Leading The Way: India’s Green Transition & Global Leadership

As 2025 unfolds, India stands at a defining moment, asserting its role as a resilient economic leader and an emerging global hub. This transformation is underpinned by a steadfast commitment to green growth and sustainable development – the key drivers for environmental health and long-term economic stability.
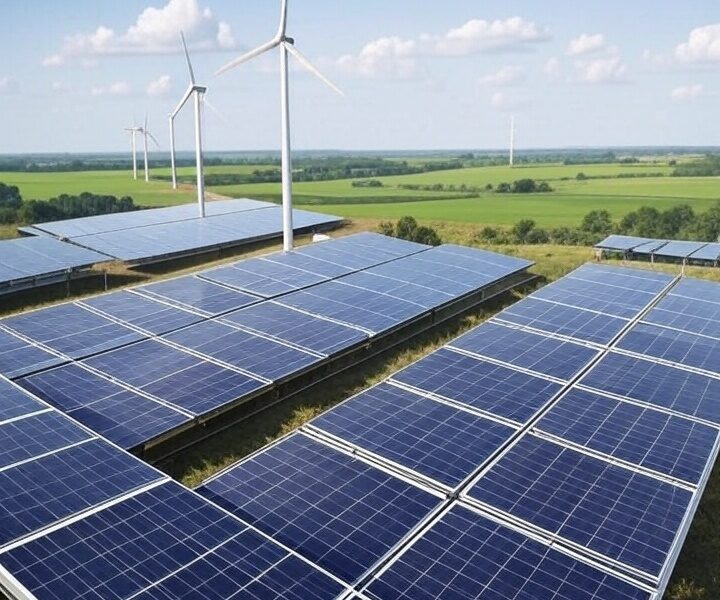
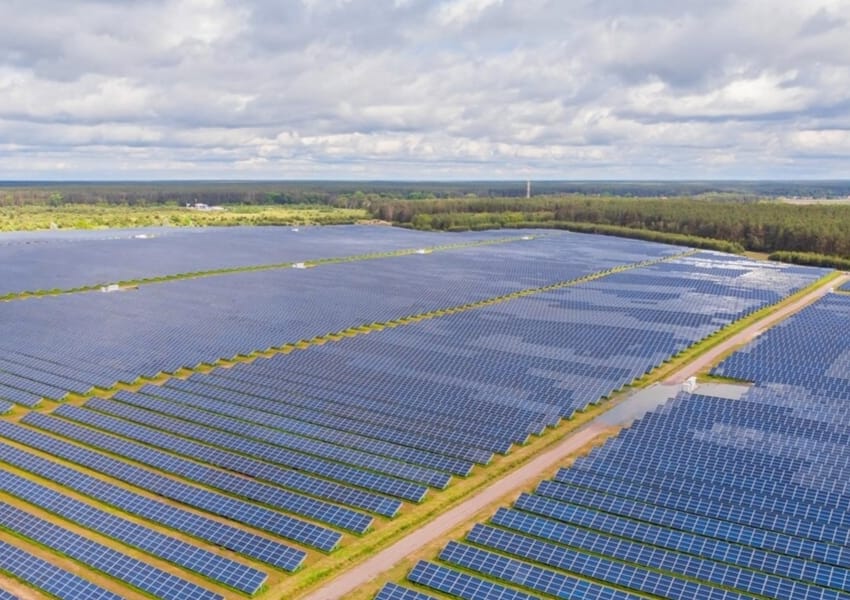
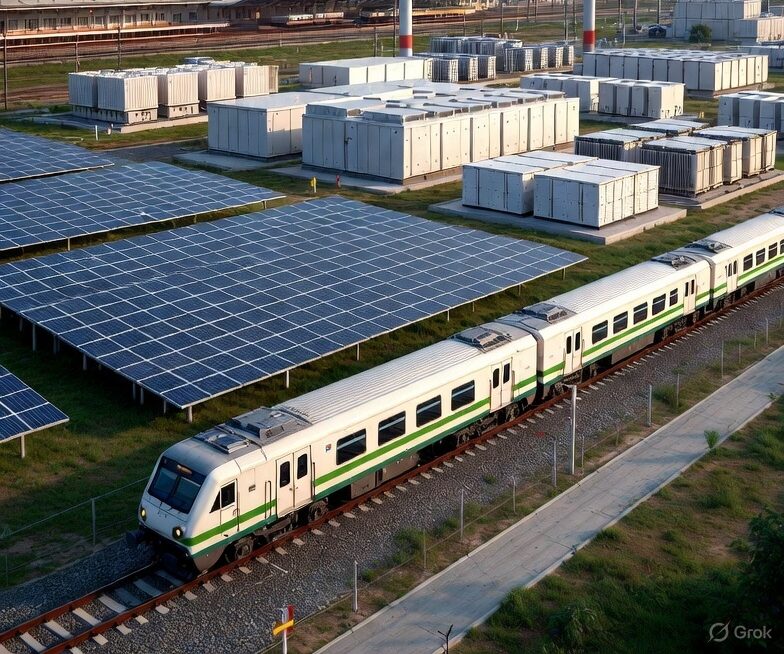
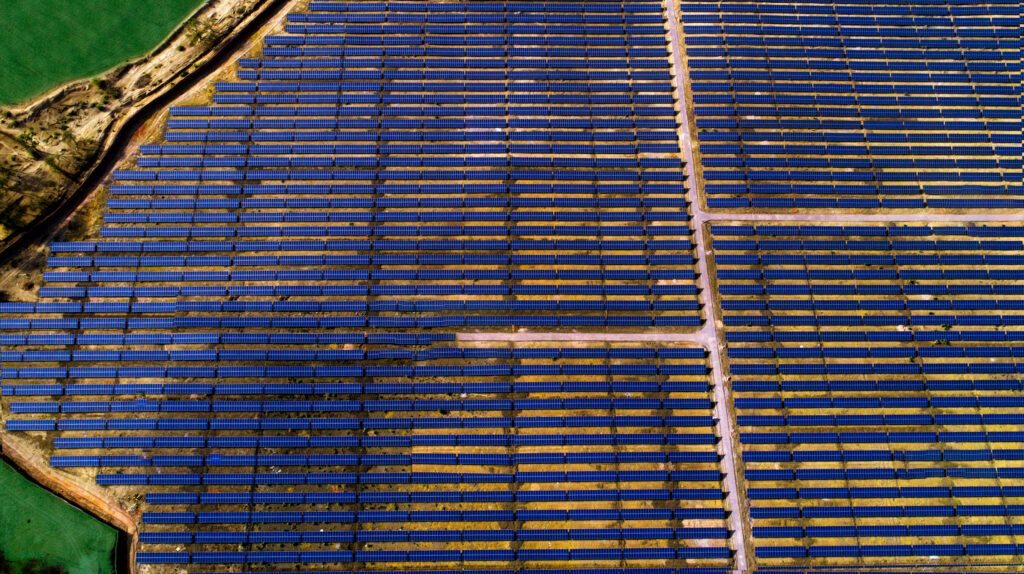
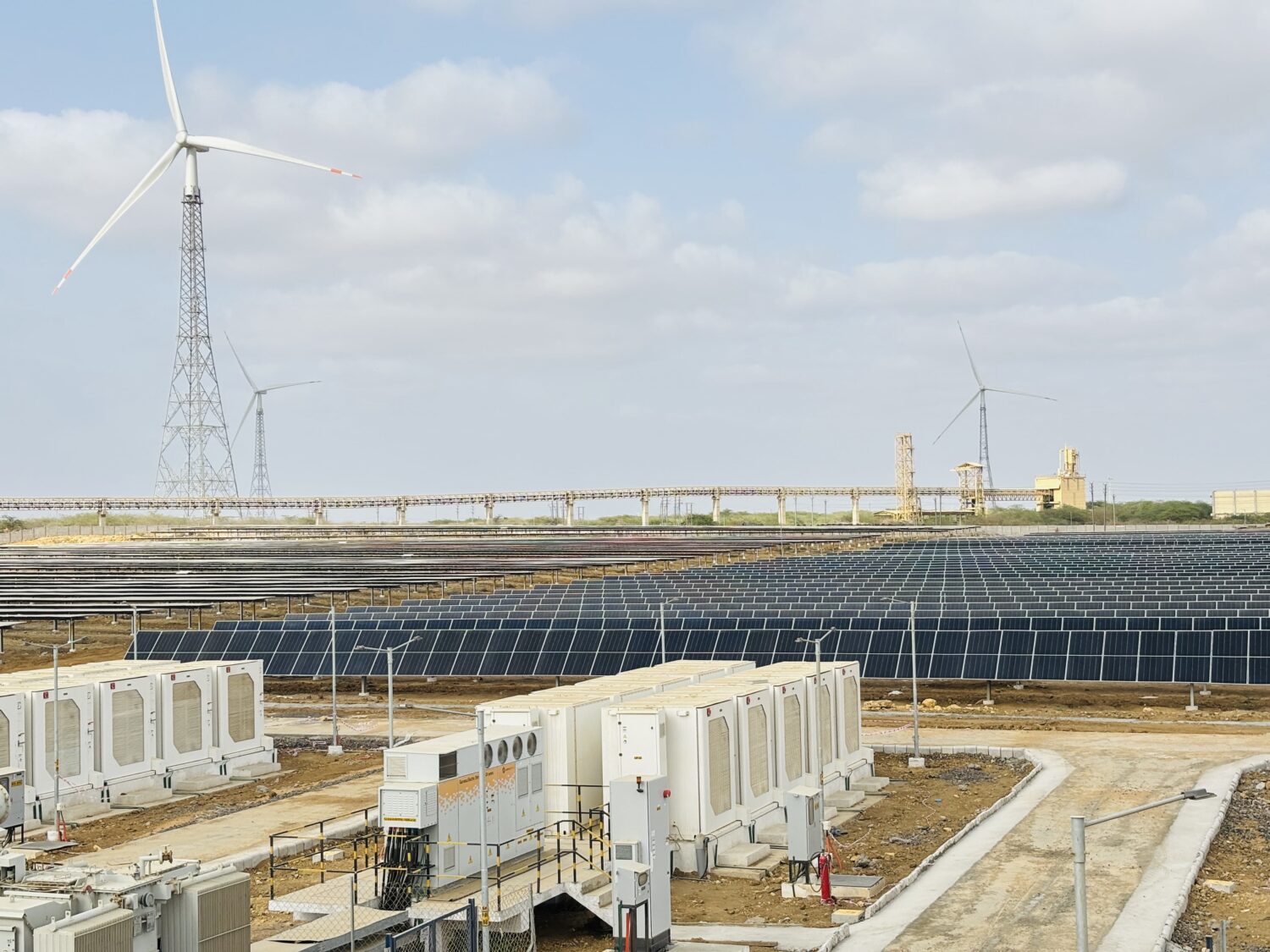
