The Contribution Of Waste Management To Mitigating Climate Change

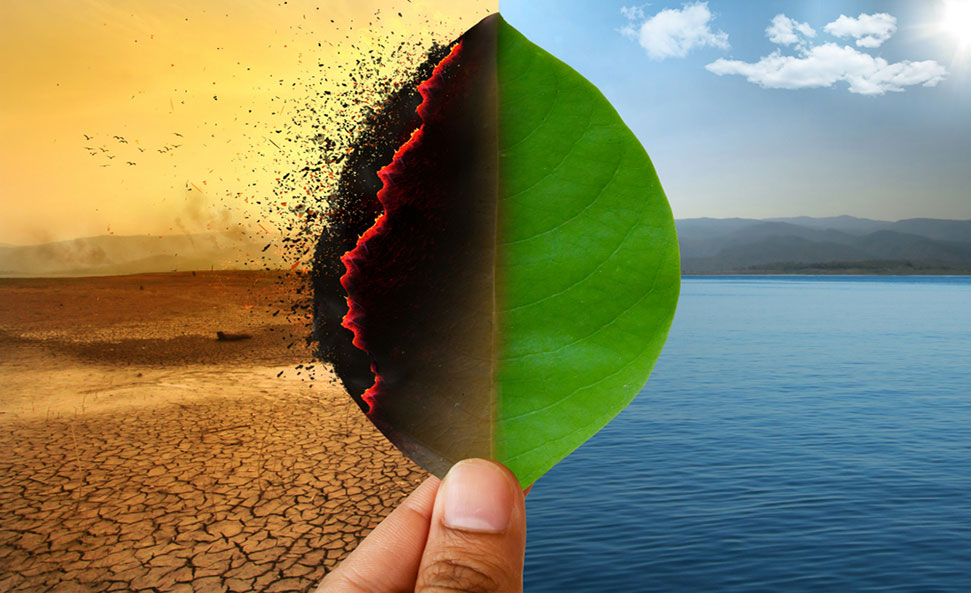
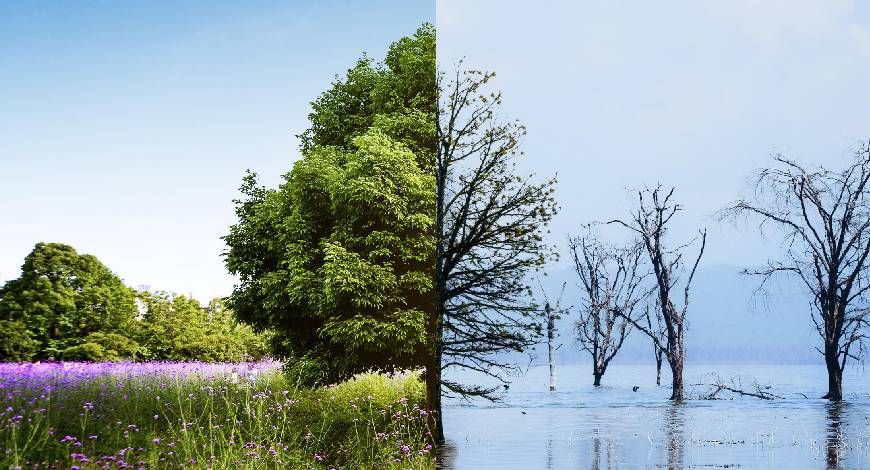
As we navigate the challenges of climate change, one crucial aspect often overlooked is the significant impact of waste management practices. The management of waste is not just about fulfilling a responsibility; it’s about wielding a powerful solution in taming the very driver of climate change—greenhouse gas emissions.
