India’s Green Growth Strategy: A Blueprint For Climate Resilience

As the world grapples with record-breaking temperatures and the escalating urgency of the climate crisis, the opportunity for resilient and ambitious climate action has never been more compelling. In a recent report released at COP29, global mean temperatures from January to September 2024 were recorded at 1.54°C above pre-industrial levels, potentially making 2024 the hottest year. This is a stark reminder of the urgency of climate action, affirming that sustainability is a critical mandate for survival and resilience.
India, one of the world’s fastest-growing economies and vulnerable to climate impacts, has taken centre stage in the global climate conversation. At COP29, India highlighted four key aspects of the Global Action Plan: scaling up innovative actions and technology transfer, prioritising climate finance as central to implementing climate action, enhancing international cooperation, and fostering mutual trust among nations.
With its ambitious energy transition, climate-resilient policies, and a commitment to a low-carbon economy, India is addressing its domestic climate goals and shaping a global pathway for sustainable and inclusive growth.
A Journey To Sustainable Energy Transition
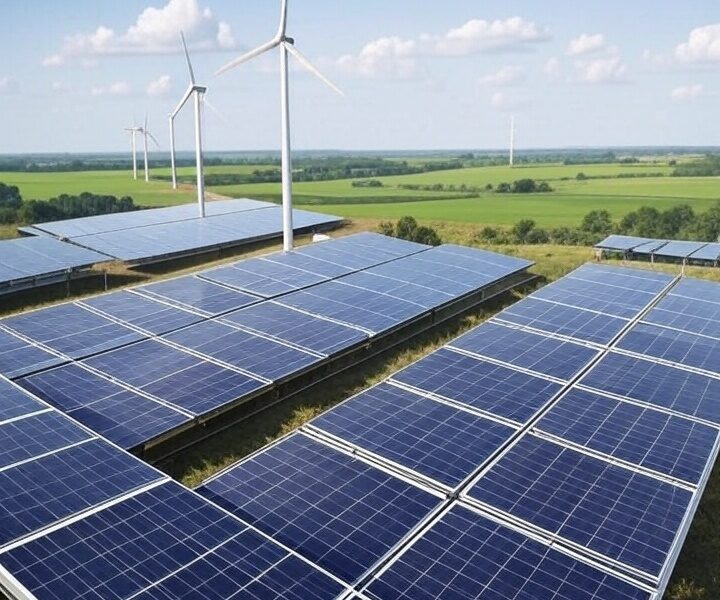
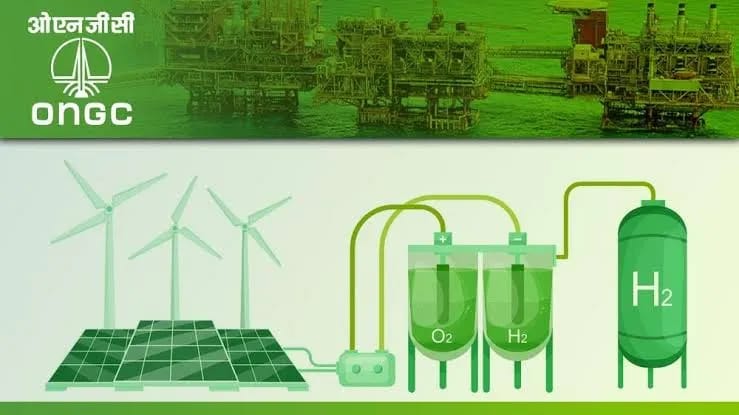
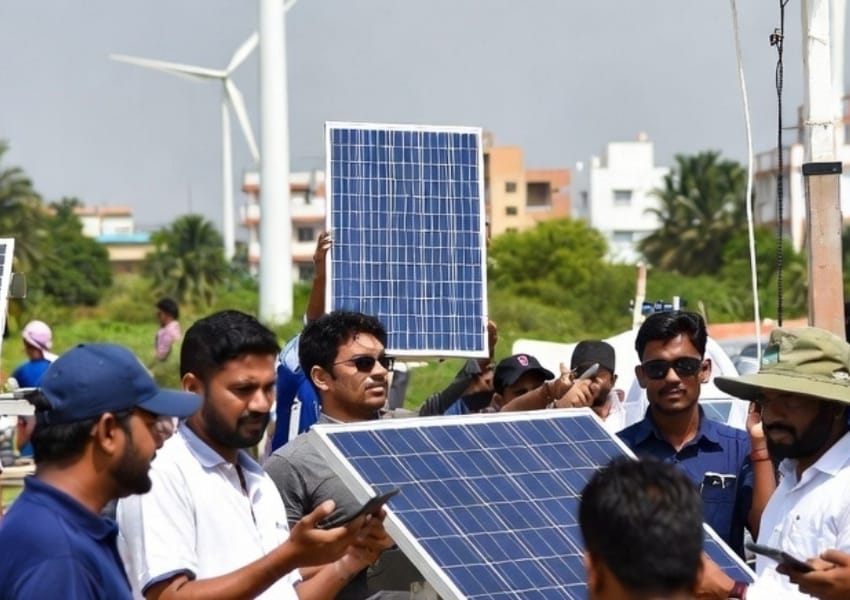
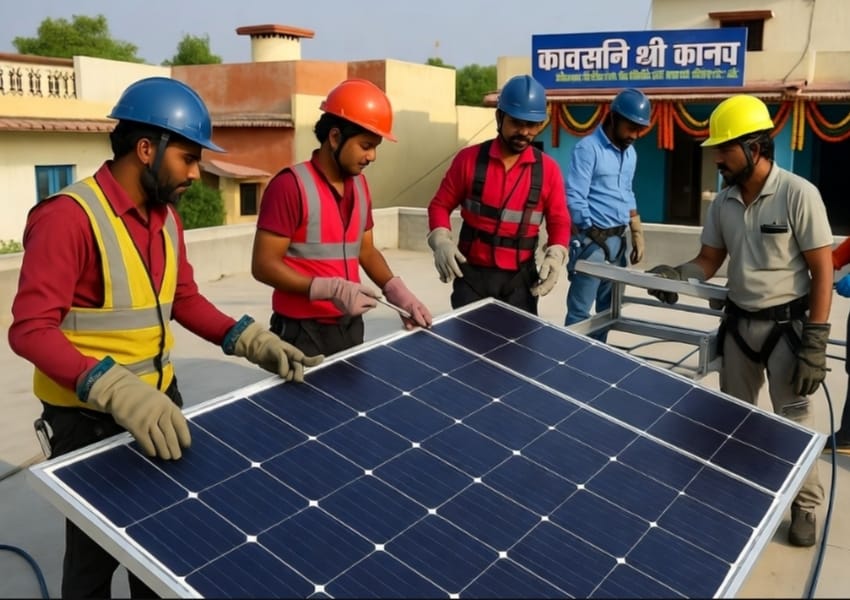
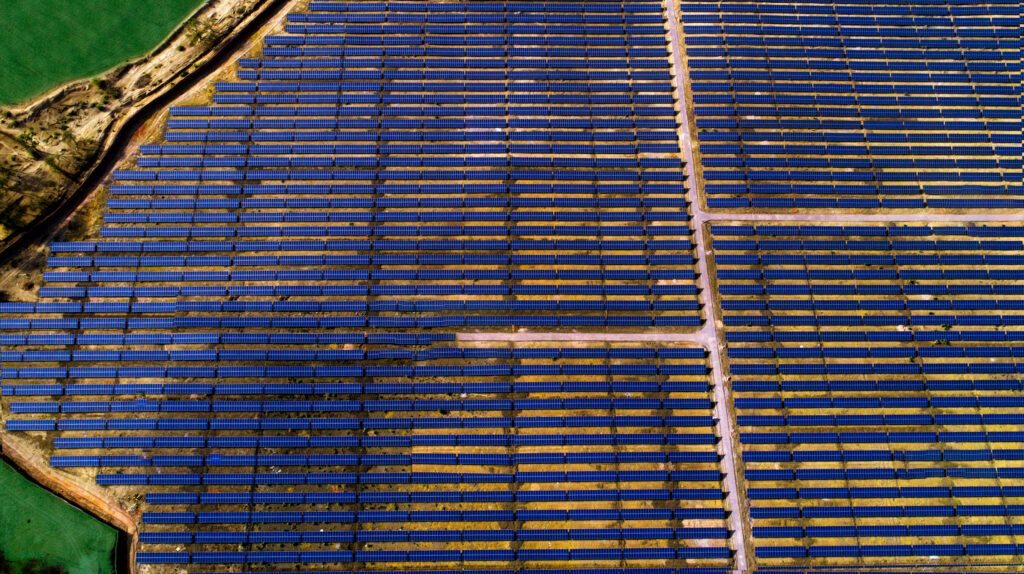
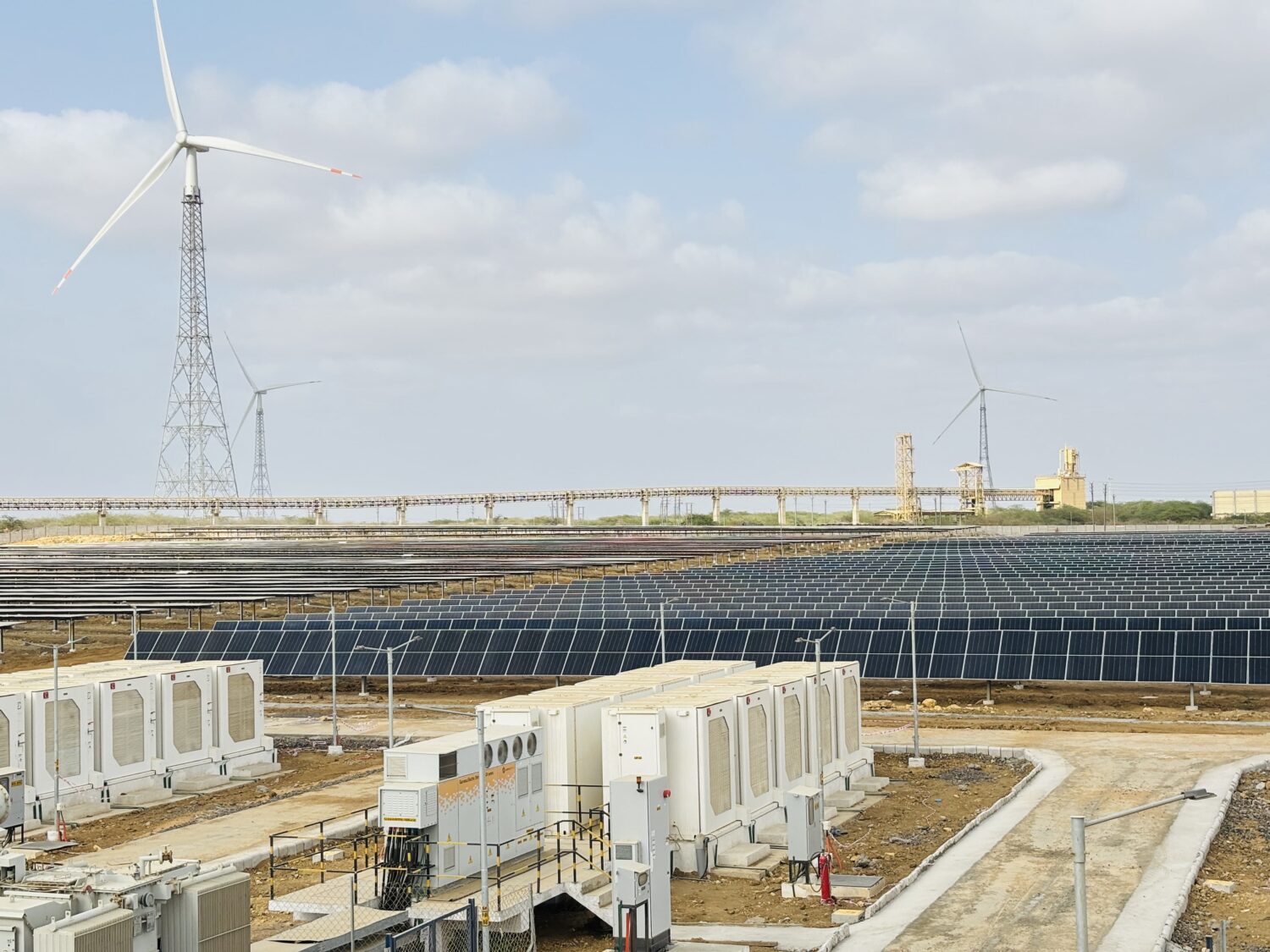
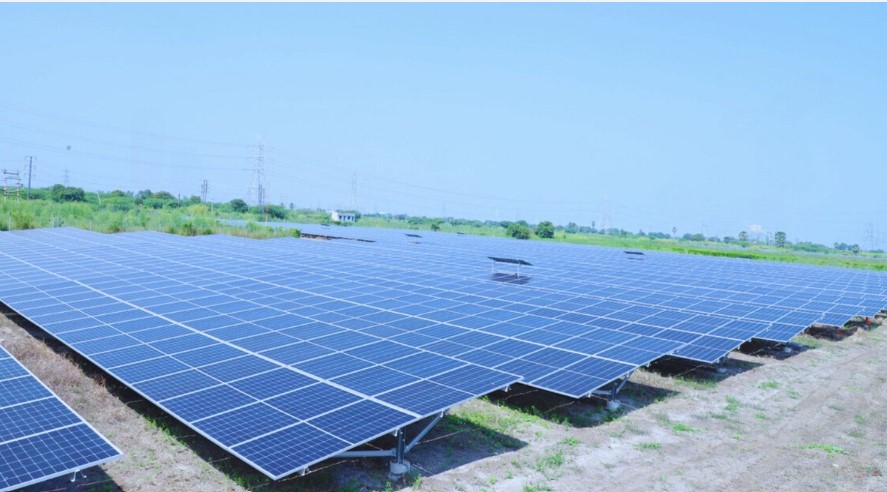
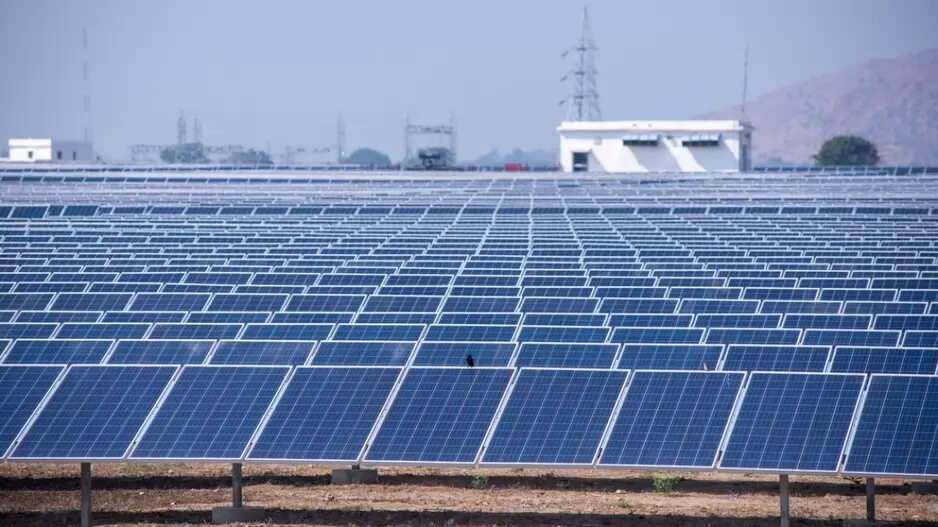
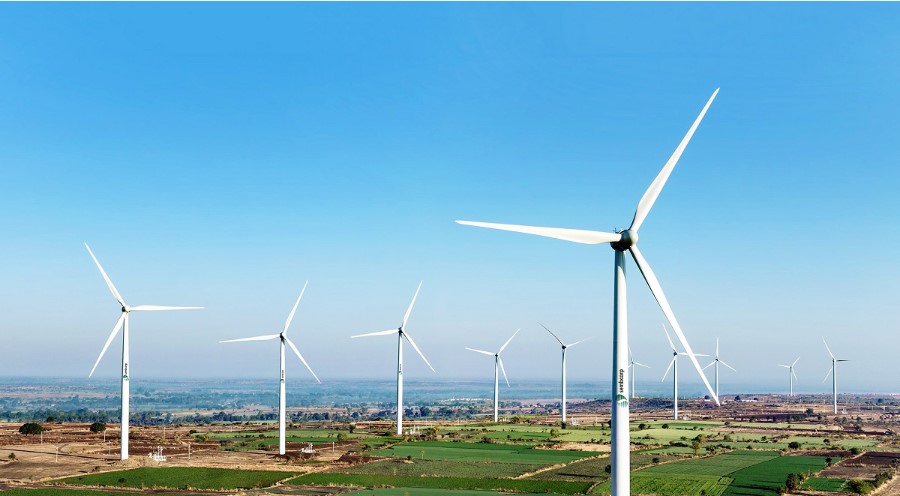