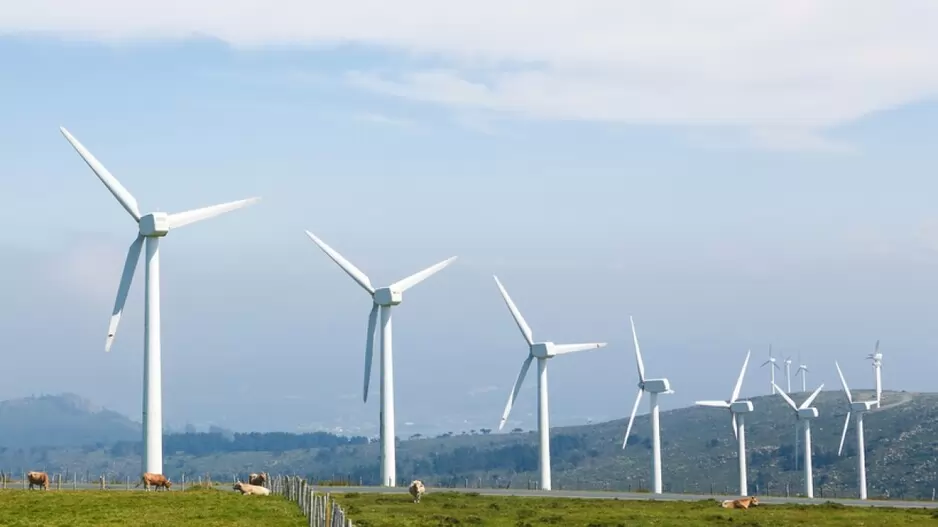
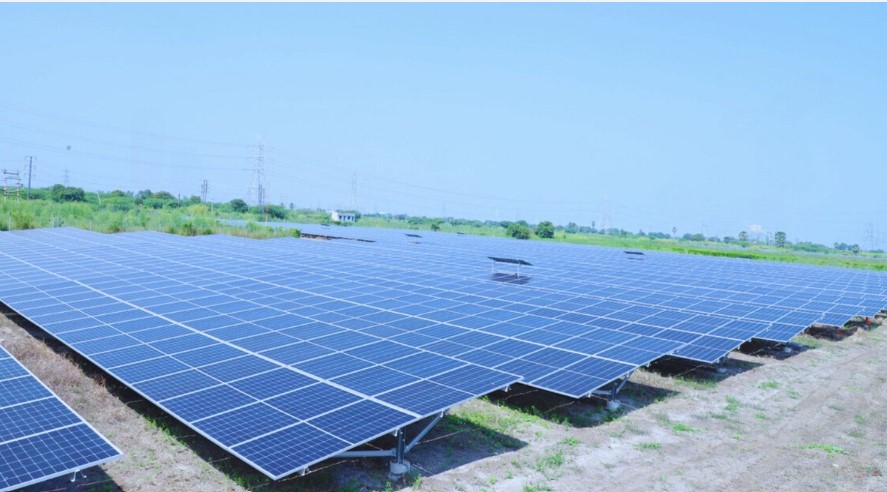
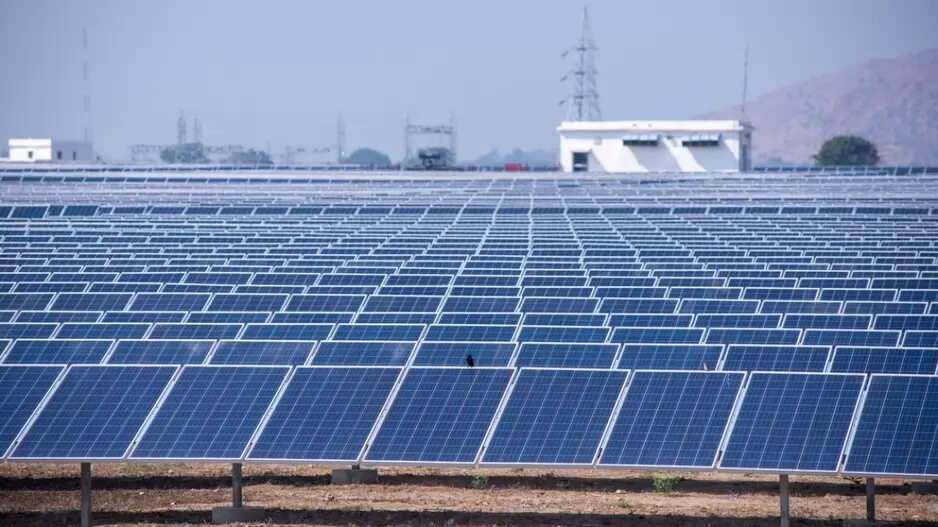
Notably, India aims to be net zero by 2070, having pledged to achieve 50 per cent cumulative electric power installed capacity from non-fossil sources by 2030. The country ranks fourth globally in renewable energy capacity, supported by a 36.5 per cent CAGR in solar over 11 years. According to an industry report, India’s role in global energy transition is driving a cleaner future, with non-fossil fuels now at 45 per cent capacity and a bold target of 500 GW by 2030.
