India To Attract Rs 479 K Cr Investment In Energy Storage By 2032

Gujarat leads the charge with 100 GW renewable target as policymakers and global stakeholders unite to accelerate energy storage deployment for a net-zero future
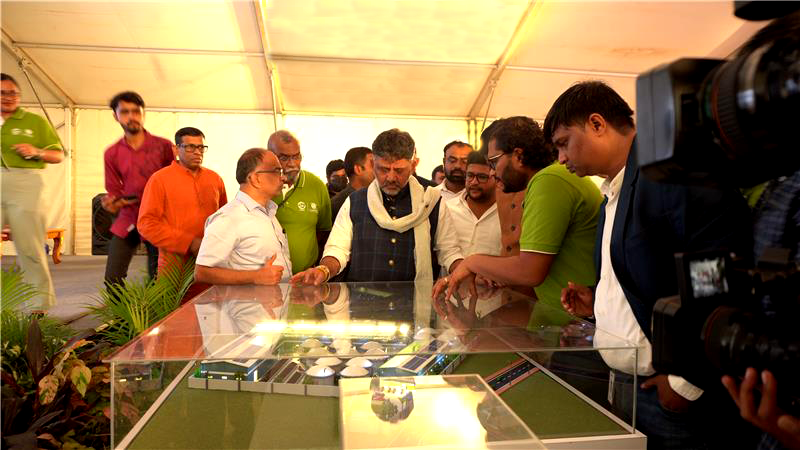
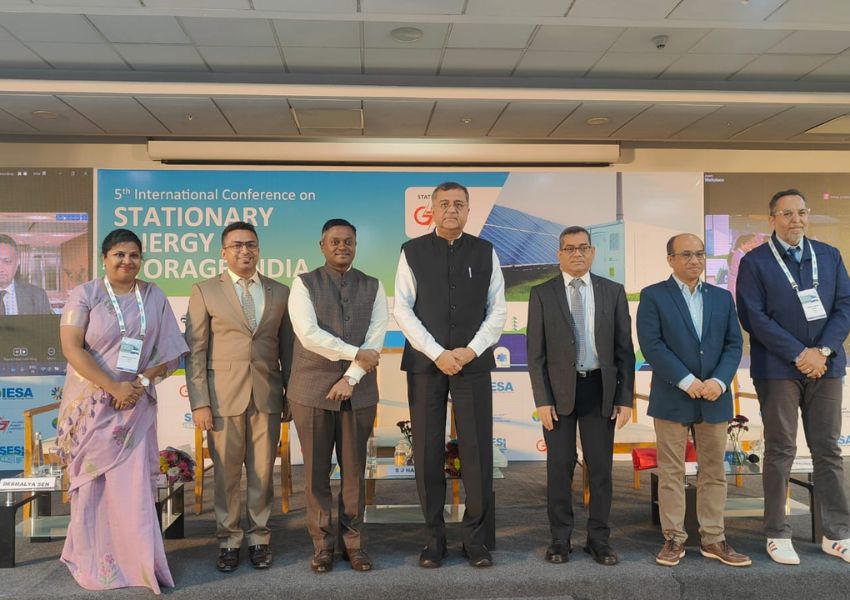
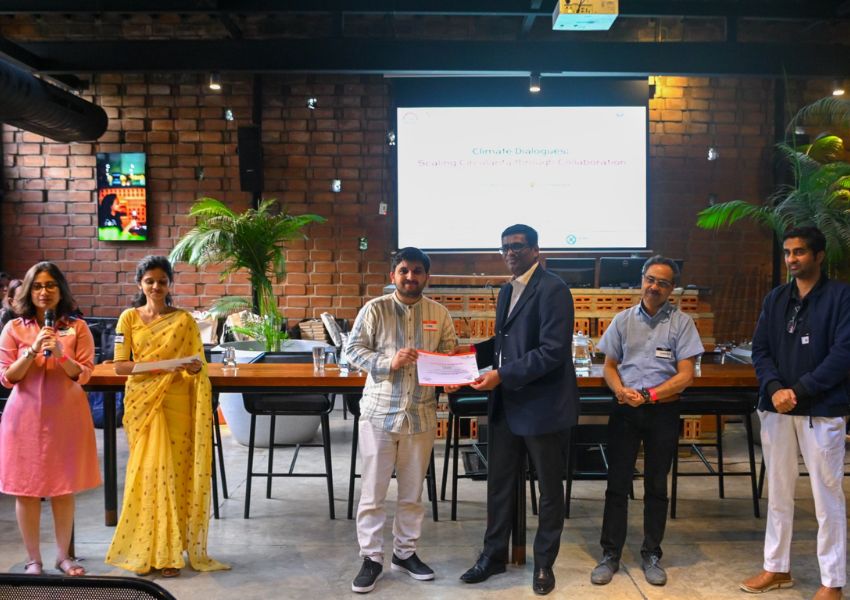
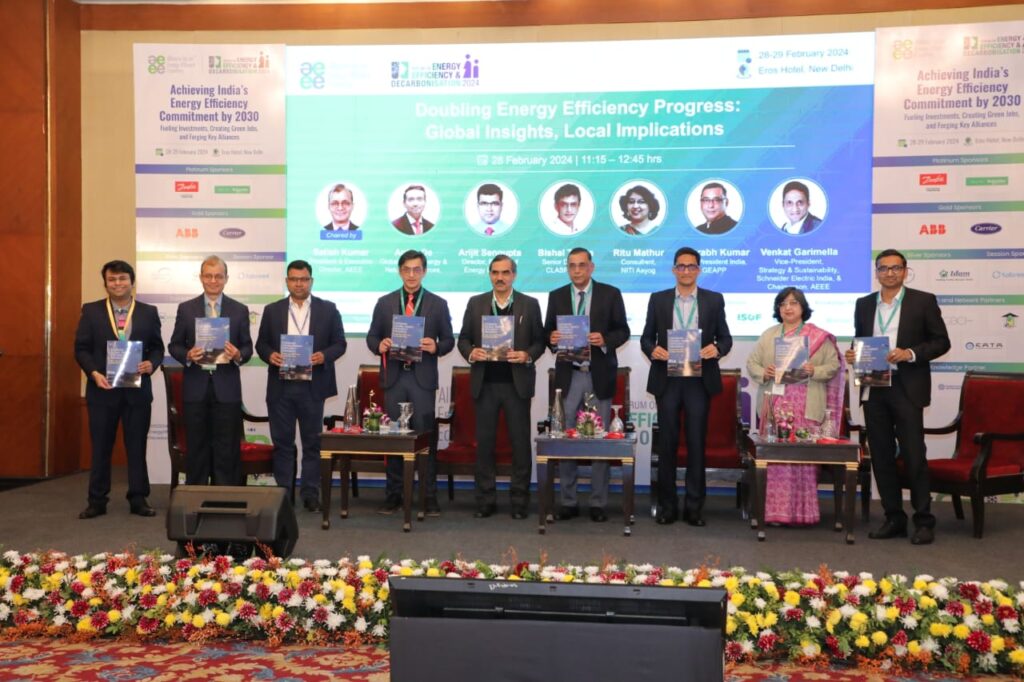
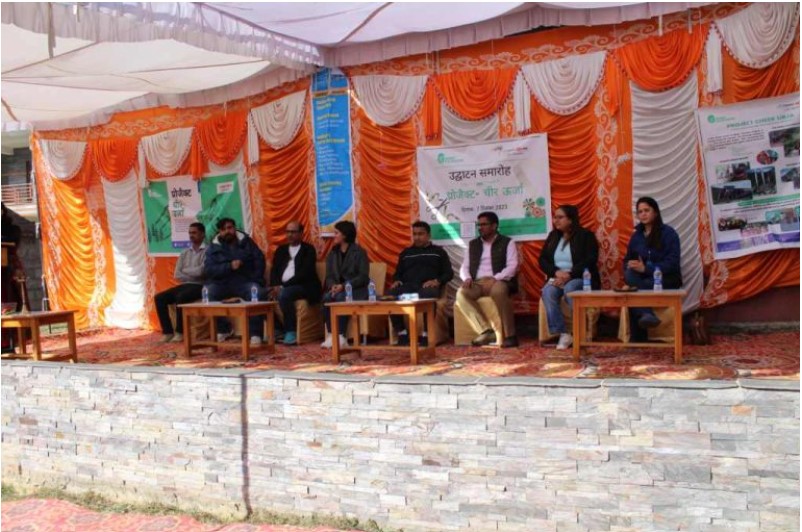
India’s energy storage sector is poised for unprecedented growth, with industry leaders projecting investments of Rs 479 thousand crore by 2032. The ambitious forecast was announced at the fifth edition of the Stationary Energy Storage India (SESI) conference held at Mahatma Mandir, Gandhinagar, where over 200 stakeholders from across the globe gathered to chart the course for India’s energy transition.
Organized by the India Energy Storage Alliance (IESA) and the SESI Council, the event emphasised the nation’s expanding role in global energy storage innovation. The forecast aligns with India’s growing renewable energy ambitions and recent government initiatives, including the approval of Viability Gap Funding for 13,200 MWh of Battery Energy Storage Systems (BESS) by 2030-31.
Reaffirming Gujarat’s leadership in the energy transition, Shri S J Haider, IAS, Additional Chief Secretary, Government of Gujarat, highlighted the state’s new 100 GW renewable energy target by 2030. “We are positioning Gujarat as a national frontrunner in integrated renewable energy and energy storage deployment,” he said.
Arun Mahesh Babu M.S., IAS, Managing Director of Gujarat Power Corporation, added, “Energy storage is now essential for peak load management and grid stability. We are already seeing strong participation in 2-hour and 4-hour tenders, and 8-hour tenders will follow soon.”