India’s energy sector is at the centre of its shift toward sustainability. As the nation works to meet its ambitious goal of 500 GW of renewable energy capacity by 2030, it has already achieved a significant milestone by surpassing 200 GW this year. This accomplishment reflects India’s commitment to sustainable energy sources, with solar, wind, hydro, and bioenergy playing pivotal roles. Technological advances, such as high-efficiency solar photovoltaic (PV) cells and next-generation wind turbines, optimise costs and accelerate renewable adoption nationwide.
Beyond power generation, India is strengthening its energy storage infrastructure, prioritising domestic battery manufacturing to reduce import dependency and support the rapidly growing electric vehicle (EV) market. Government incentives, expanding charging networks, and the decreasing cost of batteries are poised to drive a significant increase in EV adoption, especially in two- and three-wheeler segments. This transition will reduce emissions and provide economic benefits through local manufacturing and job creation. In addition, India is positioning itself as a leader in green hydrogen production, which will be essential for hard-to-abate sectors such as steel, cement, and heavy transportation.
On the infrastructure front, India’s energy grid is undergoing a digital transformation. Integrating advanced metering infrastructure (AMI), artificial intelligence (AI), and machine learning (ML) into the grid is enhancing real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, and overall efficiency.
The Evolving Regulatory Landscape
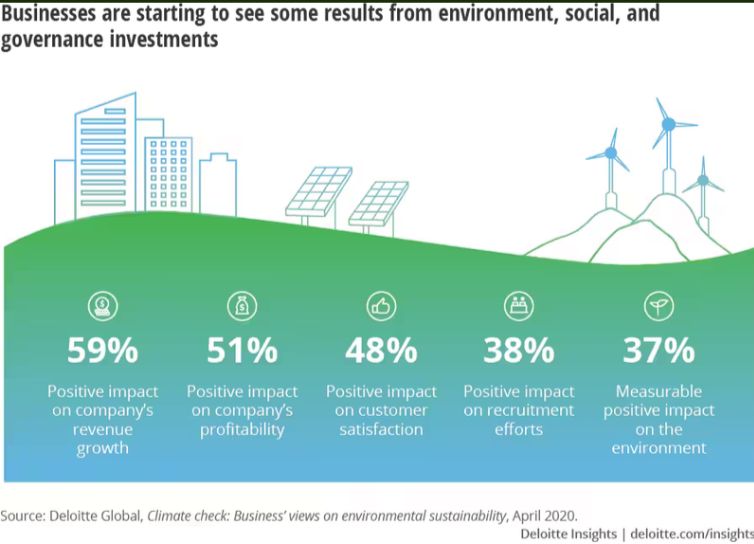
India’s regulatory framework is evolving to address the pressing need for climate action. A landmark initiative by the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI), the Business Responsibility and Sustainability Report (BRSR) mandates ESG (environmental, social, and governance) disclosures for the top 1,000 companies. This requirement drives transparency and accountability in Indian corporations, encouraging them to adopt responsible practices that align with national and global climate goals. Government regulations on emissions reduction, waste management, and sustainable business operations push companies to embed sustainability into their core business strategies. This shift reinforces India’s commitment to sustainable growth and sets the stage for more stringent regulatory action in the years ahead.