India, the world’s fastest-growing large economy, is steadfast in its ambition to achieve the status of a developed nation by 2047. Focused government spending, significant investments, and an upsurge in exports power India’s economic engine. Critical reforms in taxation, infrastructure advancement, financial inclusion and production-linked incentives have established a robust foundation for sustainable growth.
Nearly 70 per cent of India’s GDP is driven by domestic consumption, which remains the world’s fourth-largest consumer market. A thriving digital economy, strategic partnerships, a rapidly increasing manufacturing sector, and foreign portfolio investment inflows have further bolstered its economic strength. However, as the nation achieves these economic milestones, it must simultaneously address the pressing challenges of climate change and environmental degradation.
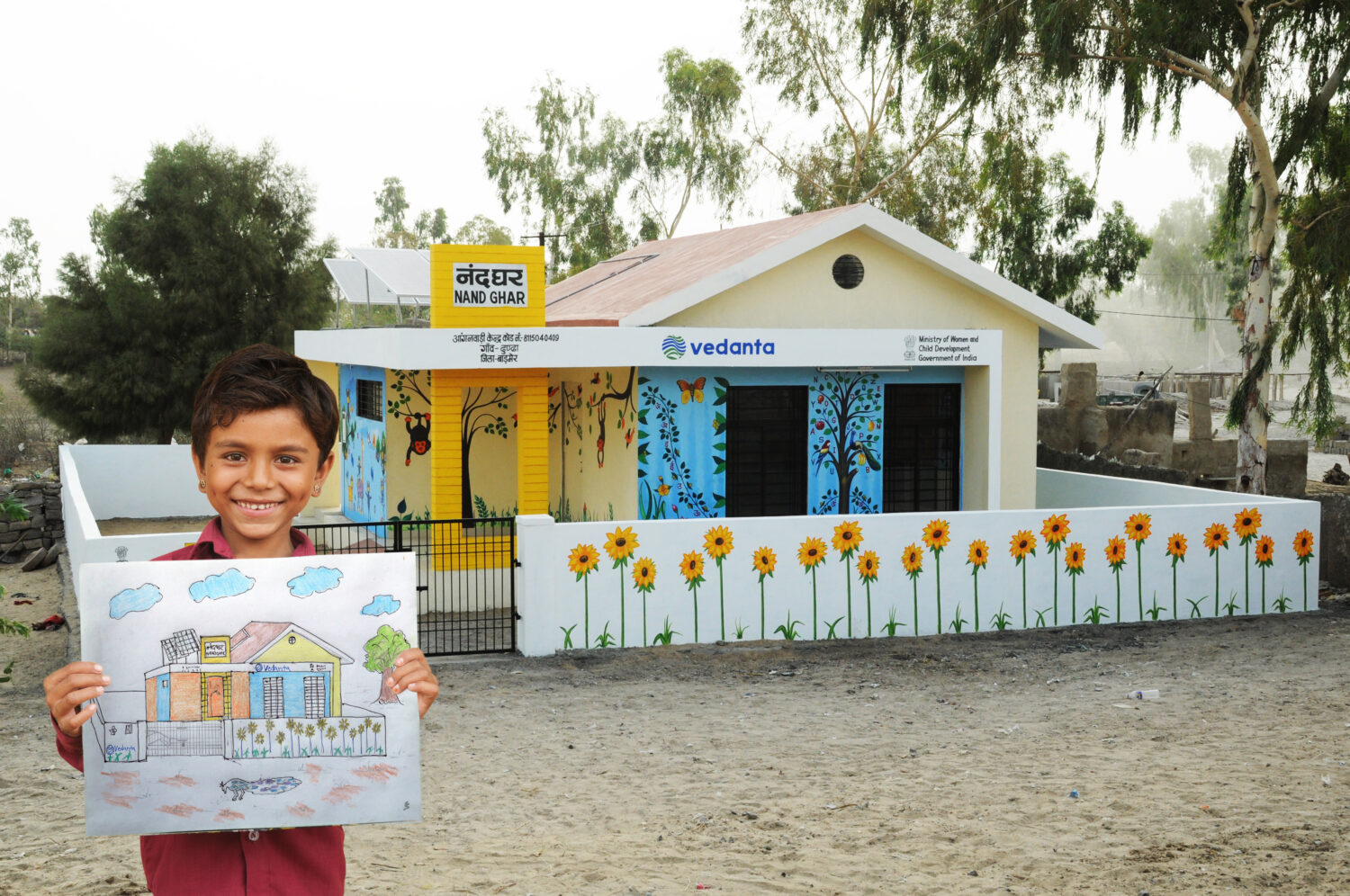
A greener, more sustainable approach underpins India’s vision for 2025, manifesting in multiple facets of governance, industry and societal behaviour. India’s commitment to the Paris Agreement is evident through its Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs). These outline actionable strategies, including significant budgetary allocations towards non-fossil electricity, introducing a vehicle scrapping policy, issuing green bonds, and launching initiatives like the Lifestyle for Environment (LIFE) program, which embeds sustainability into daily life. Further, developing a green taxonomy underscores India’s intent to provide a structured framework for sustainable economic activities.
Collaborative Efforts For Green Growth
India’s journey toward green growth highlights the need for collective action across sectors. Businesses, policymakers and industries must collaborate to drive impactful change through the following measures.