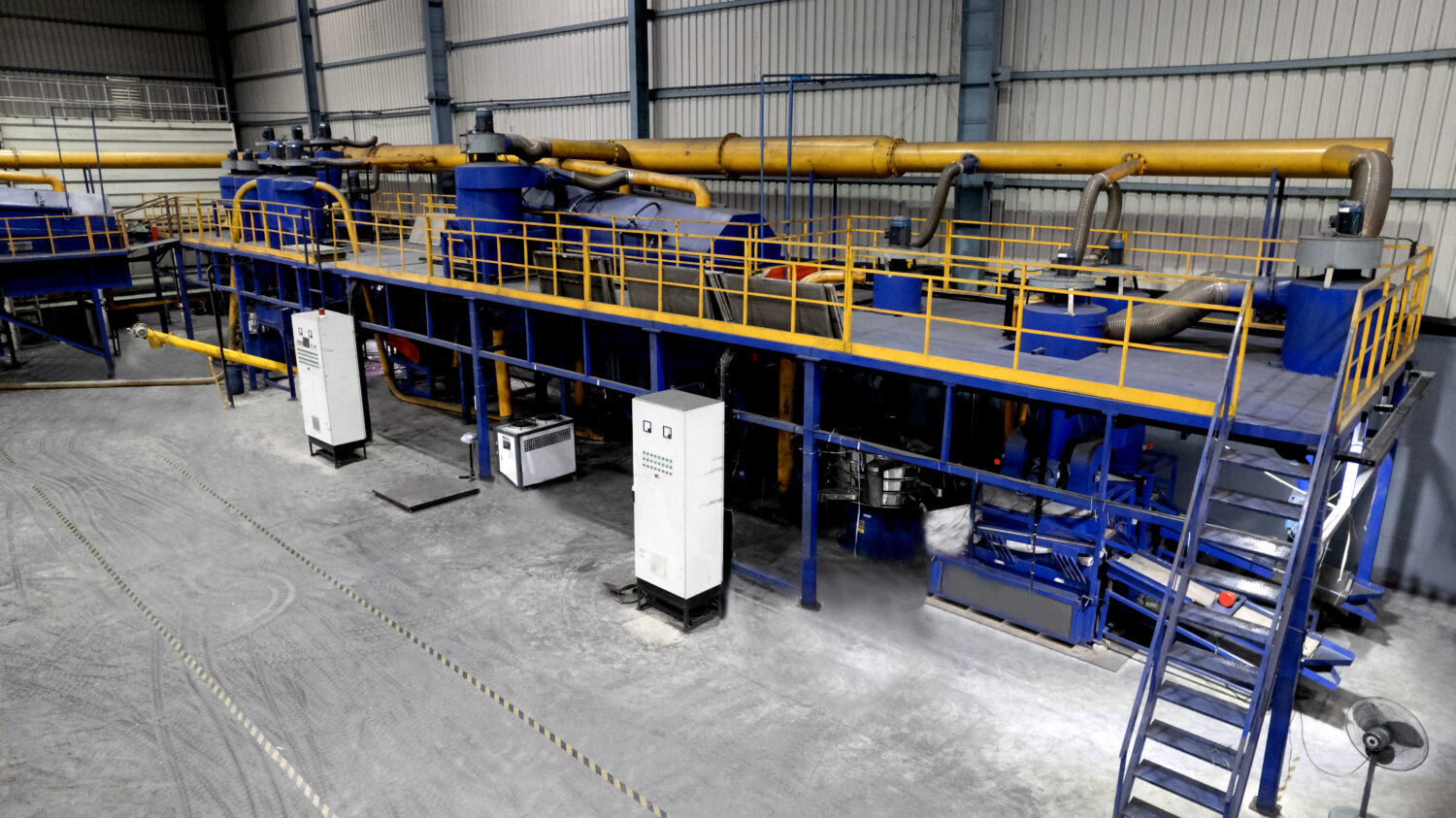
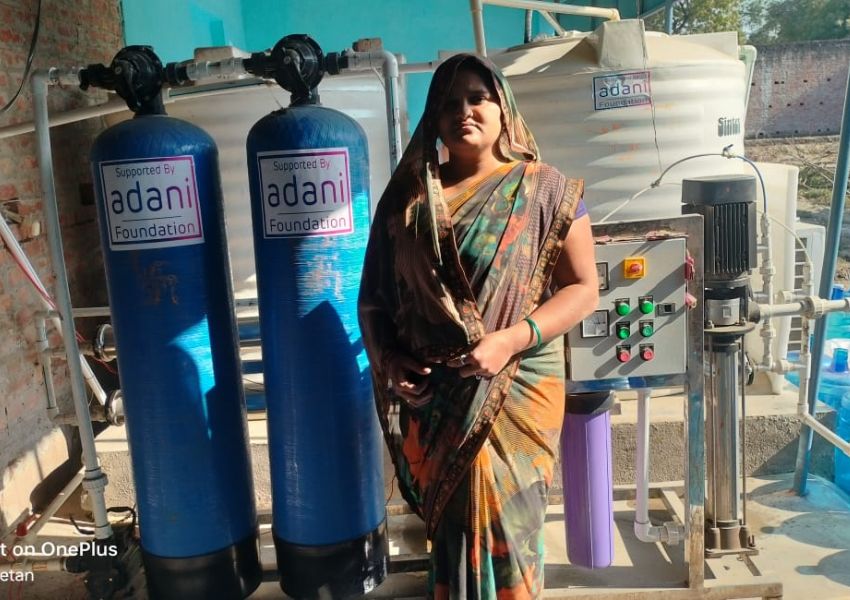
The process of waste breakdown, particularly the decomposition of organic waste in landfills, serves as a significant contributor to the introduction of greenhouse gases into our environment. Methane, an exceptionally potent greenhouse gas, is generated through this process, far surpassing carbon dioxide in its heat-trapping capabilities. Understanding this, there is an urgent drive towards implementing more intelligent waste management strategies such as composting and anaerobic digestion. These methods are transformative, converting organic waste into valuable resources such as biogas and nutrient-rich compost. And the bonus? They significantly cut down on methane emissions and gradually loosen our reliance on fossil fuels.
Complementing these strategies are waste-to-energy technologies, such as incineration with energy recovery. These technologies facilitate the conversion of non-recyclable waste into electricity or heat. While concerns about air quality and potential emissions exist, modern waste-to-energy facilities are designed with advanced pollution control technologies, ensuring that the overall environmental impact is minimized. They contribute to a more sustainable energy mix and aid in reducing the reliance on fossil fuels, a major contributor to climate change.