National leaders echoed the sentiment, with RP Gupta, CMD of Seci, outlining a vision of achieving 500 GWh of storage by 2030 and 5,000 GWh by 2047. The National Electricity Plan projects storage demand reaching 411.4 GWh by 2032, driven by both Pumped Storage Projects (PSP) and BESS.
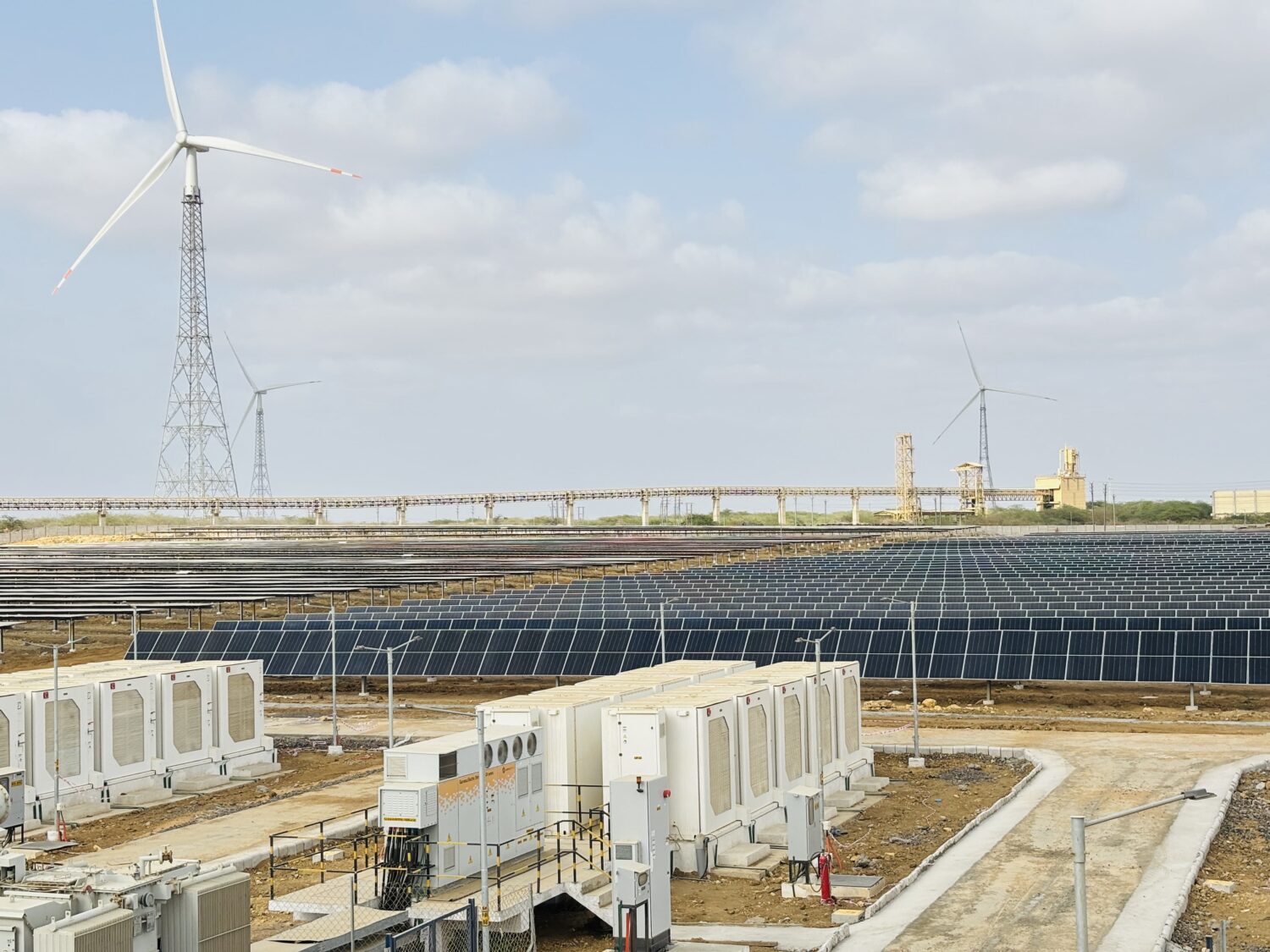
The conference spotlighted live case studies like Modhera and Kachchh, illustrating Gujarat’s progress in deploying integrated renewable and storage systems. It also emphasized the rapid reduction in energy storage costs—from Rs 10 lakh/MW/month to Rs 2.5 lakh/MW/month over the past two years.
“The road to net zero runs through robust energy storage,” said Vinayak Walimbe, MD, CES India. “Through collaboration with central and state governments, we can turn this vision into reality.”
Distinguished dignitaries including officials from MNRE, CEA, SECI, and major corporations such as Adani New Industries, JSW Energy, and Envision Energy participated, signaling strong public-private collaboration for India’s clean energy future.
As India targets 500 GW of renewable energy capacity by 2030, the role of storage becomes increasingly central. SESI 2025 has set the tone for scaling this critical infrastructure, paving the way for innovation, investment, and international cooperation in building a resilient and green energy economy.