The first among these is leveraging advanced technologies. Digital tools such as artificial intelligence (AI), the Internet of Things (IoT) and big data are transforming how we approach energy efficiency. AI-powered systems can predict energy consumption patterns, while IoT devices enable real-time monitoring, optimising energy use. Big data aids in identifying inefficiencies and opportunities for resource conservation, helping businesses and governments design smarter, sustainable cities and industries.
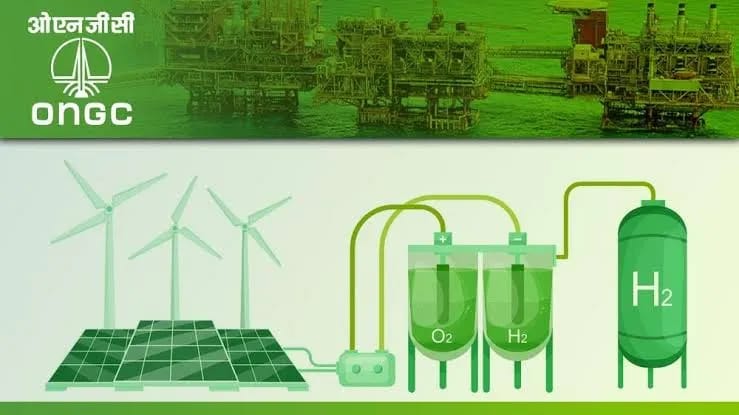
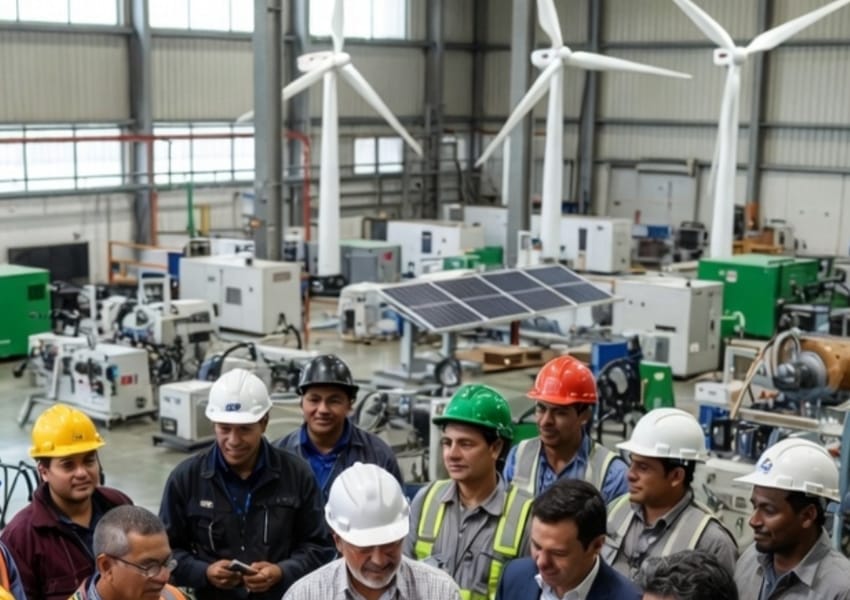
Accelerating renewable energy adoption is another measure. India’s focus on solar, wind and hydropower, supported by government policies and infrastructure development, accelerates the transition to renewable energy. Electric mobility initiatives further reduce reliance on fossil fuels, fostering a more sustainable, low-carbon economy.
Green buildings, advanced energy-saving systems, and waste management innovations are key to reducing energy consumption. Technologies that track and optimise energy use can significantly lower carbon footprints, promoting sustainable urban living.
What is also needed is raising awareness and education. Public awareness campaigns and education initiatives empower individuals to make environmentally conscious choices. Grassroots actions and strategic policy interventions ensure sustainability becomes a collective, long-term goal.
The need of the hour also lies in fostering public-private collaboration. Collaboration between governments, businesses and civil society is key to scaling green technologies and driving sustainable development. A phased approach from policymakers can guide industries and workers through the transition to green sectors, while investments in skill development will ease job shifts. Fueled by international climate finance, flexible monetary policies and fiscal strategies will help maintain macroeconomic stability during this transition.
The Inclusivity Imperative