However, this marks a crucial turning point: efficient waste management isn’t solely about emission reduction; it’s a treasure trove for resource conservation too. Think about recycling—the superstar in this space. It doesn’t just reduce our demand for new materials; it’s a game-changer in cutting down energy use during manufacturing, which means a direct impact on greenhouse gas emissions. Basically, manufacturing products using recycled materials typically demands less energy compared to producing from raw materials, resulting in reduced greenhouse gas emissions. Encouraging recycling efforts and establishing extensive waste segregation programs can notably diminish a nation’s environmental impact, fostering a path towards a more sustainable future.
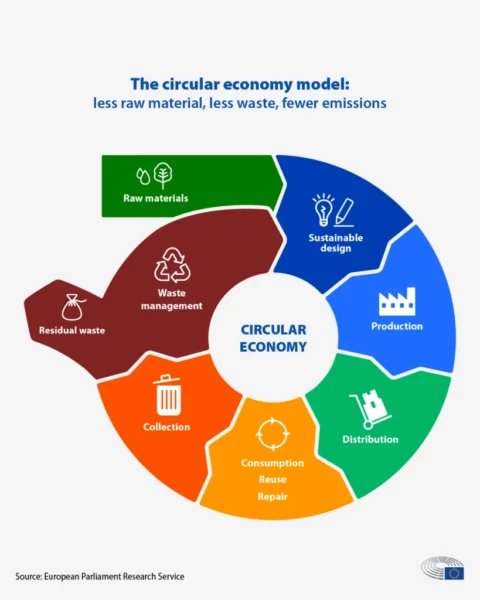
Programs such as the Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) are the fuel driving this change. These initiatives enhance resource efficiency by assigning producers the responsibility for handling a product’s end-of-life phase. This approach drives manufacturers to prioritize recyclability and environmental impact when designing products, fostering a circular economy that prioritizes continual reuse and recycling of materials. This optimization of resource usage and waste reduction directly diminishes emissions associated with extraction, production, and disposal, thus significantly contributing to mitigating climate change. Overall, it minimizes waste and maximizes resource use.