Financing Green Growth: A Sustainable Approach To Development
Green finance is essential for India to achieve its ambitious climate goals, yet current green finance efforts fulfil only about a quarter of the country’s total climate investment needs. To address this gap, leading financial institutions are rolling out frameworks that attract sustainable investments, including green bonds, sustainability-linked loans, and mutual funds. The recent introduction of the Climate Finance Taxonomy is designed to streamline sustainable investment, guiding capital toward projects that support India’s climate goals.
In addition, India’s inclusion in the Network for Greening the Financial System (NGFS) shows its commitment to aligning financial practices with environmental goals. By investing in low-carbon projects, India is securing its climate efforts and strengthening the foundation for sustainable economic growth. To support green growth, INR 350 billion was spent on a net zero transition in the Union Budget FY 2023-2024. With these measures in place, India is better positioned to achieve its sustainability objectives and drive economic growth in the future.
Redefining Corporate Responsibility: A Vision For Growth And Responsibility
As India strives to achieve its net-zero emissions target by 2070, the business sector is crucial in realising this ambition. With increasing regulatory pressure, investor expectations, and changing consumer preferences, Indian companies are progressively integrating sustainability into their core strategies. Many businesses are establishing ambitious goals to minimise environmental impact, promote innovation, and improve transparency through ESG disclosures.
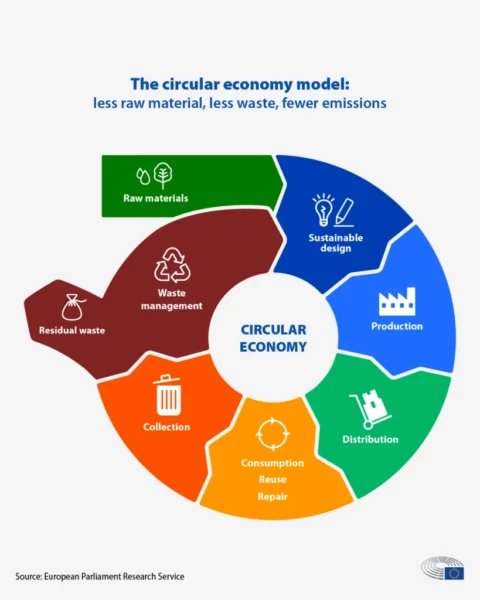
Sustainability is significant in supply chain management as companies increasingly prioritise responsible sourcing, waste reduction, and circular economy principles. With the growing emphasis on Scope 3 emissions, businesses are adopting sustainable procurement policies and integrating these efforts into their disclosures. This trend is expected to gain momentum, especially with the emergence of new ESG regulations that require industries to maintain sustainable practices throughout the value chain.
As we approach 2025, the sustainability landscape is set to evolve rapidly. Regulatory advancements, the growth of green finance, and corporate leadership in ESG will guide India’s transition to a low-carbon economy. This vision is not just an aspiration but a necessity for India’s future, its people, and its role in a sustainable global economy. With ongoing commitment and collaboration, India is well-positioned to turn its ambitions into actions, setting a strong example for sustainable development worldwide.
Author- Sandeep Chandna is the Chief Sustainability Officer, Tech Mahindra.