The path toward green growth is characterised by a commitment to inclusivity and a focus on mitigating social risks. Central to the nation’s sustainable development strategy is emphasising health and safety, improving living conditions, and ensuring equitable access to resources. This approach also seeks to build resilience in vulnerable communities, aligning economic progress with social well-being.
Given India’s vulnerability to climate change, limiting the impact on natural habitats, agriculture, and biodiversity is crucial, primarily as a significant portion of the population relies on agriculture. India is progressing towards its 2030 goals and has set ambitious targets under its ‘Panchamrit’ framework as part of its Nationally Determined Contributions under the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change.
Nonetheless, the journey to green growth presents challenges. Balancing rapid economic development with environmental preservation requires careful planning and steadfast commitment. Tackling systemic issues like waste management, water scarcity, and air pollution requires continuous efforts and innovative solutions.
The Forward Path
As we approach 2025, it becomes evident that businesses must embed sustainability into their core strategies. Industries can catalyse a broader societal shift toward sustainability by adopting green technologies, optimising resource use, and minimising carbon footprints. For instance, leveraging digital innovations can streamline processes and enhance energy efficiency while integrating renewable energy sources, significantly reducing dependence on fossil fuels.
By prioritising sustainability, India strengthens its economic framework and reaffirms its role as a responsible global player. This dual pursuit of economic resilience and environmental stewardship positions India as a beacon of sustainable progress on the world stage.
Author- Paneesh Rao, Chief Sustainability Officer, LTIMindtree.