Moreover, waste management plays a pivotal role in steering the transition towards a circular economy, where resources undergo continual reuse, recycling, and repurposing. As communities divert waste away from landfills and incinerators, they not only alleviate the environmental impact linked to waste disposal but also foster opportunities for economic growth. This shift towards circular practices diminishes the constant need for raw material extraction, consequently reducing the carbon footprint and easing the strain on ecosystems, thereby contributing significantly to mitigating climate change.
Another important contribution lies in community engagement and education. Educational initiatives empower communities to make informed decisions, encouraging choices like opting for minimally packaged products, participating in recycling programs, and supporting local waste management endeavours. These shifts in behaviour significantly contribute to the broader objective of mitigating climate change by diminishing the carbon footprint across product lifecycles.
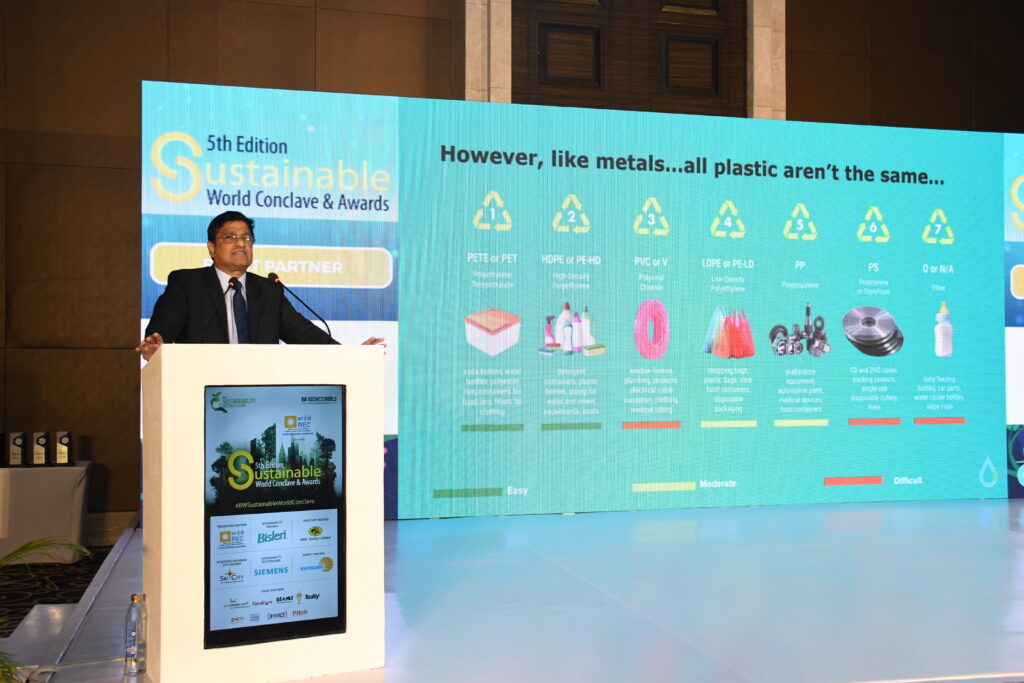
Number speaks Volume: Recycling plastics isn’t just a trend; it’s a game-changer. It can cut emissions by a staggering 1.1 to 3.0 tons of CO2-equivalent per ton of plastic waste, compared to producing brand-new plastics. And it’s not just plastics; recycling various waste types—from paper to metals—contributes to substantial CO2-equivalent emission reductions, making a tangible dent in climate change. Take India, for instance, recycling about 5.5 million metric tonnes of plastic waste annually—that’s a whopping 60 per cent of what they produce!
The transformative power of comprehensive waste management practices in mitigating climate change is nothing short of monumental. By strategically implementing innovative solutions—think recycling, waste-to-energy tech, and embracing circular economy principles—we’re not just tackling environmental woes; we’re living up to our sustainability commitments.

About the Author:
Mr Sachin Sharma is the Founder and Director of Gem Enviro Management Limited, a leading Waste Management Agency (WMA) providing a variety of sustainability services across India.