts (TW).
The report noted that while Bhutan and Nepal generate all their electricity from renewables, fossil fuels dominate generation in Bangladesh (98 per cent), India (77 per cent), Pakistan (76 per cent), China (67 per cent) and Myanmar (51 per cent). Biofuels and waste also contribute disproportionately to primary energy supply in several countries, reflecting rural reliance on wood, crop residues and dung.
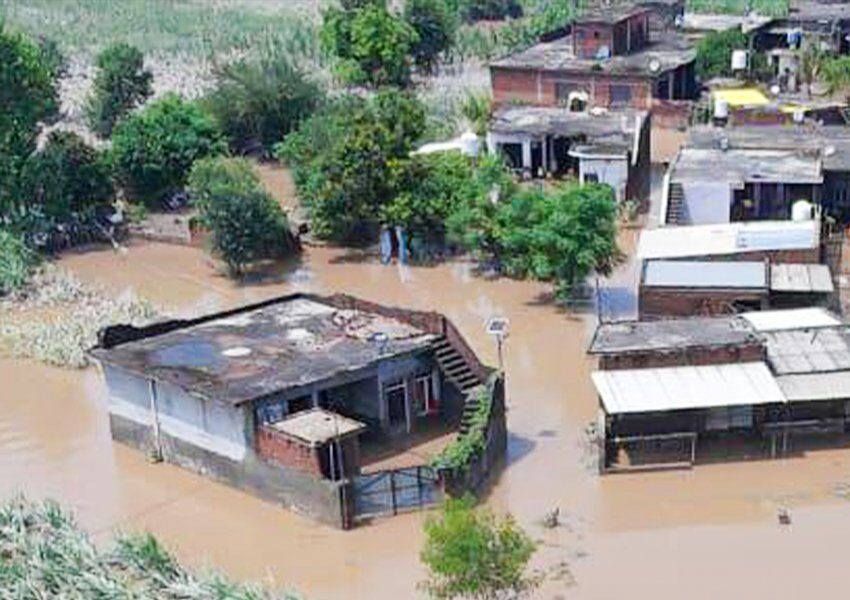
Climate change poses further risks, with altered streamflows, extreme weather and glacial lake outburst floods threatening nearly two-thirds of existing and planned hydropower projects. The study called for integrating disaster risk strategies into renewable planning and exploring “dams equivalent” alternatives such as efficient irrigation systems, urban water storage and distributed solar and wind.
Barriers to renewable expansion include high capital costs, limited public finance, weak private investment, and ecological and community concerns. “We have extraordinary renewables potential within our region… building on this competitive advantage is a tremendous opportunity to turbocharge green economic growth,” said Avishek Malla, Coordinating Lead Author of the report.